Heredity And Evolution Notes for Class 10 Science
Heredity: The passing of traits from the parents to offspring is called heredity.
Gene- Gene is the smallest part of DNA that codes for a protein .In each cell there is a nucleus, in the nucleus are chromosomes. The genes are present on chromosomes. Every person has two copies of each gene inherited one from each parent.
Genetics- The study of genes, gene variation and heredity is called genetics.
Trait – A characteristic of an organism is called a trait eg- natural eye colour, hair colour, height.
Offspring- An organism’s next generation eg- a person’s child or children
Inheritance:- Inheritance refers to the process of transmission of genes from parent to offspring. Inheritance is the passing on of genetic traits from parents to their offspring, and these offspring getall the genetic information from their parents.
Alleles : Different physical forms of a trait are called it’s alleles. For eg. Length of a pea plant has two alleles i.e. tall and short stem. There may be two or multiple alleles of a trait.
Dominant traits: The traits that express themselves in an organism in every possible combination and can be seen, are called Dominant traits. In Mendel’s experiment, we see that the tall trait in pea plants tends to express more than the short trait. Therefore, the tall trait of the plant is said to be dominant over the short trait.
Recessive traits: A trait which is not expressed in the presence of a dominant allele is known as recessive. So, recessive character/trait is present in an organism but cannot be seen if a dominant allele exists.
Genotype: Genetic arrangements of the genes for a trait(s) of an organism. For eg. RrYy or TTRr etc.
Phenotype: Physical appearance of a trait is called its phenotype. For eg. Yellow and green seeds of pea., tall or dwarf plant etc
Variation: The difference in the characteristics of individual in a population is called variation.
Cause of variation
In Asexual reproduction -> Due to the errors in DNA coping ->less variation
In Sexual reproduction ->DNA of two parent combine -> more variation
Importance of variations: –
1. Variations helps a species to survive in a changing environment.
2. They help an organism to adapt to their altered environment.
3. Variation leads evolution.
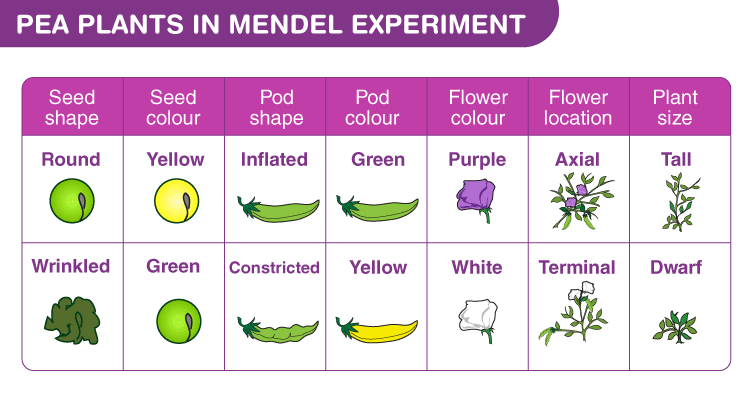
Mendel’s laws of inheritance – Gregor Johann Mendel is known as father of Genetics. He experimented self and cross fertilization on following traits of garden pea
→ Scientific name of human being is “Homo sapien”. And scientific name for pea plant is “Pisum sativum”
Mendel law of inheritance –Mendel selected garden pea (Pisum sativum) with characters asfollows:
Mendel concluded his experiments with 3 laws-
1. Law of dominance –
When parents having pure contrasting characters are crossed then only one character expresses itself in the F1 generation. This character is the dominant character and the character/factor which cannot express itself is called the recessive character. In the given monohybrid cross T gene form represents tallness and t represents shortness.

Homozygous – Having two identical forms (alleles) of a particular gene TT, RRYY
Heterozygous- Having two different forms of a particular gene like Tt, RrYY, RrYy
2. Law of segregation – During the formation of gamete, the two-alternating form of a gene are never found in the same gamete but they separate and pass on to different gametes so that one gamete receives only one form of a gene. This is called as Law of Segregation.
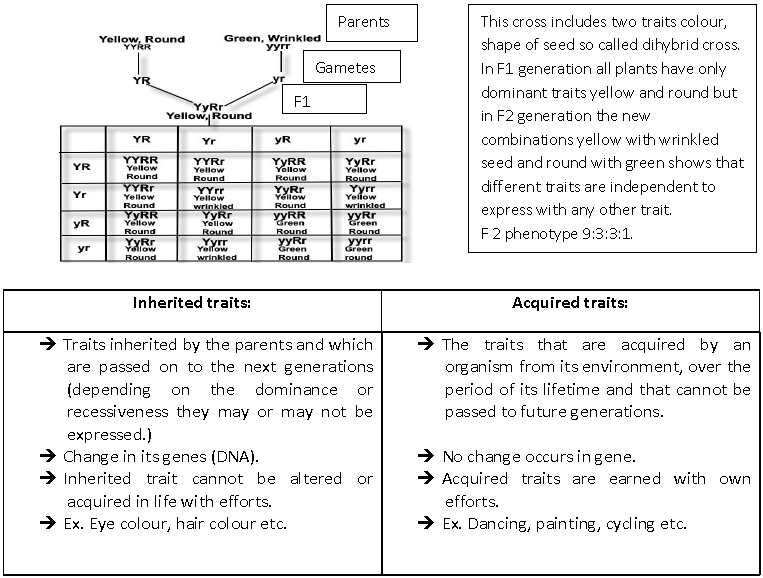
3. Law of Independent Assortment – When two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters or the members of different gene pair assort randomly and independently. This law is based on dihybrid cross.
Dihybrid cross – A cross involving two traits is called a dihybrid cross. In this example colour, and shape of seed are taken. In F1 generation all plants have only dominant traits yellow and round but in F2 generation the new combinations yellow with wrinkled seed and round with green appear. This shows that different traits are independently assorted.
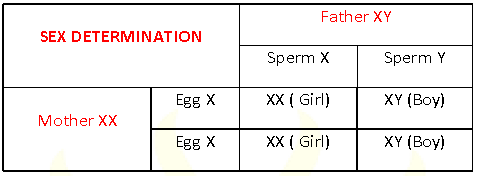
Sex determination in humans: (A mechanism by which sex of new born baby is determined).
Autosomes: These determine the somatic traits. There are 22 pairs of autosomes in humans .
Sex chromosome: Chromosome which determine the sex of a person. (X & Y). There is one pair of sex chromosome in humans which may be XX or XY
1. In male – One X chromosome and one Y chromosome
2. In female- Two X chromosome (no Y chromosome)
3. Y chromosome is responsible for sex of a boy.