Class 12 Economics Sample Paper Term 1 Set A
Please see below Class 12 Economics Sample Paper Term 1 Set A with solutions. We have provided Class 12 Economics Sample Papers with solutions designed by Economics teachers for Class 12 based on the latest examination pattern issued by CBSE. We have provided the following sample paper for Term 2 Class 12 Economics with answers. You will be able to understand the type of questions which can come in the upcoming exams.
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Economics Term 1 Set A
Section A
1. Transient poor refers to which of the following category of people?
(a) People who are never poor
(b) People who are occasionally poor
(c) People who are churning poor
(d) None of these
Answer
D
2. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Systemic record of all transactions of goods and services between residents of home country and residents of rest of the world is balance of trade.
Statement II Balance of invisible trade and balance of services are one or same thing.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
B
3. The central bank of a country functions as an advisor to ……… .
(a) commercial banks
(b) general public
(c) government
(d) All of these
Answer
C
4. The female literacy during colonial rule was ……… .
(a) 7%
(b) 10%
(c) 16%
(d) 20%
Answer
A
5. In India, poverty line is comprised of ……… criterions.
(a) calorie’s consumption
(b) monthly per capita expenditure
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
C
6. The data related to poverty in the country is collected by ……… .
(a) CSO
(b) ISI
(c) NSSO
(d) All of these
Answer
C
7. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I It is difficult to bring chronically poor people above the poverty line.
Statement II People who are much below poverty line are referred to as chronical poor.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
8. Foreign exchange reserves are considered as ……… for an economy.
(a) an asset
(b) a liability
(c) a flow variable
(d) None of these
Answer
A
9. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Regional imbalance is an objective of government budget.
Statement II Government budget uses taxes and subsidies to reduce income inequalities.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
B
10. In India, income inequality is a major concern not in terms of income but also in terms of distribution of assets and wealth. Government through its policies tries to minimise this difference. Which of the following types of tax is used in the country to reduce income inequalities?
(a) Progressive tax
(b) Regressive tax
(c) Proportional tax
(d) None of these
Answer
A
11. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Currency held by public is not a component of money supply, if hoarded by the public.
Statement II Currency notes and coins are the most liquid form of money supply.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
12. Goods which are socially non desirable are discouraged by the government through ……… .
(a) heavy subsidies
(b) low subsidies
(c) high taxes
(d) lower taxes
Answer
C
13. At a given point of time, commercial banks created ₹ 5,000 crores when they were required 25% as reserves. What should have been the amount of primary deposits with the bank?
(a) ₹1,000 crores
(b) ₹1,250 crores
(c) ₹ 2,000 crores
(d) ₹2,500 crores
Answer
B
14. The occupational structure of India was majorly divided in ……… sector(s) during colonial period.
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Answer
B
15. India meets most of its crude oil demand by the way of imports as the reserves are not sufficient for meeting demand. UAE is the most important trading partner of India in that respect. In which of the following account of BoP, will this import be recorded?
(a) Capital account
(b) Current account
(c) Accommodating account
(d) None of these
Answer
B
16. Choose the correct pair from given below
Column I Column II
A. Planned decrease in the value of domestic currency (i) Depreciation
B. Above line items of BoP (ii) Accommodating items
C. Increase in value of domestic currency (iii) Revaluation
D. Market determination as well as government intervention (iv) Managed floating rate
Codes
(a) A – (i)
(b) B – (ii)
(c) C – (iii)
(d) D – (iv)
Answer
D
17. The reduction of …………… is an inalienable component included in the conditionality of structural reforms during the new economic policy.
(a) trade deficit
(b) fiscal deficit
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
B
18. Which of the following is not an example of a commercial bank in India?
(a) LIC
(b) SBI
(c) ICICI
(d) PNB
Answer
A
19. In Indian System of Medicine (ISM) AYUSH, letter S stands for ……… .
(a) Sindhu
(b) Siddha
(c) Siddhu
(d) None of these
Answer
B
20. ……… is not a source of institutional credit in rural banking system.
(a) Commercial banks
(b) Regional rural banks
(c) Moneylenders
(d) Micro-credit institutions
Answer
C
21. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Increase in money supply in the economy leads to fall in purchasing power of money.
Statement II Money supply in the economy is controlled only by the central bank of the country.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
22. ……… is/are an indicator of poverty in India.
(a) Income level
(b) Illiteracy level
(c) Employment level
(d) All of these
Answer
B
23. India’s health infrastructure has improved a lot since independence in terms of number of hospitals, hospital bed, PHCs, CHCs, doctors, medical staff etc. In spite of all these efforts, the resources are not sufficient as compared to the few neighbouring countries due to which of the following reasons?
(a) Rapid population growth
(b) Unequal distribution in rural and urban areas
(c) Less proportion of expenditure on health by government
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
24. Various types of production included in primary sector are ………… .
(a) animal husbandry
(b) production of milk
(c) goods related to animal produce
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Section B
25. Assertion (A) Deficit in balance of payment is caused by autonomous items.
Reason (R) The aim of the country is to bring BoP in balanced situation so as to stop further inflow and outflow of foreign exchange.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
26. The calorie requirement for poverty line is in the rural areas because ……… .
(a) they can’t enjoy as much as people in the urban areas
(b) food is less expensivehigher
(c) they are engaged in mental work
(d) people are engaged in physical labour
Answer
D
27. Assertion (A) Commercial banks are the bankers for all levels of government.
Reason (R) Government need financial help whenever it faces a situation of budget deficit.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
C
28. Which of the following statements is/are true about current account of BoP?
(i) These items are non-debt creating
(ii) These are recurring in nature
(iii) It leads to assets creation
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer
A
29. Choose the incorrect pair from given below.
Column I Column II
A. Jan Dhan Yojana (i) 2014
B. MGNREGA (ii) 2005
C. Debt trap (iii) Cause and consequence of poverty
D. SJSRY (iv) Social security program for elderly people
Codes
(a) A – (i)
(b) B – (ii)
(c) C – (iii)
(d) D – (iv)
Answer
D
30. Choose the correct statement from the given below.
(a) Demand curve for foreign exchange is upward sloping.
(b) Supply curve for foreign exchange is downward sloping.
(c) Both (a) and (b) are correct
(d) Both (a) and (b) are incorrect
Answer
D
31. India’s HDI rank was too low because of ……… .
(a) poor literacy rate
(b) poor education facilities
(c) poor health services
(d) All of these
Answer
D
32. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Licencing policy was introduced during 1950s for controlled growth of public sector.
Statement II Licencing leads to privatisation and disinvestment.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
D
33. Assertion (A) Borrowings are capital receipts but payment of interest on borrowings is revenue expenditure.
Reason (R) Borrowings create liability but payment of interest does not reduce liability.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
34. Which banks come under multi-agency system?
(a) Cooperative banks
(b) Commercial banks
(c) Regional rural banks
(d) All of these
Answer
B
35. Blue revolution is associated with ……… .
(a) indigo cultivation
(b) fisheries
(c) availability of drinking water
(d) None of these
Answer
B
36. In which of the following ways, colonial government drained India’s revenue from foreign trade?
(a) Payment for losses
(b) Payment of salaries
(c) War expenses
(d) All of these
Answer
D
37. Assertion (A) Appreciation of domestic currency means a rise in the price of domestic currency.
Reason (R) Appreciation leads to decrease in exports.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
38. Choose the correct pair from given below.
Column I Column II
A. World trade organisation (i) 1948
B. Implementation of GST (ii) 2016
C. GATT (iii) 1995
Codes
(a) A – (i)
(b) B – (ii)
(c) C – (iii)
(d) All of these
Answer
D
39. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Human development and economic growth are positively related.
Statement II Human capital creates both private and social benefits.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
40. ………… policy is used to encourage public sector companies to perform better.
(a) Maharatna
(b) Navratna
(c) Miniratna
(d) All of these
Answer
D
41. Assertion (A) Agricultural subsidies are the major reason of government deficit, specially the fertiliser subsidy.
Reason (R) The economic help given to farmers leads to overuse of resources and under productivity.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
42. Rural development is the process of improving the quality of life and economic well being of people living in rural areas. It focuses on all major areas. In broad sense, which of the following categories are included in rural development?
(a) Social development
(b) Economic development
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
43. Assertion (A) The economic motive of infrastructure development during the colonial rule was to establish better administrative control.
Reason (R) Infrastructural development is one of the positive contributions of colonial government in India.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
44. Choose the correct statement from given below.
(a) If primary deficit is ₹ 3,500 and interest payment is ₹500, then fiscal deficit will be ₹3,000
(b) The difference between borrowings and interest payment is fiscal deficit
(c) Surplus budget is when estimated revenue of the government is more than estimated expenditure of the government
(d) All of the above
Answer
C
45. Assertion (A) Poverty line can lead to misleading conclusion related to the group of people who are poor.
Reason (R) Poverty line creates a line of bifurcation between people who are poor and who are not.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
46. Assertion (A) India’s poverty alleviation programmes faced major setback due to lack of proper implementation.
Reason (R) Growth rate of population has led to availability of less resources for poverty alleviation
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
47. Observe the image given below carefully.
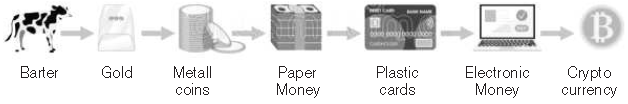
Which of the following about the money is indicated above?
(a) Money demand
(b) Components of money supply
(c) Evolution of money
(d) Modes of money supply
Answer
C
48. Assertion (A) Credit creation process increases the money supply in economy.
Reason (R) By credit creation process, commercial banks can distribute loans many more times compared to their initial deposits.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
A
Section C
Direction : – Read the following case study and answer questions 49 to 54 on the basis of the same.
On 12th May, 2020, the Prime Minister, in an address to the nation, said that the coronavirus crisis should be seen as an opportunity, laying emphasis on domestic products and “economic self-reliance”, creation of an Atmanirbhar Bharat (transl. Self-reliant India), through Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan (transl. Self-reliant India Mission).
He announced a 20 trillion rupees stimulus package, equivalent to 10% of India’s GDP, which was laid out in detail by the Finance Minister in a series of tranches. During the COVID-19 pandemic in India, Finance Minister announced a ₹ 1.70 Lakh Crore ($24 billion) relief package under Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana for the poor.
As per the estimates of the government, data is given below.
• ₹ 500 each to 19.86 crore women Jan Dhan account holders.
• ₹ LPG cylinders to be provided to 8 crore poor families for the next three months free of cost.
• ₹ 1,000 for senior citizens to tide over difficulties during the next three months.
• As of 11th April, ₹ 28,256 crores ($4 billion) were distributed through PMGKY to nearly 32 crore beneficiaries.
• ₹ 50,000 crore in Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyan for returne migrant workers.
49. The Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana indicates which of the following objectives of government budget?
(a) Reducing inequality of income and wealth
(b) Reallocation of resources
(c) Economic growth
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
50. The relief package announced by the government is an example of which of the following types of expenditures?
(a) Revenue expenditure
(b) Capital expenditure
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
51. Assertion (A) Relief packages announced by the government during the pandemic are a non-planned expenditures.
Reason (R) Non-planned expenditures are generally non-developmental in nature.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
B
52. There are various relief packages mentioned above, which of the following indicates the reallocation objective of government budget?
(a) Jan Dhan Yojana
(b) Atmanirbhar Bharat
(c) Ujjawala Yojana
(d) All of these
Answer
B
53. ‘‘₹1,000 for senior citizens to tide over difficulties during the next three months.’’ This announcement indicates which of the following objectives of budget?
(a) Reducing inequality of income
(b) Social welfare
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
C
54. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following.
Statement I Non-planned expenditures of government budget leads to revenue deficit.
Statement II No provision can be made for non-planned expenditures.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
Direction : – Read the following case study and answer questions 55 to 60 on the basis of the same.
New economic policy of India was launched in the year 1991 under the leadership of P. V. Narasimha Rao. This policy opened the door of the Indian economy for the global exposure for the first time. In this new economic policy, P. V. Narasimha Rao government reduced the import duties, opened reserved sector for the private players and devalued the Indian currency to increase the export. This is also known as the LPG Model of growth.
New economic policy refers to economic liberalisation or relaxation in the import tariffs, deregulation of markets or opening the markets for private and foreign players, and reduction of taxes to expand the economic wings of the country. Former Prime Minister, Manmohan Singh is considered to be the father of New Economic Policy (NEP) of India. He introduced the NEP on 24th July, 1991.
55. Who was the finance minister to introduced new economic policy of 1991?
(a) P.V. Narasimha Rao
(b) Dr. Manmohan Singh
(c) Indira Gandhi
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
56. Assertion (A) Indian currency was revalued during the NEP to improve the export compatibility of India.
Reason (R) Decrease in the value of domestic currency makes domestic goods cheaper in international market leading to inflow of foreign exchange.
Alternatives
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
(d) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false
Answer
C
57. Statement I New economic policy gave greater autonomy to private sector.
Statement II Increasing role of public sector in the economic functioning leads to major inefficiencies.
Alternatives
(a) Statement I is correct and Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement II is correct and Statement I is incorrect
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are incorrect
Answer
C
58. Licencing policy was not removed for few industries which includes ……… .
(a) liquor
(b) cigarette
(c) industrial explosive
(d) All of these
Answer
D
59. Tax reforms introduced as a part of liberalisation includes which of the following?
(a) Reduction in tax rate
(b) Simplification of tax payment process
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
60. Globalisation policy is an outcome of which of the following policies?
(a) Disinvestment and privatisation
(b) Disinvestment and liberalisation
(c) Liberalisation and privatisation
(d) Liberalisation, disinvestment and privatisation
Answer
C

