Human Eyes and Colourful World Notes for Class 10 Science
Following are Human Eyes and Colourful World Notes for Class 10 Science. These revision notes have been prepared by expert teachers of Class 10 Science as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books released for the current academic year. Students should go through Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World concepts and notes as these will help you to revise all important topics and help you to score more marks. We have provided Class 10 Science notes for all chapters in your book. You can access it all free and download Pdf.
Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World Notes Class 10 Science
Power of accommodation:
- Ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length.
- Relaxation of ciliary muscles → lens becomes thin → increase in focal length.
- Contraction of ciliary muscles → lens becomes thick → focal length decreases.
Near Point (N): The point at closest distance, at which an object can be seen clearly by the eye is called Near Point (N) of the eye. The distance of the near point of a normal eye is called the least distance of distinct vision. It is represented by d. For a normal eye, value of least distance of distinct vision is d=25cm.
Far Point (F): The most distant point at which an object can be seen clearly is called Far Point (F) of the eye. For a normal eye, far point lies at infinity.
Rods: Respond to the intensity of light and enable vision in dim light.
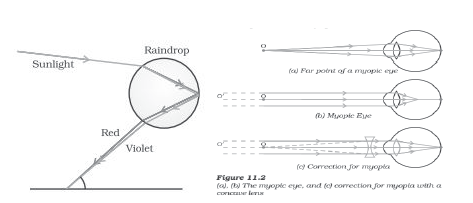
Myopia or Near-sightedness:
- Eye cannot see distant objects clearly.
- Image of distant object forms in front of retina.
- Reasons:
(i) Excessive curvature of eye lens.
(ii) Elongation of eyeball
Correction: using concave lens
Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness:
- Eye cannot see nearby objects clearly.
- Image of object nearby forms behind retina.
- Reasons:
(i) Focal length of eye lens is too long.
(ii) Eyeball becomes small
Correction: using convex lens
Presbyopia:
- Eye suffers from myopia as well as from hypermetropia.
- Due to gradual weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of eye lens.
Correction: using bifocal lens
Cataract: Milkiness of eye lens due to aging can be cured by surgery
Dispersion of Light: Splitting of light into its component colours.
White light disperses into its seven-colour components in the order VIBGYOR (violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, And Red).
Red light bends least, Violet the most.
Rainbow is formed due to refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection of sunlight by tiny droplets of water
Atmospheric Refraction: Refraction of light by the earth’s atmosphere Twinkling of stars, Advanced sunrise, Delayed sunset, Flattening of disc of sun at sunrise and sunset are due to atmospheric refraction
Tyndall effect:
- When a beam of light strikes fine particles in air, path of the beam becomes visible.
- Very fine particles scatter mainly blue light while particles of larger size scatter light of longer wavelengths
DEFECTS OF VISION

SOME NATURAL PHENOMENON &CAUSES

HUMAN EYE

TWINKLING OF STARS

FORMATION OF RAINBOWMYOPIA
SCATTERING OF LIGHTDISPERSION OF WHITE LIGHT

HYPERMETROPIA

RECOMBINATION




