Carbon and Its Compound Class 10 Science Important Questions
Please refer to Carbon and Its Compound Class 10 Science Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions and Equations in NCERT Book for Class 10 Science have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 10 Science for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compound
All Carbon and Its Compound Class 10 Science Important Questions provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of Standard 10 Science. Please learn them and let us know if you have any questions.
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question. Write the electron dot structure of ethane molecule C2H6.
Answer:

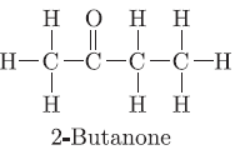
Question. Draw the structure of butanone molecule, CH3COC2H5.
Answer:
Question. Draw the structure of ethanoic acid molecule, CH3COOH.
Answer:

Question. Why do alkanes burn with blue flame?
Answer: It is because they have less carbon and more hydrogen, therefore, undergo complete combustion and produce blue flame.
Question. What is meant by saturated hydrocarbon?
Answer: Those hydrocarbons in which valency of carbon is satisfied by single bonds only are called saturated hydrocarbons.
Question. Write the molecular formula of benzene and state the number of double bonds in its structure.
Answer:

Question. How is scum formed?
Answer: Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions react with soap (sodium stearate) to form calcium and magnesium stearate which is nsoluble in water and called scum.
Question. Write the name and formula of 2nd member of the series of carbon compounds whose general formula is CnH2n.
Answer: CH2=CH—CH3, Propene
Question. Carbon has four electrons in its valence shell. How does carbon attain stable electronic configuration?
Answer: Carbon can share four electrons to acquire stable electronic configuration.
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following compounds:
a. CH3COCH3
b. C2H5COOH
Answer:
a. Ketone
b. Carboxylic acid
Question. Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n – 2.
Answer: General formula, CnH2n–2 belongs to alkyne series. The second member of this series is propyne i.e., (C3H4) or CH3 — C ≡CH.
Question. Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group —Cl.
Answer: The molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having –Cl functional group are CH3Cl and CH3CH2Cl.
Question. Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group —OH.
Answer: The molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having –OH functional group are CH3OH and CH3CH2OH.
Question. Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and 3rd member of the homologous series whose first member is ethene.
Answer: Homologous series of alkenes have general formula, CnH2n whose first member is ethene.
2nd member of homologous series of alkenes is C3H6 i.e., propene.
3rd member of homologous series of alkenes is C4H8 i.e., butene.
Question. Write the molecular formula of the 2nd and 3rd member of the homologous series whose first member is methane.
Answer: Methane, CH4 is an alkane. Alkanes have general formula, CnH2n+2.
2nd member of homologous series of alkanes is C2H6 i.e., ethane.
3rd member of homologous series of alkanes is C3H8 i.e., propane.
Question. What is homologous series of carbon compounds?
Answer: A homologous series is the family of organic compounds having the same functional group, similar chemical properties but the successive (adjacent) members of the series are differ by a CH2 unit or 14 mass units.
Question. Write the next homologue of each of the following :
(i) C2H4
(ii) C4H6
Answer: (i) C2H4 belongs to alkene series having general formula, CnH2n.
Thus, next homologue will be C3H2 × 3 = C3H6
(ii) C4H6 belongs to alkyne series having general formula, CnH2n–2.
Thus, next homologue will be C5H2 × 5 – 2 = C5H8
Question. Name the following compounds :
(a) CH3 — CH2 — OH
H
I
(b) CH3 – C = O
Answer: (a) CH3 — CH2 — OH : Ethanol
(b) CH3 — C = O
I
H
Question. Select saturated hydrocarbons from the following :
C3H6; C5H10; C4H10; C6H14; C2H4
Answer: Saturated hydrocarbons have general formula, CnH2n+2.
Among the given compounds only C4H10 and C6H14 satisfy the above formula. Thus, these are saturated hydrocarbons.
Question. Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of ethane.
Answer: The structural formula of ethane (C2H6) is :
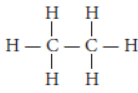
There are total 7 covalent bonds. Six C — H covalent bonds and one C — C covalent bond.
Question. Write the name and structure of an alcohol with three carbon atoms in its molecule.
Answer: An alcohol with three carbon atoms in its molecule is propanol. The structure of propanol is :
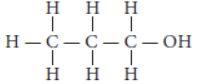
Question. State two characteristic features of carbon which when put together give rise to a number of carbon compounds.
Answer: Due to catenation and tetravalency, carbon gives rise to a number of carbon compounds.
Question. Write the name and formula of the second member of carbon compounds having functional group —OH.
Answer: CH3CH2OH, Ethanol
Question. Write the name and formula of the FIrst member of the series of carbon compounds having functional group O
II
– C – OH
Answer: Carbon compound containing O
II
– C – OH
group is called carboxylic acid. The first member of this family is methanoic acid (HCOOH).
O
II
H – C- OH
Question. List two characteristic features of carbon which when put together given rise to a number of carbon compounds.
Answer: (a) Tetravalency (b) Catenation
Question. Write the name and formula of the first member of series of carbon compound having functional group —CHO.
Answer: O
II
H-C – H Methanal
Question. Draw the structure of the hexanal molecule C5HnCHO.
Answer:

Question. Name the functional group in the following compounds:
a. CH3—CH2—CH2—COOH
b. CH3—CO—CH2—CH3
Answer:
a. Carboxylic acid
b. Ketone
Question. What happens when a small piece of sodium is dropped into ethanol?
Answer: Sodium ethoxide and H2 gas is formed 2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2
Question. Write the name and formula of the first member of carbon compounds having functional group —COOH.
Answer: O
II
H-C – OH Methanoic acid
Question. Write the electron dot structure of ethene molecule (C2H4).
Answer:

Question. Write the name and formula of 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n.
Answer: CH2=CH—CH3 is second member of alkene.
Question. Explain why washing clothes with hard water is not effective.
Answer: Soap reacts with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions present in hard water to form scum.
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following compounds:
a. HCOOH
b. C2H5CHO
Answer:
a. Carboxylic acid
b. Aldehyde
Question. State the difference between oils and fats.
Answer: Oils are unsaturated whereas fats are saturated compounds.
Question. Write the name and formula of 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n-2 .
Answer: HC / C—CH3, Propyne
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compounds:
a. C2H5—Cl
b. C2H5OH
Answer:
a. Halogen
b. Alcohol
Question. The molecular formula of A is C10H18 and B is C18H36.
Name the homologous series to which they belong.
Answer: C10H18 belongs to alkyne, C18H36 belongs to alkene.
Question: Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling point. Why?
Answer: Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points because they are made up of electrically neutral molecules. So, the force of attraction between the molecules of a ovalent compound is very weak.
Explanation: Only a small amount of heat energy is required to break these weak molecular forces. That is why covalent compound have low melting boiling points.
Question: Name a cyclic unsaturated carbon compound.
Answer: Benzene is a cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbon.
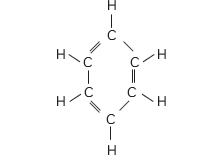
Explanation: Benzene is unsaturated hydrocarbon as it has more than one double
bond and all the carbon atoms are arranged in the form of a ring. Its molecular formula shows it has 6 carbon atoms and 6 hydrogen double atoms and it has 3 carbon-carbon double bonds, 3 carbon-carbon single bonds and ??
carbon-hydrogen single bonds.
Question: Carbon has four electrons in its valence shell. Which type of compounds can be formed by carbon atom and why? Give any one example of such compounds.
Answer: Carbon forms covalent compounds with other atoms by sharing electron pairs because of the following reasons:
(1) Carbon cannot form C4+ cation by losing four electrons, as it would require a large amount of energy to remove four electrons leaving behind a carbon cation with six protons in its nucleus holding on to just two electrons.
(2) Carbon cannot form C4– anion by gaining four electrons, as it would be diffcult forthe nucleus with six protons to hold on to ten electrons.
Example of compounds formed by carbon:
(i) Methane (CH4)
(ii) Ethene (C2H4)
(iii) Propyne (C3H4)
(iv) Ethanol (C2H5OH)
Question: Write chemical name of the compound CH3—CH2—CH2—Br.
Answer: 1-Bromo Propane
Question. Write the chemical equation to show what happen when methane is treated with chlorine in the presence of sunlight ?
Answer: When methane is treated with chlorine in the presence of sunlight then substitution reaction takes place. In this, chlorine replaces the hydrogen atom of methane.
CH4 + Cl2 Sunlight → CH3 Cl +HCl
Question. Write the respective chemical reaction to show what happens when methane is burnt in presence of oxygen?
Answer: When methane is burnt in presence of oxygen then carbon dioxide will be produced.
CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + heat + light
Question. Write one chemical equation to represent the following type of reaction of organic substances : substitution.
Answer: Substitution : In this type of reaction one or more hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon is replaced by some other atoms.
CH4 + Cl2 Sunlight → CH3 Cl + HCl
Methane Chloromethane
Question. Give reason for the following : Acetylene burns with a sooty flame.
Answer: The formula of acetylene is HC ≡ CH. It is an unsaturated hydrocarbon where carbon content is more than the hydrogen content. Hence, carbon is not completely burnt and the unburnt carbon deposits as a soot.
Question. Give reason for the following : Kerosene does not decolourise bromine water while cooking oils do.
Answer: Cooking oils (unsaturated compounds) decolourise bromine water due to formation of addition products whereas kerosene (saturated compound) does not decolourise bromine water.
Question. Butanone is a four-carbon per molecule compound. Name the functional group present in it.
Answer: Butanone is CH3 – C – C2H5.
II
O
Question: Write the molecular formula of first two members of homologous series having functional group –Cl.
Answer: Molecular formula of first two members of the homologous series having functional group –Cl is CH3Cl and C2H5Cl.
Question: Write the name and molecular formula of the fourth member of alkane series.
Answer: Butane, C4H10
Question: What is the difference in the molecular mass of any two adjacent homologues?
Answer: Two successive homologues would differ by one carbon atom and two hydrogen atoms in terms of atoms in their molecules and thus differ by 14 amu in terms of molecular mass.
Explanation: For example C4H8 and C5H10 are successive compounds. These two differ by — CH2
Atomic mass of carbon = 12
Atomic mass of Hydrogen = 1μ
Molecular mass of —CH2 = 1 x12 + 2 x 1 = 14μ
Question: Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of ethane.
Answer: Seven
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question. Name the compound formed when ethanol is heated in excess of conc. sulphuric acid at 443 K. Also write the chemical equation of the reaction stating the role of conc. sulphuric acid in it. What would happen if hydrogen is added to the product of this reaction in the presence of catalyst such as palladium or nickel?
Answer: If hydrogen is added to ethene in presence of palladium or nickel catalyst then one atom of hydrogen adds to each carbon atom of ethene to form ethane.
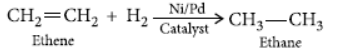
Question. Distinguish between ionic and covalent compounds under the following properties :
(i) Strength of forces between constituent elements.
(ii) Solubility of compounds in water.
(iii) Electrical conduction in substances.
Answer: (i) Ionic compounds have strong forces between its constituent elements because they are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction. On the other hand, covalent compounds have weaker forces of attraction between its constituent elements as bond is formed by sharing of electrons.
(ii) Ionic compounds are highly soluble in water but they are insoluble in non-polar organic solvents. On the other hand, covalent compounds are generally insoluble in water but they are soluble in non-polar solvents.
(iii) Ionic compounds conduct electricity in aqueous state or in molten state because they produce ions which are good conductors of electric current. On the other hand, covalent compounds are bad conductors of electricity due to absence of ions.
Question. Write the name and structure of an alcohol with four carbon atoms in its molecule.
Answer: An alcohol with four carbon atoms is butanol and its structure is :
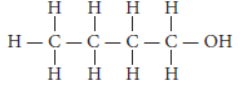
Question. Write the name and structure of an aldehyde with four carbon atoms in its molecule.
Answer: An aldehyde with four carbon atoms is butanal and its structure is :
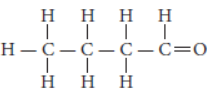
Question. Which element exhibits the property of catenation to maximum extent and why?
Answer: Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation.
Carbon shows catenation due to its small size and stronger carbon-carbon bond strength.
Question. Write the name and molecular formula of the fourth member of alkane series.
Answer: The general formula of the alkane series is CnH2n+2. For fourth member of alkane series, n = 4 ∴ C4H2 × 4 + 2 = C4H10 i.e., butane.
Question. Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of butane, C4H10.
Answer: Butane (C4H10) has the following structural formula as :
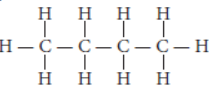
Total number of covalent bonds is 13 in which 10 C — H and 3 C – C covalent bonds.
Question. Write the name of each of the following functional groups :
(a) — OH
(b) – C –
II
O
Answer: (a) —OH : Alcohol
(b) – C – : Ketone
II
O
Question. Write the name and molecular formula of the FIrst member of the homologous series of alkynes.
Answer: General formula for alkyne is CnH2n–2.
First member of homologous series of alkyne has the formula, C2H2 × 2–2 ≡ C2H2 i.e., ethyne.
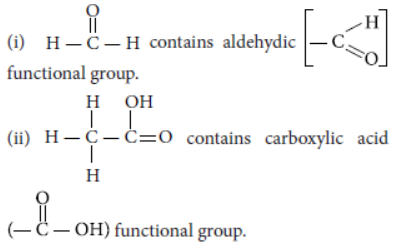
Question. DeFIne the term functional group. Identify the functional group present in
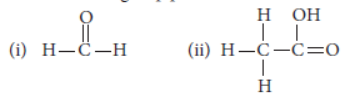
Answer: An atom or a group of atoms present in a molecule which largely determines its chemical properties, is called functional group.
Question. Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compounds :
(i) C2H5Cl
(ii) C2H5OH
Answer: (i) C2H5Cl contains —Cl (chloro) group which belongs to halo functional group.
(ii) C2H5OH contains —OH group which belongs to alcoholic functional group.
Question. Write the name and formula of the second member of the carbon compounds having functional group –OH.
Answer: Those having —OH as functional group belong to alcohol family. Second member of this family is ethanol, C2H5OH.
Question. Write chemical equation of the reaction of ethanoic acid with the following :
(a) Sodium;
Write the name of one main product of each reaction.
Answer: Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium as well as sodium hydroxide to form sodium ethanoate.
(a) 2CH3COOH + 2Na → 2CH COONa + H2↑
Ethanoic acid Sodium
ethanoate
Question. (i) What would be observed on adding a 5% solution of alkaline potassium permanganate solution drop by drop to some warm ethanol taken in a test tube?
(ii) Write the name of the compound formed during the chemical reaction?
Answer: (i) Colour of KMnO4 will get discharged.
(ii) The chemical compound formed is ethanoic acid.
CH3CH2OH + 2[O] alkaline → KMnO4 CH3COOH + H2O
Ethanol Ethanoic acid
Question. On dropping a small piece of sodium in a test tube containing carbon compound ‘X’ with molecular formula C2H6O, a brisk effervescence is observed and a gas ‘Y’ is produced. On bringing a burning splinter at the mouth of the test tube the gas evolved burns with a pop sound. Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’. Also write the chemical equation for the reaction. Write the name and structure of the product formed, when you heat ‘X’ with excess conc. sulphuric acid.
Answer: Ethanol reacts with sodium to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas is liberated which burns with a pop sound.
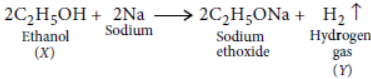
Thus, compound X is ethanol and gas Y is hydrogen gas.
When ethanol is heated with excess of concentrated sulphuric acid then it gets dehydrated to form ethene.
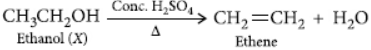
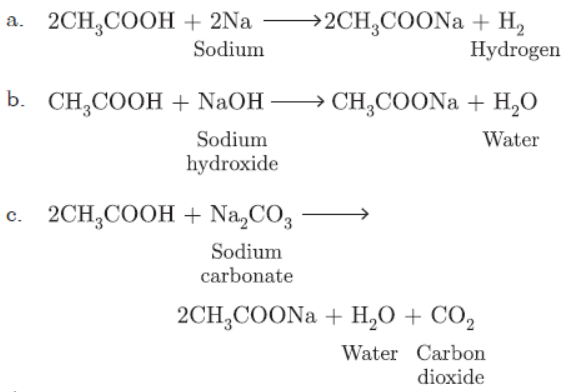
Question. Write three different chemical reactions showing the conversion of ethanoic acid to sodium ethanoate. Write balanced chemical equation in each case. Write the name of the reactants and the products other than ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate in each case.
Answer: Ethanoic acid reacts with Na2CO3 to form sodium ethanoate and CO2 gas is liberated.
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + CO2
Ethanoic Sodium Sodium Carbon
acid carbonate ethanoate dioxide + H2O Water
With sodium hydrogen carbonate it forms sodium ethanoate.
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + CO2
Ethanoic Sodium Sodium Carbon
acid bicarbonate ethanoate dioxide + H2O Water
With NaOH it forms sodium ethanoate.
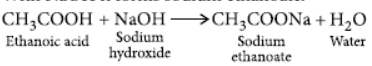
Question. Write the name and molecular formula of an organic compound having its name suffixed with ‘ol’ and having two carbon atoms in its molecule. Write balanced chemical equation to indicate what happens when this compound is heated with excess conc. H2SO4 and the name of main product formed. Also state the role of conc. H2SO4 in the reaction.
Answer: Those organic compounds having suffix ‘ol’ are alcohols. As the alcohol having two carbon atoms in its molecule so, it is ethanol.
Question. An organic compound ‘P’ is a constituent of wine. ‘P’ on reacting with acidiffed K2Cr2O7 forms another compound ‘Q’. When a piece of sodium is added to ‘Q’, a gas ‘R’ evolves which burns with a pop sound. Identify P, Q and R and write the chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Answer: ‘P’ is ethanol which is a constituent of wine.
Ethanol on reacting with acidiffed potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) solution gives ethanoic acid ‘Q’.
CH3CH2OH acidic K2Cr2O7 → Δ CH3COOH
Ethanol (P) Ethanoic acid (Q)
When a piece of sodium is added to ethanoic acid then sodium salt of ethanoic acid is formed with the liberation of hydrogen gas which burns with a pop sound.
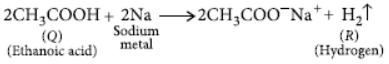
Question. What are esters? How are they prepared? List two uses of esters.
Answer: Esters are generally volatile liquids which have pleasant fruity smell.
Esters are prepared when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of small amount of concentrated H2SO4. For example, when ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol it forms an ester (i.e. ethyl ethanoate).
CH3COOH + C2 H5 OH conc. → H2SO4 CH3COOC2H5
Ethanoic acid Ethanol Ethyl ethanoate + H2O
Uses of ester :
1. It is used in making perfumes.
2. It is used in making artificial Faavours and essences used in ice-creams, sweets and cold drinks.
Question. Describe a chemical test to distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid.
Answer: Chemical test for ethanol and ethanoic acid is :
Ethanoic acid reacts with Na2CO3 or NaHCO3 to
give brisk effervescence of CO2 gas.
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + CO2↑+ H2O
While ethanol does not react with Na2CO3 or NaHCO3.
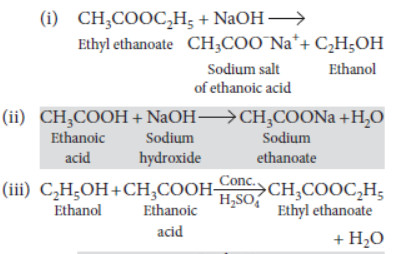
Question. Complete the following chemical equations :
(i) CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH →
(ii) CH3COOH+ NaOH →
(iii) C H5OH+CH COOH Conc.H2SO4 →
Answer:
Question. A carboxylic acid (molecular formula, C2H4O2) reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form a compound ‘X’. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acidification gives the same carboxylic acid C2H4O2. Write the name and structure of (i) carboxylic acid, (ii) alcohol and (iii) the compound ‘X’.
Answer: The molecular formula of carboxylic acid is C2H4O2. Thus, it should be acetic acid (ethanoic acid).
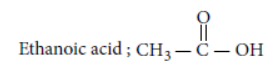
It reacts with alcohol in presence of acid catalyst to give compound ‘X’.
As alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 gives the same acid i.e. ethanoic acid, hence alcohol must contain two carbon atoms. Thus, formula for alcohol is CH3CH2OH i.e. ethanol.
Reactions involved are :
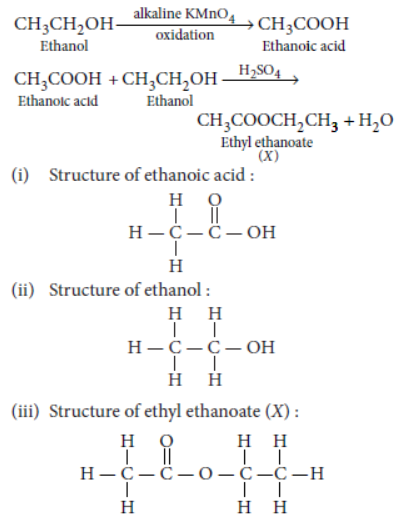
Question. Write the chemical equation to explain what happens when ethanol is heated with alkaline solution of potassium permanganate.
Mention two physical properties and two uses of ethanol.
Answer: When ethanol is heated with alkaline solution of potassium permanganate then oxidation of ethanol takes place to form ethanoic acid.
CH3 CH2OH alkaline KMnO4 → CH3 COOH
Ethanol Ethanoic acid
Two physical properties of ethanol are :
1. It is liquid at room temperature.
2. It is soluble in water in all proportions.
Two uses of ethanol are :
1. It is used as a liquor for drinking purpose.
2. It is a good solvent and hence, it is used in medicines such as tincture of iodine, cough syrup and many tonics.
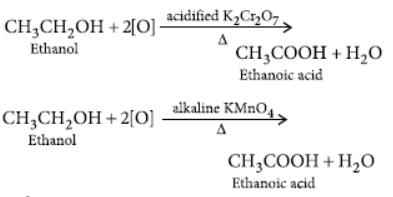
Question. Write chemical equations to describe two examples of different oxidations of ethanol.
List two uses of ethanol.
Answer: Addition of oxygen to any substance is called oxidation.
Ethanol gets oxidised to ethanoic acid as :
Question. (a) The structural formula of an ester is
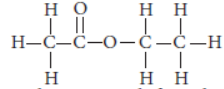
Write the structural formulae of the corresponding alcohol and the acid.
(b) (i) Mention experimental conditions involved in obtaining ethene from ethanol.
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the above reaction.
Answer: (a) The structural formula of ester is
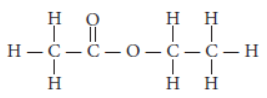
So, the corresponding alcohol and acid from which it is formed will be :
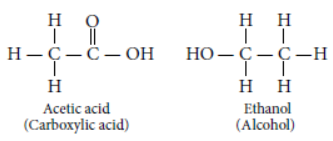
Question. List two tests for experimentally distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid and describe how these tests are performed.
Answer: Tests for distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid are :
(i) Litmus test : When we place a drop of carboxylic acid on blue litmus paper it turns red while alcohol will not change the colour of blue litmus paper.
(ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate test/sodium
carbonate test : If a pinch of NaHCO3 or Na2CO3 is added to two test tubes containing alcohol and carboxylic acid respectively. tHen test tube containing carboxylic acid will show the evolution of colourless gas with brisk effervescence while test tube containing alcohol does not show any reaction.
Question. An organic acid X is a liquid which often freezes during winter time in cold countries, has the molecular formula C2H4O2. On warming it with ethanol in the presence of a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid a compound Y with a sweet smell is formed.
(i) Identify X and Y.
(ii) Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer: ‘X’ is CH3COOH (ethanoic acid) which freezes during winter time in cold countries.
On warming ethanoic acid with ethanol in presence of a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid, a fruity smelling ester is formed.
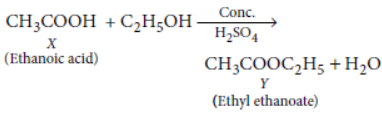
Question. Complete the following reactions:
a. CH3COOH + N2CO3 →
b. CH4 + O2 →
c. C2H5OH + Na →
Answer:
a. 2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
b. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
c. 2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2
Question. Classify the following carbon compounds into two homologous series and name them.
C3H4, C3H6, C4H6, C4H8, C5H8, C5H10
Answer:
The series of organic compounds having same functional group and similar chemical properties is called homologous series.
Alkene: C3H6, C4H8, C5H10
Alkyne: C3H4, C4H6, C5H3
Question. a. Chemical properties of ethanol is different from methyl ethanoate. Justify the statement with proper reason.
b. Methyl ethanoate is used in making perfume.
c. Ethanol is converted into ethene when excess of cone. H2SO4 is added. Justify with the help of reaction.
Answer:
a. Chemical properties of a compound depends on its functional group. Ethanol and methyl ethanoate have different functional group thus behave differently. CH3CH2OH has functional group —
OH. It has specific smell, reacts with Na metal to liberate H2. CH2COOCH3 has ester (RCOOR’) as functional group. It has pleasant fruity smell,
undergoes saponification reaction with NaOH.
b. It is due to pleasant fruity smell.
c. Conc H2SO4 dehydrates ethanol to ethene.
CH3 CH2OH ConcH2SO4 → 442K CH2 = CH2 + H2O
Question. With the help of a suitable example explain in brief the process of hydrogenation mentioning the conditions of the reaction and also state any one physical property of substances changes due to hydrogenation.
Answer:

Liquid oil changes to solid ghee
Question. a. Why are most carbon compounds poor conductors of electricity?
b. Write the name and structure of a saturated compound in which carbon atoms are arranged in a ring. Give the number of single bonds present in this compound.
Answer: a. It is because covalent compounds do not form ions, therefore, do not conduct electricity 100
It has 18 single bonds.
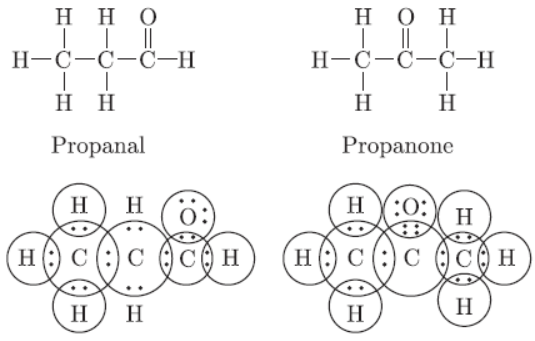
Question. Draw the structural formula of all the possible isomers of the compound with the molecular formula C3H6O and also give electron dot structures.
Answer:
Question. Write the structural formula of ethanol. What happens when it is heated with excess of conc. H2SO4 at 443 K?
Write the chemical equation for the reaction stating the role of cone. H2SO4 in this reaction.
Answer: CH3CH2OH, Ethanol C2H5OH Cone.H2SO4→ 443K CH2=CH2 + H2O
Concentrated H2SO4 is dehydrating agent.
Question. Draw the electron dot structure of ethyne. A mixture of ethyne and oxygen is burnt for welding. In your opinion, why cannot we use a mixture of ethyne and air for this purpose?
Answer:
HC ≡ CH, Ethyne,
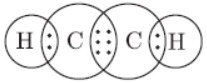
Ethyne and oxygen will produce lot of heat on combustion needed for welding whereas ethyne and air will not produce enough heat needed for welding purposes.
Question. What happens when:
(Write chemical equation in each case)
a. Ethanol is burnt in air?
b. Ethanol is heated with excess cone. H2SO4 at 443K?
c. A piece of sodium is dropped in ethanol.
Answer:
a. CO2 and H2O are formed.
C2H5—OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
b. Ethene is formed
CH3CH2OH Con.H2SO4 → 443K CH2=CH2 + H2O
c. Hydrogen gas evolves out
2CH3CH2OH + 2Na → 2CH3CH2ONa + H2
Question. Explain esterification reaction with the help of a chemical equation. Describe an activity to show esterification.
Answer: Esterification is the process in which carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol in presence of conc. H2SO4 to form pleasant fruity smelling compound ester.
C2H5OH + CH3COOH ConcH2SO4 → CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
Activity:
To carry out esterification reaction.
• Take 2 mL of ethanol (100% alcohol) in a test tube.
• Add 2 mL of glacial acetic acid.
• Add few drops of conc. H2SO4.
• Set the apparatus as shown in diagram.
• Heat the mixture in test tube in water bath for 5 to 10 minutes observe what happens.
• Observation: Pleasant fruity smell is observed.
• Conclusion: Ester is formed.

Question. What is meant by isomers? “We cannot have isomers of first three members of alkane series.” Give reason to justify this statement. Draw the structures of two isomers of pentane, C5H12.
Answer: Isomers are those compounds which have same molecular formula but different structural formula.
CH3– CH2– CH2– CH2– CH3
Pentane
CH3 – CH – CH2 – CH3
I
CH3
2 – Methylbutance
Question. An ester has the molecular formula C4H8O2. Write its structural formula. What happens when this ester is heated in the presence of sodium hydroxide solution?
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the products. What is a saponification reaction.
Answer:

When ester is heated with NaOH, sodium salt of acid and alcohol are formed. It is called saponification reaction.

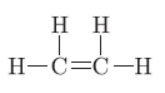
Question. What are hydrocarbons? Write the general formula of (a) saturated hydrocarbons (b) unsaturated hydrocarbons and draw the structure of one hydrocarbon of each type.
Answer:
Hydrocarbons are compounds of carbon and hydrogen only
a. CnH2n+2 is general formula of saturated hydrocarbon. For example, CH4

b. CnH2n(alkenes) and CnH2n-2 (alkynes) are general formulae of unsaturated hydrocarbons. For example,
Question. Two carbon compounds ‘X’ and ‘Y’ have the molecular formula C3H6 and C4H10 respectively. Which one of the two is most likely to show addition reaction? Also give chemical equation to explain the process of addition in this case.
Answer: C3H6 will undergo addition reaction because it has double bond.
CH2=CH—CH3 + H2 Ni → CH3—CH2—CH3
Propene Heat Propane
Question. Complete the following chemical reactions:
a. C2H5OH + O2 →
b. C2H5OH Cone.H2SO4→443K
c. CH3COOH + NaHCO3 →
Answer:
a. C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
b. C2H5OH Cone.H2SO4→443K CH2=CH2 + H2
c. CH3COOH + NaHCO3 →
CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
Question. When ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in presence of cone. H2SO4, a substance with fruity smell is produced. Answer the following questions:
a. State the class of compounds to which fruity smelling compounds belong. Write the chemical equation and write the chemical name of the product formed.
b. State the role of cone. H2SO4 in this reaction.
Answer:
a. The fruity smelling compounds are esters
CH3 COOH + C2H5OH Con.HSO4 → CH3 COOC2H5 + H2O
Ethanoic acid Ethanol Ethyl Ethanoate Water
b. Cone. H2SO4 acts as dehydrating agent.
Question. Name the compound formed when ethanol is heated with excess of cone. H2SO4 at 443 K. Also write the chemical equation of the reaction stating the role of cone. H2SO4 in it. What would happen if hydrogen is added to the product in presence of catalyst such as Pd or Ni?
Answer:

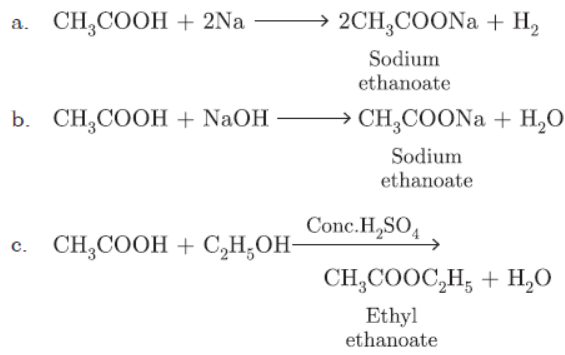
Question. Write the chemical equation of the reaction of ethanoic acid with the following:
a. Sodium
b. Sodium hydroxide,
c. Ethanol.
Write the name of one main product of each reaction.
Answer:
Question. Write three different chemical reactions showing the conversion of ethanoic acid to sodium ethanoate.
Write balanced chemical equation in each case. Write the name of the reactants and products other than ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate in each case.
Answer:
Question: Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element.
It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon.
Compare the ability of the catenation of the two elements. Give reasons.
Answer: Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Carbon exhibits catenation much more than silicon in- fact no other element exhibits the property of catenation to the extent seen in carbon compounds.
Silicon forms compounds with hydrogen which have chains of upto seven or eight atoms, but these compounds are very reactive. The carbon-carbon bond is very strong and hence stable. This gives us the large number of compounds with many carbon atoms linked to each other.
Carbon has a valency of four and it is capable of bonding with four other atoms of carbon or atoms of some other mono-valent element.
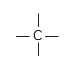
The bonds formed by carbon atoms are very strong and do not break easily so carbon compounds are stable.
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question: Explain, giving reason, why carbon neither forms C4+ cations nor C4– anions, but
forms covalent compounds which are bad conductors of electricity and have low melting point and low boiling point.
Answer: Carbon could form C4+ cation by losing four electrons, but it would require a large amount of energy to remove four electrons leaving behind a carbon cation with six protons in its nucleus holding on to just two electrons.
Carbon could form C4– anion by gaining four electrons, but it would be diffcultforthenucleus with six protons to hold on to ten electrons, that is, four extra electrons.
Therefore, carbon forms covalent bonds with other atoms by sharing electron pairs and in this process both atoms attain the noble gas configuration.
Covalent compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity since the electrons are shared between atoms and no charged particles are formed.
Covalent compounds have generally low melting and boiling points as the intermolecular forces are weak.
Question: The general formula of the organic compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ is CnH2n. Their boiling points are – 162 ºC, – 42.2 ºC and – 0.5 ºC respectively. Based on this information answer the following:
(A) Which type of compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ are and why?
(B) Which of these has maximum number of carbon atoms in the molecule and why?
(C) Write the name and structural formula of the second member of this series.
Answer: (A) A, B and C are Alkenes because their general formula is CnH2n.
(B) Compound C has maximum number of carbon atoms because boiling point increase with molecular mass which depends on number of C atom.
(C) Name: Propene
Structural formula: CH3 — CH = CH2
Question: Write two points of difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons
giving one example of each. Write the general formula of alkyne series. Write the name and structure of second member of this series.
Answer:

The general formula of alkyne series is CnH2n–2 The second member of this series is Propyne (C3H4)

