Class 12 VBQs Biology Microbes in Human Welfare
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. How is lactic acid bacteria beneficial to us other than helping in curdling the milk ?
OR
Name the nutrient that gets enhanced while curdling of milk by Lactobacillus.
Answer : Lactic acid bacteria improves the nutritional quality by increasing Vitamin B12.
OR
Vitamin B12
Question. Name the gas released and the process responsible for puffing up of the bread dough when Saccharomyces cerevisiae is added to it.
Answer : Gas – Carbon dioxide
Process – Fermentation
Question. Write the scientific name of the microbe used for fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices.
Answer : Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Question. Which of the following in the baker’s yeast is used in fermentation : Saccharam barberi, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Answer : Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Question. Bottled fruit juices are clearer as compared to those made at home. Explain.
Answer : Bottled fruit juices are clearer as compared to those prepared at home because they are treated with enzyme pectinase and protease. This enzymes acts on juices and make them clearer.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. List the events that reduce the Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) of a primary effluent during sewage treatment.
Answer : Effluent from the primary settling tank passed into aeration tank, agitated mechanically and air is pumped into it, vigorous growth of aerobic microbes into flocs, microbes consume major part of the organic matter in effluent.
Detailed Answer :
The primary effluent is passed into large aeration tanks where it is constantly agitated mechanically and air is pumped into it. This allows vigorous growth of useful aerobic microbes into flocs. While growing, these microbes (flocs) decompose the major part of the organic matter in the effluent. This decreases the biological oxygen demand (BOD) of the effluent.
Sewage is treated till the BOD is significantly reduced.
Question. Mention a product of human welfare obtained with the help of each one of the following microbes :
(i) LAB
(ii) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
(iii) Propionibacterium shermanii
(iv) Aspergillus niger
Answer : (i) Milk to curd
(ii) Bread / ethanol / alcoholic drinks / whiskey / brandy / beer/ rum
(iii) Swiss cheese
(iv) Citric acid
Question. Explain the process of secondary treatment given to the primary effluent up to the point it shows significant change in the level of biological oxygen demand (BOD) in it.
Answer : Supernatant from the primary treatment is passed into large aeration tanks during secondary treatment. In these tanks, the effluent is agitated mechanically and air is pumped into it. This causes vigorous growth of bacteria that lead to the formation of floc, which consists of bacteria and fungal filaments in a mesh like structure. While growing, these microbes consume the major part of organic matter in the effluent, it decreases the biological oxygen demand (BOD). After a significant drop in BOD is observed, effluent is passed into the settling tank.
Question. Name two groups of organisms which constitute ‘flocs’. Write their influence on the level of BOD during biological treatment of sewage.
Answer : The bacteria and fungal mycelium constitute flocs. These microorganisms bring about the decomposition aerobically of the major part of organic matter in primary effluent and thus helps in lowering the BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) of the effluent.
Question. Name the bacterium responsible for the large holes seen in ‘Swiss cheese ‘. What are these holes due to ?
Answer : The large holes in ‘Swiss cheese’ are due to the production of a large amount of CO2 by a bacterium named Propionibacterium shermanii.
Question. Mention the importance of lactic acid bacteria to humans other than setting milk into curd.
Answer : (i) While converting milk into curd, lactic acid bacteria (LAB) improve its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin B12.
(ii) In our stomach, LAB play beneficial role in preventing growth of disease-causing microbes.
Question. Name the enzyme produced by Streptococcus bacterium. Explain its importance in medical sciences.
Answer : Streptokinase.
It is used as a ‘clot buster’ for removing clots from the blood vessels of patients who have undergone myocardial infarction leading to heart attack. It helps in clearing blood clots inside the blood vessels through dissolution of intravascular fibrin.
Question. Write the binomials of two fungi and mention the products/bioactive molecules they help to produce.
Answer : Trichoderma polysporum, cyclosporin A
Aspergillus niger, citric acid
Monascus purpureus, statin
Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ethanol / alcohol
Penicillium notatum, Penicillin
Question. During the production of curd, a small amount of curd is added as a starter to the fresh milk at a suitable temperature. Explain the changes the milk undergoes when it sets into curd.
OR
Why is ‘starter’ added to set the milk into curd ? Explain
Answer : When a small amount of curd is added as a starter to the fresh milk at a suitable temperature, amicroorganism Lactobacillus and lactic acid bacteria grows in milk in millions. These bacteria convert the lactose sugar of milk into lactic acid which coagulates and partially digests milk protein casein. This causes curdling of milk and converts milk into curd.
Question. Name a bioactive molecule, its source organism and the purpose for which it is given to organ transplant patients.
Answer : Cyclosporin A.
Source – Trichoderma polysporum.
Purpose – Immuno suppressive agent.
Question. Name the source of statin and state its action on human body.
Answer : Statin is produced by a yeast called Monascus purpureus. It’s use lowers the blood cholesterol level in the body. It acts by inhibiting the activity of the enzyme which brings about the synthesis of cholesterol.
Question. What are methanogens ? How do they help to generate biogas.
Answer : Micro-organisms that produce methane along with CO2 and H2 gases under anaerobic conditions are called methanogens Example, Methanobacterium.
These are the bacteria found in cattle dung (gobar) and in anaerobic sludge during sewage treatment, They grow anaerobically on cellulosic material and produce a large amount of methane (main constituent of biogas) along with CO2 and H2. Thus, methanogens are used in biogas production.
Question. “Determination of Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) can help in suggesting the quality of a water body.” Explain.
Answer : High BOD in a water body indicates more number of micro-organisms in water, resulting in bad quality of water / death of aquatic creatures, more polluting potential.
Lower BOD of water body indicates less number of micro-organisms in water, good quality of water / aquatic life flourishes / less polluting potential.
Question. Given below is a figure of a biogas plant.
(i) Identify A and justify its floating nature.
(ii) Identify the products B and C and discuss their significance.
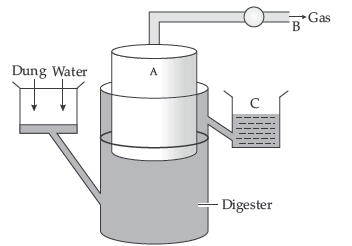
Answer : (i) A is the floating cover which is placed over the slurry, wh ich keeps on rising as the gas is produced in the tank due to the microbial activity.
(ii) B is the biogas which is a mixture of gases consisting of methane, hydrogen sulphideand carbon dioxide. It can be used as a source of energy to nearby houses as it is inflammable.
C is the spent slurry or sludge which is removed through another outlet and may beused as fertiliser.
Question. Identify a, b, c, d, e and f in the table given below :
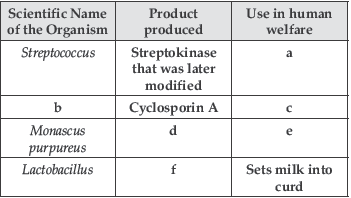
Answer : (a) Clot buster for removing clots from blood vessels.
(b) Trichoderma polysporum.
(c) Antifungal, anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent in organ transplant, prevents reactions in organ transplantation.
(d) Statins.
(e) Blood cholesterol lowering agent.
(f) Lactic acid.
Question. Explain the different steps involved in the secondary treatment of sewage.
Answer : (a) Primary effluent is passed into large aeration tanks with constant mechanical agitation and air supply. Useful aerobic microbes grow rapidly and form flocs.
(b) Flocs while growing consume organic matter and thus reduce the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), the effluent is passed into settling tank.
(c) The bacterial flocs settle at the bottom of the tank and it forms activated sludge, a small part this is used as an inoculum in the aeration tank and the remaining part is passed into large tanks called anaerobic sludge digesters.
Question. Describe how do ‘flocs‘ and ‘activated sludge‘ help in Sewage Treatment.
Answer : Flocs : Aerobic microbes consume the major part of the organic matter in the effluent, significantly reduces BOD.
Activated sludge : Small part of activated sludge is used as inoculum and pumped back to aeration tank / pumped into anaerobic sludge digesters where microbes or bacteria grow anaerobically to produce CH4 or H2S or CO2 or biogas.
Question. Describe how biogas is generated from activated sludge. List the components of biogas.
Answer : After the significant decline of BOD of the sewage, the effluent is passed into the settling tank. In these tanks, the bacterial flocs sediment forming the activated sludge. A small part of activated sludge is pumped back into aeration tanks to serve as the inoculum. The remaining major part of the sludge is pumped into large tanks called anaerobic sludge digesters.
Other kinds of bacteria, that grow anaerobically, digest the bacteria and fungi in the sludge. During this digestion, bacteria produce a mixture of gases called biogas.
The components of biogas are :
(i) Methane (CH4)
(ii) Hydrogen sulphide (H2S)
(iii) Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Question. (i) Why are the fruit juices bought from market clearer as compared to those made at home ?
(ii) Name the bioactive molecules produced by Trichoderma polysporum and Monascus purpureus.
Answer : (i) The fruit juices prepared at home are turbid due to the presence of fibers and pectin in it whereas those purchased from the market are clearer because of the use of enzymes like proteases and pectinases which remove turbidity.
(ii)
| Source | Bioactive molecule produced |
| (a) Trichoderma polysporum | Cyclosporin A. |
| (b) Monascus purpureus | Statin. |
Question. (i) How is activated sludge formed during sewage treatment ?
(ii) This sludge can be used as an inoculum or as a source of biogas. Explain.
Answer : (i) When the BOD of sewage or waste is reduced significantly, the effluent is then passed into a settling tank where the bacterial ‘flocs’ are allowed to sediment. This sediment is called activated sludge.
(ii) A small part of the activated sludge is pumped back into aeration tanks to serve as the inoculum. The remaining major part of the sludge is pumped into large tanks called anaerobic sludge digesters. Other kinds of bacteria, which grow anaerobically, digest the bacteria and the fungi in the sludge. During this digestion, bacteria produce a mixture of gases such as methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide. These gases form biogas and can be used as a source of energy as it is inflammable.
Question. Identify a, b, c, d, e and f in the table given below :

Answer : a – Statins.
b – Blood cholesterol lowering agent.
c – Penicillium notatum.
d – Penicillin.
e – Trichoderma polysporum.
f – Immuno-suppressive agent in organ transplant patients.
Question. Make a list of three household products along with the names of the micro-organism producing them.
Answer : Lactic acid bacteria ; curd
Saccharomyces cerevisiae ; bread
Propionibacterium shermanii ; swiss cheese
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Describe the process of waste-water treatment under the following heads :
(i) Primary treatment.
(ii) Secondary treatment.
OR
Explain the process of sewage water treatment before it can be discharged into natural water bodies. Why is this treatment essential ?
Answer : (i) Primary treatment
(a) Physical removal of particles like debris, soil, sand or silt through filtration, sedimentation in stages.
(b) Solids settle to form primary sludge, the supernatants form the primary effluent.
(ii) Secondary Treatment : It is the biological treatment.
(a) Effluent passed into aeration tanks.
(b) Vigorous growth of useful aerobic microbes into flocs.
(c) Significant reduction of BOD due to use of organic matter by microorganisms.
(d) After fall in the level of BOD, the effluent is passed on to settling tanks where bacterial flocs settle to form activated sludge.
(e) Activated sludge is passed on to anaerobic sludge digester, where bacteria and fungi are anaerobically digested.
Detailed Answer :
Sewage water can be purified by passing it through sewage treatment plants with the help of the action of microorganisms. In this plant, the solids are separated from liquid by physical processes and the liquids are purified by biological processes.
There are three stages of this treatment i.e. primary, secondary and tertiary. The primary treatment is physical, secondary treatment is biological while the tertiary treatment is chemical.
Sewage Treatment (In STP’s Binary Treatment Plants):
(i) Primary Treatment :
Physical particles like debris and soil, sand, silt etc. are removed by :
(i) sequential filtration. (ii) sedimentation.
The substances that settle down forms primary sludge and the effluent is primary effluent.
(ii) Secondary Treatment :
Biological treatment in which primary effluent is passed to large aeration tanks and is constantly agitated and supplied with air/O2.
This causes creation of flocs or association of useful aerobic bacteria and fungal filaments into a mesh-like structure.
In this process, the microbes use up organic matter in the polluted water and hence reduce the BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand).
Once the BOD is sufficiently reduced, it is allowed to pass to a settling tank where flocs are allowed to settle down – activated sludge.
A little sludge is pumped back to the aeration tank to serve as inoculums but most is passed to the anaerobic sludge digester where it is degraded by useful anaerobic bacteria (e.g., methanogens) releasing a mixture of gases like CH4, CO2, H2, H2S, etc. (biogas).
The water coming out after this treatment is hence purified and can be discharged into water bodies.
This treatment is essential to :
(i) Avoid pollution of the natural water bodies by excessive accumulation of harmful chemicals, organic matter and nutrients which may lead to eutrophication.
(ii) Prevent the spread of infectious water borne diseases caused due to the deadly pathogens in polluted water.
Question. (i) Name the category of microbes occurring naturally in sewage and making it less polluted during the treatment.
(ii) Explain the different steps involved in the secondary treatment of sewage.
Answer : (i) Aerobic microbes.
(ii) The primary effluent is passed into large aeration tanks where it is constantly agitated mechanically and air is pumped into it. This allows vigorous growth of useful aerobic microbes into flocs (masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh like structures). While growing, these microbes consume the major part of the organic matter in the effluent. This significantly reduces the BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) of the effluent. The sewage water is treated till the BOD is reduced. Once the BOD of sewage or waste water is reduced significantly, the effluent is then passed into a settling tank where the bacterial ‘flocs’ are allowed to sediment. This sediment is called activated sludge. A small part of the activated sludge is pumped back into the aeration tank to serve as the inoculum. The remaining major part of the sludge is pumped into large tanks called anaerobic sludge digesters. Here, other kinds of bacteria, which grow anaerobically, digest the bacteria and the fungi in the sludge.
During this digestion bacteria produce a mixture of gases such as methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide. These gases form biogas and can be used as source of energy as it is inflammable. The effluent from the secondary treatment plant is generally released into natural water bodies like rivers and streams.
