Locomotion and Movement Class 11 Biology Important Questions
Please refer to Locomotion and Movement Class 11 Biology Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement in NCERT Book for Class 11 Biology have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 11 Biology for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 11 Biology Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement
Objective Questions
Question. Striated muscle fibres are found in
(a) urinary bladder
(b) lungs
(c) gall bladder
(d) leg muscles
Answer
D
Question. Cardiac muscles are different from that of skeletal muscles as the former are
(a) striated but involuntary.
(b) non striated and involuntary.
(c) smooth or unstriated.
(d) voluntary in action.
Answer
A
Question. Which set clearly identify striated muscles?
(a) Cylindrical, Syncytial and Unbranched
(b) Spindle, Unbranched and Uninucleated
(c) Cylindrical, Striped and Nucleated
(d) Cylindrical, Striped and Branched
Answer
A
Question. Anisotropic band is
(a) thick and dark
(b) thin and dark
(c) thick and light
(d) thin and light
Answer
A
Question. Troponin
(a) produces sliding movement of microtubules
(b) contains globular head
(c) binding to Ca+2 produces skeletal muscle contraction.
(d) covers the active site of actin.
Answer
D
Question. A sarcomere is best described as a
(a) movable structural unit within a myofibril bounded by H zones.
(b) fixed structural unit within a myofibril bounded by Z lines.
(c) fixed structural unit within a myofibril bounded by A bands.
(d) movable structural unit within a myofibril bounded by Z lines.
Answer
D
Question. During resting stage the binding site of actin for myosin remains masked by
(a) troponin
(b) G-actin
(c) tropomyosin
(d) meromyosin
Answer
A
Question. Red muscle fibres are rich in
(a) golgi bodies
(b) mitochondria
(c) lysosomes
(d) ribosomes
Answer
B
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. What is the correct order that a motor nerve impulse travels when triggering a muscle contraction?
(a) Motor nerve→synaptic cleft→sarcolemma→ sarcoplasmic reticulum→troponin.
(b) Motor nerve→synaptic cleft→sarcolemma→troponin →sarcoplasmic reticulum.
(c) Motor nerve→sarcoplasmic reticulum→synaptic cleft→sarcolemma→troponin.
(d) Motor nerve→sarcolemma→sarcoplasmic reticulum→ synaptic cleft→troponin.
Answer
A
Question. In which option the number of bones of two corresponding parts are not the same?
(a) Thigh and upper arm
(b) Sole and palm
(c) Ankle and wrist
(d) Leg and arm
Answer
C
Question. Convexity of one bone articulate with concavity of other bone in
(a) pivot joint
(b) hinge joint
(c) gliding joint
(d) ball and socket joint
Answer
D
Question. Long uninucleate muscles are found in
(a) diaphragm
(b) alimentary canal
(c) tongue
(d) eye
Answer
B
Question. Muscles of alimentary canal are mainly
(a) striated and myogenic
(b) striated and neurogenic
(c) unstriated and neurogenic
(d) unstriated and myogenic
Answer
C
Question. A cricket player is fast chasing a ball in the field. Which one of the following groups of bones are directly contributing in this movement?
(a) Femur, malleus, tibia, metatarsals
(b) Pelvis, ulna, patella, tarsals
(c) Sternum, femur, tibia, fibula
(d) Tarsals, femur, metatarsals, tibia
Answer
D
Question. Eye-lid muscles have
(a) thick fibres with abundant mitochondria.
(b) thick fibres without myoglobin.
(c) thin fibres with myoglobin.
(d) thin fibres with lesser mitochondria.
Answer
B
Question. Muscle contraction is triggered
(a) when high levels of oxygen and sugar are released by the sarcolemma.
(b) when a surplus of ATP is released by a nerve motor unit.
(c) by release of a neurotransmitter at a synapse that directly causes actin and myosin to slide.
(d) by the nerve releasing a neurotransmitter, which triggers a flow of calcium that attaches to actin filaments and exposes the myosin binding sites.
Answer
D
Question. Given below are some events which occur during muscle contraction.
i. ATP is hydrolyzed.
ii. Myosin heads bind to actin.
iii. Hemoglobin concentration in muscle fibers increases.
iv. Calcium concentration in the sarcomere increase.
v. I bands shorten and H zones disappear.
Select the correct events which occur during muscle contraction.
(a) i only
(b) ii, iii & iv only
(c) i, ii, iv & v only
(d) All of these.
Answer
C
Question. What will happen if the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the muscle fibres is damaged?
(a) Binding of ATP to actin will be affected.
(b) Release of inhibition on Z discs will stop.
(c) Exposure of myosin binding sites on the actin will be affected.
(d) Transmission of action potential along the sarcolemma will increase.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not the function of skeleton?
(a) It allows movement.
(b) It supports the body.
(c) It connects muscle to joints.
(d) It protects the internal part of the body.
Answer
C
Question. A person is suffering from an age related disorder “X”. X is characterized by decreased bone mass and increased chances of fractures. Identify X and its common cause.
(a) Tetany, Increased levels of estrogen
(b) Osteoporosis, Decreased levels of estrogen
(c) Myasthenia gravis, Decreased levels of estrogen
(d) Muscular dystrophy, Increased levels of estrogen
Answer
B
Diagram Type Questions
Question. The label X in the given figure of an act in filament represents

(a) actin
(b) myosin
(c) tropomyosin
(d) troponin
Answer
D
Question. Refer the following figure and answer the question.
Fusion of which of the following marked bones (1- 6) are responsible for the formation of coxal bones?
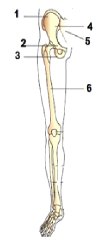
(a) 1, 2, 3
(b) 4, 5, 6
(c) 1, 2, 5
(d) 3, 5, 6
Answer
A
Question. The given figure shows the diagrammatic cross sectional view of a muscle with their parts marked as 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Which part is held together by a common collagenous connective tissue layer?
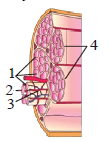
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
D

