Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Term 1 Set B
Please see below Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Term 1 Set B with solutions. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Sample Papers with solutions designed by Chemistry teachers for Class 12 based on the latest examination pattern issued by CBSE. We have provided the following sample paper for Term 1 Class 12 Chemistry with answers. You will be able to understand the type of questions which can come in the upcoming exams.
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry Term 1 Set B
Section ‘A’
1. When XeF4 is partially hydrolysed, it yields :
(A) XeSO3
(B) XeOF2
(C) XeOF4
(D) XeF2
Answer
C
2. What is the coordination number in a square close packed structure in two dimensions ?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 6
Answer
C
3. A molar solution is one that contains one mole of a solute in :
(A) 1000 g of the solvent
(B) one litre of the solvent
(C) one litre of the solution
(D) 22.4 litre of the solution
Answer
C
4. Examine the given defective crystal :
A+ B– A+ B– A+
B– 0 B– A+ B–
A+ B– A+ 0 A+
B– A+ B– A+ B–
How is the d ensity of the crystal affected by this defect ?
(A) Density increases
(B) Density decreases
(C) No effect on density
(D) Density first increases then decreases
Answer
B
5. Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo SN1 reaction most readily ?
(A) (CH3)3C—F
(B) (CH3)3C—Cl
(C) (CH3)3C—Br
(D) (CH3)3C—I
Answer
D
6 When 1 mole of benzene is mixed with 1 mole of toluene the vapour will contain : (Given : vapour of benzene = 12.8 KPa and vapour pressure of toluene = 3.85 KPa).
(A) equal amount of benzene and toluene as it forms an ideal solution.
(B) unequal amount of benzene and toluene as it forms a non ideal solution.
(C) higher percentage of benzene.
(D) higher percentage of toluene.
Answer
C
7. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points :

(A) (ii) < (i) < (iii)
(B) (i) < (ii) < (iii)
(C) (iii) < (i) < (ii)
(D) (iii) < (ii) < (i)
Answer
C
8. The IUPAC name of the compound shown below is :

(A) 2-bromo-6-chlorocyclohex-1-ene
(B) 6-bromo-2-chlorocyclohexene
(C) 3-bromo-1-chlorocyclohexene
(D) 1-bromo-3-chlorocyclohexene
Answer
C
9. The order of reactivity of following alcohols with halogen acids is :
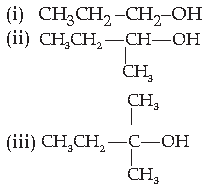
(A) (i) > (ii) > (iii)
(B) (iii) > (ii) > (i)
(C) (ii) > (i) > (iii)
(D) (i) > (iii) > (ii)
Answer
B
10. Interstitial compounds are formed when small atoms are dropped under the curved lattice of metals.
Whether the following is not the characteristic property of interstitial compounds ?
(A) They have high melting points in to pure metals .
(B) They are very hard.
(C) They retain metallic conductivity.
(D) They are chemically very reactive.
Answer
D
11. The correct order of increasing reactivity of

C—X bond towards nucleophile in the following compounds is :
(A) I < II < IV < III
(B) II < III < I < IV
(C) IV < III < I < II
(D) III < II < I < IV
Answer
A
12. The compound A on treatment with Na gives B, and with PCl5 gives C. B and C react together to give diethyl ether. A, B and C are in the order :
(A) C2H5Cl, C2H6, C2H5OH
(B) C2H5OH, C2H5Cl, C2H5ONa
(C) C2H5OH, C2H6, C2H5Cl
(D) C2H5OH, C2H5ONa, C2H5Cl
Answer
D
13. The conversion of an alkyl halide into an alcohol by aqueous NaOH is classified as :
(A) a dehydrohalogenation reaction
(B) a substitution reaction
(C) an addition reaction
(D) a dehydration reaction
Answer
B
14. Which of the following is not chiral ?
(A) 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid
(B) 2-Butanol
(C) 2, 3-Dibromopentane
(D) 3-Bromopentane
Answer
D
15. Which of the following structures is enantiomeric with the molecule (a) given below ?

Answer
A
16. Give IUPAC name of the compound given below :

(A) 2-Chloro-5-hydroxyhexane
(B) 2-Hydroxy-5-chlorohexane
(C) 5-Chlorohexan-2-ol
(D) 2-Chlorohexan-5-ol
Answer
C
17. Which of the following compounds will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water ?
(A) C6H5OH
(B) C6H5CH2OH
(C) (CH3)3COH
(D) C2H5OH
Answer
A
18. In the preparation of compounds of Xe, Bartlett had taken O2 +PtF6 – as a base compound. This is because :
(A) both O2 and Xe have same size.
(B) both O2 and Xe have same electron gain enthalpy.
(C) both O2 and Xe have same ionisation enthalpy.
(D) both Xe and O2 are gases.
Answer
C
19. Semi-permeable membrane is that which permits the passage of :
(A) Solute molecules only.
(B) Solvent molecules only.
(C) Both solute and solvent molecules.
(D) Neither of the two
Answer
B
20. In which of the following reactions conc. H2SO4 is used as an oxidizing reagent ?
(A) CaF2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2HF
(B) 2HI + H2SO4 → I2 +SO2 + 2H2O
(C) Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + 2SO2
(D) NaCl + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HCl
Answer
B
21. Complete the following reaction : Xe + PtF6 →
(A) Xe + PtF6 → XeF4 + PtF2
(B) Xe + PtF6 → XeF6 + Pt
(C) Xe + PtF6 → Xe+[PtF6]–
(D) Xe + PtF6 → XeO2F4 + Pt
Answer
C
22. When chlorine reacts with cold and dilute solution of sodium hydroxide it forms :
(A) Cl– and ClO–
(B) Cl– and ClO3–
(C) Cl– and ClO2–
(D) Cl– and ClO4–
Answer
B
23. Name the product obtained on hydrolysis of acetone and methyl magnesium chloride :
(A) Secondary butyl chloride
(B) Isobutyl alcohol
(C) Tertiary butyl alcohol
(D) Iso propyl alcohol
Answer
C
24. IUPAC name of the compound.

(A) 1-methoxy-1-methylethane
(B) 2-methoxy-2-methylethane
(C) 2-methoxypropane
(D) isopropylmethyl ether
Answer
C
25. Flow of solvent molecules from solvent side to solution side through semi-permeable membrane is known as :
(A) Diffusion
(B) Osmosis
(C) Filtration
(D) Crystallization
Answer
B
Section ‘B’
26. Methanol is industrially prepared by :
(A) oxidation of CH4 by steam at 900°C
(B) reduction of HCHO using LiAlH4
(C) Reaction of HCHO with a solution of NaOH
(D) reduction of CO using H2 and ZnO—Cr2O3.
Answer
D
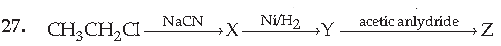
(A) CH3CH2CH2NHCOCH3
(B) CH3CH2CH2NH2
(C) CH3CH2CH2CONHCH3
(D) CH3CH2CH2CONHCOCH3
Answer
A
28. Noble gases have very low melting point. This indicates :
(A) Strong Vander Waals forces between the atoms of noble gases.
(B) Weak vander waals forces between the atoms of noble gases.
(C) The electronic configuration of noble gases is ns2np8.
(D) Noble gases do not react with others.
Answer
B
29. DNA molecule has ___________ internucleotide linkage and __________ sequence of the different nucleotides.
(A) regular, regular
(B) regular, irregular
(C) irregular, regular
(D) irregular, irregular
Answer
B
30. Propene, CH3CH==CH2 can be converted into 1-propanol by oxidation. Indicate which set of reagents amongst the following is ideal for the above conversion ?
(A) KMnO4 (alkaline)
(B) Osmium tetroxide (OsO4/CH2Cl2)
(C) B2H6 and alk. H2O2
(D) O3/Zn.
Answer
C
31. Dinitrogen is inert at room temperature because :
(A) The two nitrogen atoms are bonded by strong triple bond.
(B) The two nitrogen atoms are bonded by weak double bond.
(C) The two nitrogen atoms are bonded by weak bond.
(D) The two nitrogen atoms are bonded by strong single bond.
Answer
A
32. Choose the incorrect statement :
(A) Halogens have strong oxidizing power.
(B) They are highly electronegative.
(C) They can easily accept electrons.
(D) They can easily get oxidized.
Answer
D
33. The reaction
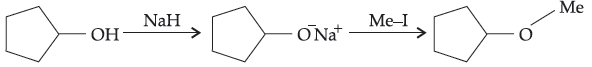
can be classified as :
(A) dehydration reaction
(B) Williamson alcohol synthesis reaction
(C) Williamson ether synthesis reaction
(D) alcohol formation reaction.
Answer
C
34. Which of the following pairs of compounds are enantiomers ?

Answer
A
35. The correct order of N-compounds in its decreasing order of oxidation states is :
(A) HNO3, NH4Cl, NO, N2
(B) HNO3, NO, NH4Cl, N2
(C) HNO3, NO, N2, NH4Cl
(D) NH4Cl, N2, NO, HNO3
Answer
C
36. DNA has a ___________ backbone
(A) phosphate-purine
(B) pyrimidines-sugar
(C) phosphate-sugar
(D) purine-pyrimidine
Answer
C
37. Repeated use of which one of the following fertilizers would increase the acidity of the soil ?
(A) Ammonium sulphate
(B) Superphosphate of lime
(C) Urea
(D) Potassium nitrate
Answer
A
38. The vacant space in bcc lattice unit cell is :
(A) 48%
(B) 23%
(C) 32%
(D) 26%
Answer
C
39. The tendency of BF3, BCl3 and BBr3 to behave as Lewis acid decreases in the sequence :
(A) BCl3 > BF3 > BBr3
(B) BBr3 > BCl3 > BF3
(C) BBr3> BF3 > BCl3
(D) BF3 > BCl3 > BBr3
Answer
B
40. Methanol is industrially prepared by :
(A) oxidation of CH4 by steam at 900°C.
(B) reduction of HCHO using LiAlH4.
(C) reaction of HCHO with a solution of NaOH.
(D) reduction of CO using H2 and ZnO—Cr2O3.
Answer
A
41. Which of the following compounds is most acidic ?

Answer
C
42. AlF3 is soluble in HF only in presence of KF. It is due to the formation of :
(A) K3[AlF3H3]
(B) K3[AlF6]
(C) AlH3
(D) K[AlF3H]
Answer
B
43. The reaction,

is called :
(A) Etard reaction
(B) Gattermann-Koch reaction
(C) Williamson synthesis
(D) Williamson continuous etherification process
Answer
C
44. On sulphonation of C6H5Cl :
(A) Benzene sulphonic acid is formed.
(B) Meta-chloro benzene sulphonic acid is formed.
(C) Ortho- chloro benzene sulphonic acid is formed.
(D) Ortho and para chloro benzene sulphonic acid is formed.
Answer
D
From Q.45 to Q.49, Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R) and at the end of each question give the following line select the most appropriate answers from the options given below :
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
45. Assertion (A) : Bismuth forms only one well characterised compound in +5 oxidation state.
Reason (R) : Elements of group-15 form compounds in +5 oxidation state.
Answer
B
46. Assertion (A) : It is difficult to replace chlorine by –OH in chlorobenzene in comparison to that in chloroethane.
Reason (R) : Carbon-chlorine (C—Cl) bond in chlorobenzene has a partial double bond character due to resonance.
Answer
D
47. Assertion (A) : NaCl reacts with concentrated H2SO4 to give colourless fumes with pungent smell.
But on adding MnO2 the fumes become greenish yellow.
Reason (R) : MnO2 oxidizes HCl to chlorine gas which is greenish yellow.
Answer
A
48. Assertion (A) : Silicon and germanium belong to group 14 of the periodic table and can be doped with group 15 elements.
Reason (R) : The place where the fourth valence electron is missing is called electron hole or electron vacancy.
Answer
B
49. Assertion : The osmotic pressure of a solution obtained by mixing 100 ml of 3.4 % solution of urea and 100 ml of 1.6% solution of cane sugar at 293K is 7.46 bar.
Reason : The total osmotic pressure will be equal to the sum of partial osmotic pressure.
Answer
A
Section ‘C’
50. Out of the four different kinds of nitrogenous bases which are commonly found in DNA, ___________ has been replaced in some organisms.
(A) adenine
(B) guanine
(C) cytosine
(D) thymine
Answer
C
51. Percentage of lead in lead pencil is :
(A) Zero
(B) 20
(C) 80
(D) 70
Answer
A
52. Vinyl chloride on reaction with dimethyl copper gives :
(A) Ethyl chloride
(B) Ethene
(C) Ethyne
(D) Polyvinyl chloride
Answer
D
CASE 1 : Read the passage given below and answer the following questions 53-55
Solution plays a very important role in our daily life. Alloys, a homogeneous mixture of metal are solutions of solid in solid. 1 ppm (parts per million) of fluoride ions prevent tooth decay. All intravenous injections must be isotonic with our body fluids, i.e. should have the same concentration as blood plasma. Diabetic patients are more likely to have a heart attack and high blood pressure due to the higher glucose levels in the blood. Common salt increases blood pressure because Na+ mixes up with blood. Aquatic species are more comfortable in cold water than warm water.
53. What will happen if blood cells are kept in hypertonic solution?
(A) They swell
(B) They shrink
(C) They remain same
(D) They die
Answer
B
54. When solvent and solution are separated by semi-permeable membrane, and the pressure applied on the solution side is more than the osmotic pressure, the process which takes place is :
(A) Diffusion
(B) Osmosis
(C) Reverse osmosis
(D) Disintegration
Answer
C
55. Calculate the molarity of 30 g of Co(NO3)2. 6H2O in 4.3 liter of solution.
(molar mass of solute =290.7g/mol)
(A) 0.103 M
(B) 0.24M
(C) 0.48 M
(D) 30M
Answer
B
