Ecosystem Notes for Class 12 Biology
Following are Ecosystem Notes for Class 12 Biology. These revision notes have been prepared by expert teachers of Class 12 Biology as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books released for the current academic year. Students should go through Chater 14 Ecosystem concepts and notes as these will help you to revise all important topics and help you to score more marks. We have provided Class 12 Biology notes for all chapters in your book. You can access it all free and download Pdf.
Chapter 14 Ecosystem Notes Class 12 Biology
Important Questions Ecosystem Class 12 Biology
Question. What is stratification in a forest?
Answer : The vertical levels of trees in a forest
Question. Name the pioneers and climax of primary succession in water and on rocks.
Answer : Phytoplanktons and forest, lichens and forest
Question. What are the producers in grass land and oceans .How is GPP different from NPP? Why is the productivity in oceans lesser than on land?
Answer : Grass, phytoplankton’s, GPP is the rate of Biomass production /g/yr whereas NPP is the rate of Biomass converted into plant matter and available for the consumers (NPP=GPP-Respiration),Oceans have less solar energy available compared to land hence productivity is lower.
Question. The type and number of animals and decomposers also change as succession proceeds. why?
Answer : Vegetational changes, affect food and shelter for various types of animals
Question. Justify the statement succession and evolution would have been parallel processes at that time when life started on earth.
Answer : Succession starts from the pioneer species giving way to serial communities before establishing the climax. Evolution also involves change of environmental factors followed by change in the communities containing fittest species.
Question. Define ecological succession. What is sere?
Answer : Gradual fairly predictable change, in the species composition of a given area. The entire sequence of communities that change in a given area during the succession
Question. How is a food web formed?
Answer : Interconnecting food chains/one organism in different trophic levels
Question. What characteristic features are seen in Ecological succession?
Answer : There is increase in diversity, species increase and increase in number, increase in biomass
Question. Why is there a restriction on trophic levels in a grazing food chain? Is there such a limitation in the detritus food chain? Explain.
Answer : Energy decreases with successive levels. 10% only transferred to next level.
Question. Humans do a disservice to nature by creating a desert from a forest. Comment.
Answer : Ecosytem services include regulating the climate, hence livelihood and food of animals and people. Conversion of range land fed cropland, rain or irrigated cropland to desert like and, with a drop in agricultural productivity of 10%ormore.It is usually caused by a combination of overgrazing, soilerosion, prolonged drought and climate change. The soil becomes unsuitable for crops and vegetation food would also become scarce besides water and oxygen.
Question. Schematically show the flow of energy in a grazing food chain from the sun.
Answer : Sun—-1%——-plants—-2-10%——-herbivores——10% —— carnivore
Question. With a flow chart explain the process of decomposition .What factors affect this process?
Answer : Breakdown of complex organic matter by decomposers. a)Process- i)fragmentation ii)
leaching iii)catabolism. Humification and mineralization–humification leads to accumulation of dark colour substance called humus. Mineralisation result inrelease of in orgranic substances a)climatic factor– i)temp ii)soil b)chemical quality of detritus. Higher temp and moist condition – high rate of decomposition. Drysoil, High temp–Low rate
Question.
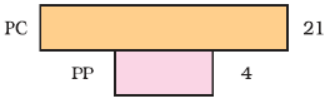
Identify the type of the given ecological pyramid and give one example each of pyramid of number and pyramid of biomass in each case.
Answer : Inverted pyramid =1
Inverted pyramid of biomass in a lake – phytoplankton-→ zooplankton → fish =1/2
Inverted pyramid of number – tree → insects → birds = 1/2
Question. What is the importance of humus?
Answer : The colloidal matter resistant to microbial action ,reservoir of nutrients, breaks down slowly
Question. What are the limitations of ecological pyramids?
Answer : Decomposers are not taken into account, two trophic levels may be taken up by the same species which is not considered, a food web is not accommodated
Question. Why is secondary succession faster than primary succession?
Answer : Soil already formed, spores, seeds remnants of vegetation
Question. Why is it reasonable to think that biodiversity should carry a hefty price tag? Justify.
Answer : Ecosystem services include 1) maintaining soil 2) regulating rainfall 3) preventing erosion of soil,4) pollination 5)providing materials of medicinal, food and other values
Question. Define standing crop? How is it measured?
Answer : The mass of living matter at a given time measure of biomass ,dry weight of living matter at a given time
Question. a, Why are Carbon and Phophorus essential to living organisms?
b, What are the natural reservoirs of these elements and in what form?
c, Give the important differences between the two cycles in nature ?
Answer : Carbon part of all organic compounds, Phosphorus for ATP, DNA etc Gaseous-Reservoir in atmosphere, Nitrogen cycle b)Sedimentary-Soil, eg-phosphorus. No gaseous component in phosphorus and reservoirs of the two are atmosphere and sediments respectively
Question. What are the major functions of an ecosystem? How do the structural components work as a unit to perform the function?
Answer : Productivity-producers, nutrient cycling and energy flow through the food chains-GFC & DFC, decomposition by the detritivores and decomposers
Question. In general all pyramids are upright. Explain. What are the exceptions to this generalization?
Answer : The producers are the most, in terms of energy, biomass and number and subsequent levels are fewer in number, energy and Biomass .Energy decreases with successive
levels, The pyramid of Biomass in the oceans and pyramid of number in the case of a fruiting tree supporting hundreds of consumers, the pyramids can be inverted.
