Political Parties Notes for Class 10 Social Science
Following are Political Parties Notes for Class 10 Social Science. These revision notes have been prepared by expert teachers of Class 10 Social Science as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books released for the current academic year. Students should go through Chapter 3 Political Parties concepts and notes as these will help you to revise all important topics and help you to score more marks. We have provided Class 10 Social Science notes for all chapters in your book. You can access it all free and download Pdf.
Chapter 3 Political Parties Notes Class 10 Social Science
Key terms and their meaning
1. Political Parties : A group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government.
2. Ruling Party : Political party that runs the government.
3. Defection : Changing party allegiance from the party on which a person got elected to a different party.
4. Affidavit : A signed document submitted to an officer where a person makes a sworn statement regarding his/her personal information.
5. Partisan : A person who is strongly committed to a party, group or faction. Partisanship is marked by a tendency to take a side and inability to take a balanced view on an issue.
6. One Party System : In some countries only one party is allowed to control and run the government. These are called one party system. For ex. China.
7. Alliance or Front : When several parties in a multi party system join hands for the purpose of contesting elections and winning power it is called an alliance or front.
8. State Funding of Election : The government should give parties money to support thier election expenses.
9. Components of Political Parties : The political leaders, the active members and the followers.
10. Opposition Party : The largest non government party or coalition of parties.

Functions of Political Parties
• To contest elections
• Make policies and programmes
• Make laws
• Run Government
• Play role of opposition
• Launch movements for the resolution
• Introduce welfare schemes
• Shape public opinion
How many parties should we have
• It is not something a country can choose.
• It evolves over a long time.
• Depends on the nature of society its social and religious divisons.
• Depends on its history of politics and system of election.
• It cannot be changed very quickly.
Types of Political Party Systems

Necessity of Political Parties
• Modern democracies cannot exist without political parties
• Without parties every candidate in the elections will be independent so no one will be able to make any promises to people about any major policy change.
• Government may be formed but its utility will remain ever uncertain.
• Elected representatives will be accountable to their constituency for what they do in the locality.
• No one will be responsible for how the country will be run.

Difference between National parties and State Political Parties

National Parties : There were seven recognised national parties in the country in 2018.
As per latest information after 2019 elections there are 8 national parties in India.



Some Regional Parties of India


Some interesting Facts
• First General Election held in India in 1951-52 after Independence.
• Pt. Jawahar Lai Nehru became the First Prime Minister of India.
• W.C. Banerjee was the first chairperson of Indian National Congress.
• Shayama Prasad Mukherjee was the first chairperson of Bhartiya Janta Party.
• Sh. Kashiram was the the first chairperson of Bahujan Samaj Party.
• In 1985 Anti-Defection act comes into the power.
State Parties


Objective Type Questions
Question. What is meant by ‘Political Party’?
(a) A group of politically sound people.
(b) A group of people comes together to contest elections to hold power in the government.
(c) A group of people who want to be in power.
(d) A group of people who want to amend the Constitution.
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
Question. The Bahujan Samaj Party stands for what cause?
(a) Securing the interest of the oppressed people.
(b) Equal rights for women.
(c) No discrimination on the basis of religion.
(d) Economic emancipation of women.
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
Question. Who among the following is the founder of the Bahujan Samaj Party?
(a) Kanshi Ram
(b) B. R. Ambedkar
(c) Shahu Maharaj
(d) Jyotiba Phule
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
Question. Name the alliance formed by the Congress Party.
(a) National Democratic Alliance (NDA)
(b) All India Congress (AIC)
(c) All India Congress Committee (AICC)
(d) United Progressive Alliance (UPA)
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
Question. Study the following picture and answer the question that follows:

Which of the following leaders is shown in this cartoon?
(a) Berlusconi
(b) Putin
(c) Kwame Nkrumah
(d) Mussolini
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
Question.
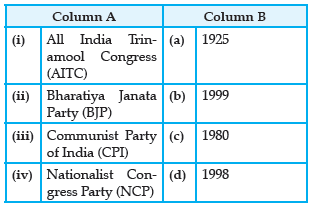
(a) (i)-(d), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
(b) (i)-(b), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(d)
(c) (i)-(a), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(c)
(d) (i)-(c), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(b), (iv)-(a)
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
Question. Analyze the information given below, considering one of the following correct options:
Formed in 1984 under the leadership of Kanshi Ram. Seeks to represent and secure power for the bahujan samaj which includes the dalits, adivasis, OBCs and religious minorities. Draws inspiration from the ideas and teachings of Shahu Maharaj, Mahatma Phule, Periyar Ramaswami Naicker and Babasaheb Ambedkar. Stands for the cause of securing the interests and welfare of the dalits and oppressed people.
(a) Communist Party of India-Marxist (CPI-M)
(b) Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP)
(c) Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
(d) Indian National Congress (INC)
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
Question. Analyze the information given below, considering one of the following correct options:
One of the oldest parties in the world. Founded in 1885 and has experienced many splits. Played a dominant role in Indian politics at the National and State level for several decades after India’s Independence. Under the leadership of Jawaharlal Nehru, the party sought to build a modern secular democratic republic in India.
(a) Communist Party of India (CPI)
(b) All India Trinamool Congress (AITC)
(c) Indian National Congress (INC)
(d) Nationalist Congress Party (NCP)
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Question. Find the incorrect options:
(a) In a democracy, a large number of similar opinions have to be grouped to provide a direction in which policies can be formulated by the governments.
(b) That is what the parties do.
(c) A party reduces a vast multitude of opinions into a few basic positions which it supports.
(d) A government is expected to base its policies on the line taken by the opposition party.
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
Question. Find the incorrect options:
(a) Every party in the country has to register with the Election Commission.
(b) While the Commission treats all parties equally.
(c) It offers some special facilities to large and established parties.
(d) These parties are given an ordinary symbol–only the official candidates of that party can use that election symbol.
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
Assertion and Reason Based Questions
Question. Assertion (A): Political parties are easily one of the most visible institutions in a democracy.
Reason (R): For most ordinary citizens, democracy is equal to political parties.
Option:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
Question. Assertion (A): Parties play a decisive role in making laws for a country.
Reason (R): Opposition parties also mobilize opposition to the government.
Option:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
Question. Assertion (A): The rise of political parties is directly linked to the emergence of representative democracies.
Reason (R): As societies became large and organised, they do not need any agency to gather different views on various issues and to present these to the government.
Option:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Question. Assertion (A): Parties put forward different policies and programmes and the voters choose from them.
Reason (R): Each of us has similar opinions and views on what policies are suitable for society.
Option:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why is one party political system not considered a good democratic system?
Answer : Because one party system has no democratic option.
Question. When was the Communist Party of India – Marxist (CPI-M) formed?
Answer : CPI-M was formed in 1964.
Question. Name a country that has one party system.
Answer : China.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name any six ‘Regional Political Parties’ of the four Southern States of India.
Answer : Tamil Nadu — AIADMK (All India Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam), DMK.
Andhra Pradesh — Telugu Desam, Lok Satta
Kerala — Kerala Congress (Joseph)
Puducherry — AINRC (All India N. R. Congress)
Question. Describe any three main features of Two-party system.
Answer : Main features of the Two-party system:
(i) Power usually changes between two parties, several other parties may exist.
(ii) In such a system, people get a clear choice.
(iii) The party that wins the majority forms the government and the other sits in Opposition.
(iv) Strong opposition is good for democracy.
Question. What is meant by a ‘National Political Party’? State the conditions required to be a National Political Party.
Answer : National Political Parties have units in the various States, they follow the same policies, programmes and strategy that is decided at the National level.
Conditions required:
(i) A party that secures at least 6% of the total votes in general elections of Lok Sabha or Assembly elections in four states.
(ii) Wins at least 4 seats in Lok Sabha.
Question. “Nearly every one of the State Parties wants to get an opportunity to be a part of one or the other national level coalition.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : State Parties seeking National Level Coalition:
Before the general elections of 2014, in three General Elections, no one National Party was able to secure on its own a majority in Lok Sabha. As a result, the national parties were compelled to form alliances with state or regional parties. Since 1996, nearly every one of the state parties has got an opportunity to be a part of one or the other National Level Coalition Government. This has contributed to the strengthening of Federalism and Democracy.
Question. What is meant by ‘Regional Political Party’? State the conditions required to be recognized as a ‘Regional Political Party’.
Answer : A Regional Party is a party that is present in only some states. Conditions required for a party to be recognized as a Regional Political Party are:
(i) A Party that secures at least six per cent of the total votes in an election to the Legislative Assembly of a State.
(ii) Wins at least two seats in the Legislative Assembly.
Question. Name the ‘Regional Political Parties’ that are predominant in Jharkhand, Maharashtra and Odisha respectively with their symbols.
Answer :Jharkhand — JMM—Jharkhand Mukti Morcha, its symbol is Bow & Arrow.
Maharashtra — INC—Indian National Congress, its symbol is Hand.
Odisha — BJD—Biju Janata Dal, its symbol is Conch.
Question. “Serious efforts were made by the legal organizations to reform political parties in India.” Support the statement.
Answer : Efforts made by the legal organizations to reform Political Parties in India are:
(i) To check defection, the Constitution was amended to prevent elected MLA’s and MPS’s from changing Parties.
(ii) The Supreme Court passed an order to reduce the influence of money and criminals, by making it mandatory to produce an affidavit giving details of the property and criminal cases pending against the Candidate.
(iii) The Election Commission passed an order making it necessary for political parties to hold their organisational elections and file their Income tax returns.
Question. “Dynastic succession is one of the most serious challenges before the Political Parties”. Analyse the statement.
Answer : Dynastic succession is one of the most serious challenges before the Political Parties because:
(i) Most political parties do not practice open and transparent procedures for their functioning.
(ii) There are few ways for an ordinary worker to rise to the top of a Party.
(iii) In many Parties, the top positions are always controlled by Members of one family.
(iv) This practice is unfair to other members of that party and is also bad for Democracy.
Question. State the conditions as laid down by the Election Commission to recognize a ‘State Party’ and ‘National Party’.
Answer : The difference between a State and a National Party can be identified as follows:
(i) In a State Party, the party members aim to highlight regional interests. On the other hand, a national Party gives due importance to national interests.
(ii) A State Party can contest in elections only in a particular state, whereas a national party can contest in elections all across the Country.
(iii) Example: BJP and Congress are National Parties, whereas Akali Dal and Trinamool Congress are State-level Parties.
Question. Which three challenges do you feel are being faced by Political Parties in India? Give your opinion.
OR
What are the various challenges faced by Political Parties?
Answer : The three challenges faced by political parties in India are:
(i) Lack of Internal democracy.
(ii) Challenge of Dynastic succession.
(iii) Growing role of money and muscle power.
(iv) Often parties do not seem to offer a meaningful choice to the voters.
Question. What do you understand by the Bi-party system? Write its one merit and one demerit.
Answer :Bi-party system:
In some countries, power usually changes between the two main parties. It is also known as the two party system. In this system, the government is formed by one party and the other plays the role of opposition.
Merit: This system allows stability of the government as no coalition is there.
Demerit: In this system, only two main parties have a serious chance of winning majority seats to form the government.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What is a Political Party? Explain any four characteristics of a Political Party.
OR
What are the characteristics of a Political Party?
Answer : “A Political Party is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government.” They agree on some policies and programmes for promoting national interest. Since, there can be different views on what is good for all, parties try to persuade people why their policies are better than the others.
Characteristics of a Political Party:
(i) Political parties contest elections and share power.
(ii) They agree on some policies and programmes for the society to promote collective good.
(iii) If a political party is unable to win a majority, it makes an alliance with other parties to form a Coalition Government.
(iv) Political parties try to persuade people that their policies are better than others. The above characteristics also show that political parties are necessary for a Democracy.
Question. Explain two functions each of the Ruling Party as well as of the Opposition Parties.
Answer : Functions of the Ruling Parties:
(i) They play a major role in making laws for the country.
(ii) They form the government and run the country.
(iii) They recruit leaders, train them and then make ministers run the government.
Functions of the Opposition Parties:
(i) They oppose the government by voicing different views.
(ii) They criticise the government for its failure and wrong policies.
(iii) They mobilise opposition to the government.
Question. What is meant by National Parties? State the criteria for recognizing a party as National and State party.
Answer : Democracies that follow a Federal System all over the world tend to have two kinds of Political Parties—Parties that are present in only one of the federal units and parties that are present in several or all units of the federation. Those parties, which are countrywide, are called National Parties.
National and State Parties:
(i) A Party that secures at least six per cent of the total votes in an election to the Legislative Assembly of a State and wins at least two seats is recognized as a State Party.
(ii) A Party that secures at least six per cent of the total votes in Lok Sabha elections or Assembly elections in four States and wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha is recognized as a National Party.
Question. Describe any five functions of Political Party.
OR
Explain any five needs to have Political Parties in a Democratic Country.
OR
Describe any five major functions of Political Parties performed in a Democracy.
OR
Describe the importance of Political Parties in a Democratic Government.
OR
Describe any five major functions of Political Parties.
OR
“Political Parties play a major role in democracy.” Explain any five points to justify this statement.
OR
“Political parties are rightly called the government in disguise.” Justify the statement in reference to democratic politics by giving five arguments.
Answer : Introduction: Political parties perform many crucial functions in democracy.
(a) It contest elections; parties choose candidates to contest elections. The process of choosing candidates varies, e.g., in the USA, party members choose the candidates while in India top party leaders choose.
(b) It puts forward policies and programmes and people choose them. They pile up similar opinions into a major stances that the parties support usually on the line of ruling the party.
(c) They make laws. Legislature makes laws since the majority of the members are from a party, they go by the lines parties take. Moreover, they train and make people (party members) leaders who constitutes the executive.
Question. Illustrate the situations which display lack of Internal Democracy within a Political Party.
OR
“Lack of Internal Democracy within Parties is the major challenge to political parties all over the World.” Analyse the statement.
OR
In what way lack of Internal Democracy is seen in the Political Parties?
Answer : Situations which display a lack of Internal Democracy within a Political Party are:
(i) Parties do not keep membership registers, do not hold organisational meetings and do not conduct internal elections regularly.
(ii) Ordinary members of the party do not get sufficient information on what happens inside the Party.
(iii) They do not have the means or the connections needed to influence the decisions. As a result, the leaders assume greater power to make decisions in the name of the Party.
(iv) Since one or a few leaders exercise paramount power in the party, those who disagree with the leadership find it difficult to continue in the Party.
(v) More than loyalty to party principles and policies, personal loyalty to the leader becomes more important.
Question. Describe the importance of Regional Political parties in strengthening democracy.
Answer : Importance of Regional Political Parties:-
Over the last three decades, the number and strength of regional parties have expanded. This made the Parliament of India politically more and more diverse. No one national party can secure on its own a majority in Lok Sabha. As a result, the National Parties are compelled to form alliances with state parties since 1996. Nearly everyone of the state parties has got an opportunity to be a part of one or the other National level coalition government. This has contributed to the strengthening of federalism and democracy in our country.
Question. Why is there a lack of Internal Democracy within the Political Parties in India? Explain with examples.
Answer : There are various reasons for lack of Democracy within the Political Parties in India:
(i) Concentration of power in one or a few Leaders at the top.
(ii) Details of Membership are not registered in the Parties.
(iii) No Organisational Meetings.
(iv) No Internal Elections for Membership within the Party.
(v) Top Leaders have unanimous power of decisionmaking.
Question. Suggest any five effective measures to reform Political Parties.
OR
Suggest and explain any five measures to reform Political Parties.
OR
Suggest some reforms to strengthen parties so that they perform their functions well.
Answer : Effective measures to reform Political Parties are:
(i) A law should be made to regulate the internal affairs of Political Parties.
(ii) It should be made compulsory for political parties to maintain a register of its Members.
(iii) It should be made mandatory for political parties to give a minimum number of tickets, about 1/3rd to its Women candidates.
(iv) There should be a quota for women in the decision making bodies of the Party.
(v) There should be state funding of elections.
(vi) The government should give parties money to support their election expenses in kind of petrol, paper, telephone, etc. or cash.
(vii) Vote casting should be made compulsory in each election.
Case Based Questions
I. Read the given extract and answer the questions that follow:
In some countries, power usually changes between two main parties. Several other parties may exist, contest elections and win a few seats in the National legislatures. But only the two main parties have a serious chance of winning majority of seats to form government. Such a party system is called twoparty system. The United States of America and the United Kingdom are examples of two-party system. If several parties compete for power and more than two parties have a reasonable chance of coming to power either on their own strength or in alliance with others, we call it a multi party system. Thus, in India, we have a multi party system. In this system, the government is formed by various parties coming together in a coalition. When several parties in a multi-party system join hands for the purpose of contesting elections and winning power, it is called an alliance or a front. For example, in India there were three such major alliances in 2004 parliamentary elections– the National Democratic Alliance, the United Progressive Alliance and the Left Front. The multiparty system often appears very messy and leads to political instability. At the same time, this system allows a variety of interests and opinions to enjoy political representation.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
1. Countries having Bi- party system:
(a) USA
(b) India
(c) China
(d) All of these
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
2. The multi-party system:
(a) appears very messy.
(b) leads to political instability.
(c) not free to form a political party.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
3. The Government is formed by various parties coming together in a/an ________.
(a) alliance
(b) front
(c) coalition
(d) opposition
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
4. Which party leads the ruling NDA government at the Centre?
(a) Indian National Congress
(b) Bharatiya Janata Party
(c) Bahujan Samaj Party
(d) Communist Party of India
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
II. Read the given extract and answer the questions that follow:
Democracies that follow a federal system all over the world tend to have two kinds of political parties: parties that are present in only one of the federal units and parties that are present in several or all units of the federation. This is the case in India as well. There are some countrywide parties, which are called National parties. These parties have their units in various states. But by and large, all these units follow the same policies, programmes and strategy that is decided at the National level. Every party in the country has to register with the Election Commission. While the Commission treats all parties equally, it offers some special facilities to large and established parties. These parties are given a unique symbol – only the official candidates of that party can use that election symbol. Parties that get this privilege and some other special facilities are ‘recognised’ by the Election Commission for this purpose. That is why these parties are called, ‘Recognised Political Parties’. The Election Commission has laid down detailed criteria of the proportion of votes and seats that a party must get in order to be a recognised party. A party that secures at least six per cent of the total votes in an election to the Legislative Assembly of a State and wins at least two seats is recognised as a State party. A party that secures at least six per cent of the total votes in Lok Sabha elections or Assembly elections in four States and wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha is recognised as a National Party.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
1. What does the Election Commission of India allot to all Parties so that they are called ‘Recognised Political Parties’?
(a) Emblem
(b) Motif
(c) Symbol
(d) Flag
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
2. A party is called ‘National Party’ only when it polls _________ of total valid votes in at least ______ states and in addition it wins _________ Lok Sabha Seats.
(a) 2%, Four, 4
(b) 6%, Four, 4
(c) 4%, Four, 4
(d) 2%, Four, 3
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
3. Every party in the country has to register with:
(a) Prime Minister
(b) President
(c) Election Commission
(d) All of these
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
4. Two regional parties of West Bengal are:
(a) Forward Bloc and Trinamool Congress
(b) All India Trinamool Congress and Forward Bloc
(c) National Congress Party and Forward Bloc
(d) Indian National Congress and Forward Bloc
Answer : Option (a) is correct.



