Quadrilaterals MCQ Class 9 Mathematics
Please refer to Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals MCQ Class 9 Mathematics with answers below. These multiple-choice questions have been prepared based on the latest NCERT book for Class 9 Mathematics. Students should refer to MCQ Questions for Class 9 Mathematics with Answers to score more marks in Grade 9 Mathematics exams. Students should read the chapter Quadrilaterals and then attempt the following objective questions.
MCQ Questions Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals
The Quadrilaterals MCQ Class 9 Mathematics provided below covers all important topics given in this chapter. These MCQs will help you to properly prepare for exams.
Question. In parallelogram ABCD, ∠DAB = 70°, ∠DBC = 70°, then ∠CDB is equal to
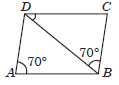
(a) 40°
(b) 60°°
(c) 70°
(d) 30°
Answer
A
Question. In the adjoining figure, PQRS is a parallelogram in which PQ is produced to T such that QT = PQ. Then, OQ is equal to
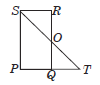
(a) OS
(b) OR
(c) OT
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. A blackboard is in the shape of a
(a) Parallelogram
(b) Rhombus
(c) Rectangle
(d) Kite
Answer
C
Question. If M and N are the mid-points of non parallel sides of a trapezium PQRS, then which of the following conditions is/are true?
(a) MN || PQ
(b) MN = 1/2 (PQ + RS)
(c) MN = 1/2 (PQ – RS)
(d) Both (a) and(b)
Answer
D
Question. In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a square. A line segment DX cuts the side BC at X and the diagonal AC at O such that ∠COD = 105° and ∠OXC = x°. Find the value of x.
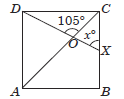
(a) 75°
(b) 80°
(c) 60°
(d) 45°
Answer
C
Question. The measure of all the angles of a parallelogram, if an angle is 24° less than twice the smallest angle, is
(a) 37°, 143°, 37°, 143°
(b) 108°, 72°, 108°, 72°
(c) 68°, 112°, 68°, 112°
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. How many angles are there in a quadrilateral?
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 1
(d) 3
Answer
A
Question. The triangle formed by joining the midpoints of the sides of an equilateral triangle is
(a) scalene
(b) right angled
(c) equilateral
(d) isosceles
Answer
C
Question. In a quadrilateral ABCD, ∠A + ∠C is 2 times ∠B + ∠D. If ∠A = 140° and ∠D = 60°, then ∠B =
(a) 60°
(b) 80°
(c) 120°
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram, what is the sum of the angles x, y and z?
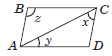
(a) 180°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not true?
(a) The diagonals of a rectangle are equal.
(b) Diagonals of a square are equal.
(c) Diagonals of a parallelogram are not always equal.
(d) Diagonals of a kite are equal.
Answer
D
Question. Which type of quadrilateral is formed when the angles A, B, C and D are in the ratio 2 : 4 : 5 : 7 ?
(a) Rhombus
(b) Square
(c) Trapezium
(d) Rectangle
Answer
C
Question. In a parallelogram ABCD, if ∠A = 75°, then the measure of ∠B is
(a) 10°
(b) 20°
(c) 105°
(d) 90°
Answer
C
Question. The triangle formed by joining the midpoints of the sides of a right angled triangle is
(a) scalene
(b) isosceles
(c) equilateral
(d) right angled
Answer
D
Question. The angle between the diagonals of a rhombus is
(a) 45°
(b) 90°
(c) 30°
(d) 60°
Answer
B
Case Based MCQs
Read the following passage and answer the questions
Anjali and Meena were trying to prove mid point theorem. They draw a triangle ABC, where D and E are found to be the midpoints of AB and AC respectively. DE was joined and extended to F such that
DE = EF and FC is also joined.
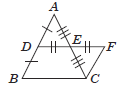
Question. ∠ECF is equal to which angle?
(a) ∠EAD
(b) ∠ADE
(c) ∠AED
(d) ∠B
Answer
A
Question. CF is parallel to
(a) AE
(b) CE
(c) BD
(d) AC
Answer
C
Question. ΔADE and ΔCFE are congruent by which criterion?
(a) SSS
(b) SAS
(c) RHS
(d) ASA
Answer
B
Question. CF is equal to
(a) EC
(b) BE
(c) BC
(d) AD
Answer
D
Question. ∠EFC is equal to which angle?
(a) ∠DAE
(b) ∠EDA
(c) ∠AED
(d) ∠DBC
Answer
B
Read the following passage and answer the questions
After summervacation, Manit’s class teacher organised a small MCQ quiz, based on the properties of quadrilaterals.

During quiz, she asks different questions to students.
Some of the questions are listed below.
Question. If AX and CY are the bisectors of the angles A and C of a parallelogram ABCD, then
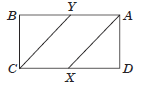
(a) AX || CY
(b) AX || CD
(c) AX || AB
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is/are the condition(s) for ABCD to be a quadrilateral?
(a) The four points A, B, C and D must be distinct and co-planar.
(b) No three of points A, B, C and D are collinear.
(c) Line segments i.e., AB, BC, CD, DA intersect at their end points only.
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. If angles of a quadrilateral are in ratio 3 : 5 : 5 : 7, then find all the angles.
(a) 54°, 80°, 80°, 146°
(b) 34°, 100°, 100°, 126°
(c) 54°, 90°, 90°, 126°
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is wrong condition for a quadrilateral said to be a parallelogram?
(a) Opposite sides are equal
(b) Opposite angles are equal
(c) Diagonal can’t bisect each other
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. ABCD and AEFG are two parallelograms. If ∠C = 63°, then determine ∠G.
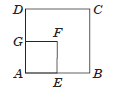
(a) 63°
(b) 117°
(c) 90°
(d) 120°
Answer
B
