Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science Important Questions
Please refer to Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations in NCERT Book for Class 10 Science have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 10 Science for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
All Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science Important Questions provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of Standard 10 Science. Please learn them and let us know if you have any questions.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question: Why does a layer of silver deposit on copper wire when dipped in silver nitrate solution?
Answer: When copper wire is dipped in a solution ofsilver nitrate, displacement reaction takes place in which copper displaces silver from silver nitrate solution as copper is more reactive than silver.
Cu + AgNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + Ag
Copper nitrate
Question: What happens when sodium sulphate solution is added to barium chloride solution?
Answer: When sodium sulphate solution is added to barium chloride solution, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed.
The equation of the reaction taking place is:
Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
Question: What type of reaction is represented by:
A + BC → AC + B ?
Answer: This is an example of displacement reaction in which A displaces B from its compound BC.
Question: A student took 2-3 g of a substance X in a glass beaker & poured water over it slowly.
He observed bubbles along with hissing noise. The beaker becomes quite hot. Identify X. What type of reaction is it?
Answer: X is quick lime or calcium oxide which reacts vigorously with water to form slaked lime releasing a large amount of heat.
Equation for the reaction taking place is:
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + Heat.
Question: A white compound on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and a yellow residue is left behind. Write chemical equation of the reaction stating its type.
Answer: The white compound is lead nitrate and brown fumes are of nitrogen dioxide and yellow residue is lead oxide.
The chemical equation of the reaction taking place is:
2Pb(NO3)2(s) → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
The type of reaction is decomposition reaction.
Question: Why are oil and fat containing food items flushed with nitrogen while packing them?
Answer: Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen while packing them as nitrogen is an inert gas and prevents fried food materials from getting rancid.
SHORT ANSWER
Question: Identify the type of each of the following reactions stating reason for your answers :
(A) Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe + heat
(B) Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI → PbI2 + 2KNO3
(C) ZnCO3 heat→ ZnO + CO2
Answer: (A) Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe + Heat
Single Displacement Reaction Aluminium (Al) being more reactive then iron (Fe) displaces less reactive metal Fe from its compound Fe2O3. This displacement is highly exothermic and releases a lot of heat.
Question: Study the figure given below and answer the following questions:
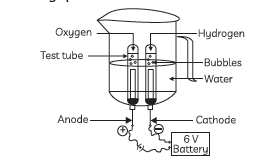
(A) Name the process depicted in the diagram.
(B) Write the composition of the anode and the cathode.
(C) Write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction taking place in this case.
(D) The reaction does not take place if a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid are not added to water. Why?
Answer: (A) Electrolytic decomposition of water/ electrolysis of water.
(B) The gas collected at cathode is hydrogen and it is double the volume of than that of oxygen.
The gas collected at anode is oxygen which has volume half than that of hydrogen.
The deficiency of iodine in the diet of a person produces less thyroxine hormone and causes goitre.
The deficiency of insulin hormone in the body causes a disease known as diabetes.
(C) 2H2O(l) Electric → Current 2H2(g) + O2(g)
(D) The reaction does not take place if a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid are not added to water. Water is not a good conductor of electricity sulphuric acid is added in the water to make, it a good conductor of electricity.
Question: Identify the reducing agent in the following reactions:
(A) 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O
(B) 2H2O + 2F2 → 4HF + O2
(C) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
(D) 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Answer: (A) NH3 is the reducing agent because it gets oxidized to NO by the removal of hydrogen and addition of oxygen. O2 has been reduced to H2O by the addition of hydrogen.
(B) H2O is the reducing agent. Here, F2 gets reduced to HF (addition of hydrogen) and H2O gets oxidized to O2 (removal of hydrogen).
(C) CO is the reducing agent. Here, CO has been oxidized to CO2 by the addition of oxygen. Fe2O3 has been reduced to Fe by the removal of oxygen.
(D) H2 is the reducing agent as it gets oxidized to H2O by the addition of oxygen. O2 has been reduced to H2O by the addition of hydrogen.
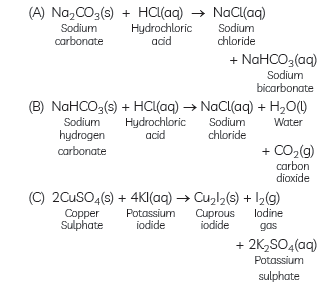
Question: Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
(A) Sodium carbonate on reaction with hydrochloric acid in equal molar concentrations gives sodium chloride and sodium hydrogen carbonate.
(B) Sodium hydrogen carbonate on reaction with hydrochloric acid gives sodium chloride and water, and liberates carbon dioxide.
(C) Copper sulphate on treatment with potassium iodide precipitates cuprous iodide (Cu2I2), liberates iodine gas and also forms potassium sulphate.
Answer:
Question: What happens when food materials containing fats and oils are left for a long time? List two observable changes and suggest three ways by which this phenomenon can be prevented.
Answer: When food materials containing fats and oils are left for a long time, they start giving unpleasant smell and taste.
When fats and oils are oils are oxidised by the air, they become rancid.
The condition produced by oxidation of fats and oils in foods is marked by unpleasant smell and taste called rancidity. Rancidity spoils the food material and make it unfit for use.
Prevention:
(1) When food is stored in air-tight containers, then there is a little exposure to oxygen of air and the oxidation of fats and oils present in food is slowed down.
(2) Anti-oxidants prevent the oxidation as the fats and oils present in the foods do not get oxidised easily and hence do not get rancid.
(3) When packaged food bags are flushed with nitrogen gas which prevent the food from getting oxidised.
Question: A substance X, which is an oxide of a group 2 element, is used intensively in the cement industry. This element is present in bones also. On treatment with water, it forms a solution which turns red litmus blue. Identify X and also write the chemical reactions involved.
Answer: The element is calcium and the substance X is calcium oxide (CaO). Calcium oxide is used extensively in the cement industry and calcium is present in our bones in the form of calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2. Calcium oxide (CaO) is also known as quick lime.
Calcium oxide dissolves in water to form a basic solution which turns red litmus blue.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2
Calcium Water Calcium hydroxide
oxide (slaked lime)
Explanation: In this reaction, two compounds, namely calcium oxide and water have combined to form a single compound i.e. Calcium hydroxide so it is a combination reaction. The other type of reaction is exothermic as a lot of
heat is released.
Question: In the reaction:
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
(A) Name the compound (i) oxidised, (ii) reduced.
(B) Define oxidation and reduction on its basis.
Answer: (A) In the given reaction:
(1) The compound oxidized is Hydrochloric acid as it loses hydrogen atom to form Chlorine gas.
(2) The compound reduced is Manganese dioxide as it loses Oxygen atom to form manganese dichloride.
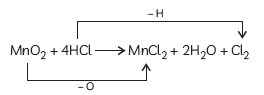
(B) Oxidation is the addition of oxygen to a substance or the removal of hydrogen from a substance.
Reduction is the addition of hydrogen to a substance or the removal of oxygen from a substance.
Question: Which among the following changes are
exothermic or endothermic in nature?
(A) Decomposition of ferrous sulphate
(B) Dilution of sulphuric acid
(C) Dissolution of sodium hydroxide in water
(D) Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water
Answer: (A) The decomposition of ferrous sulphate absorbs heat during reaction. Therefore, it is an example of endothermic reaction.
(B) When we dissolve sulphuric acid in water, a large amount of heat is liberated, so it is an exothermic reaction.
(C) When we dissolve sodium hydroxide in water, a large amount of heat is liberated, so it is an exothermic reaction.
(D) The mixing of ammonium chloride in water absorbs heat from the reaction mixture. Therefore, it is an example of endothermic reaction.
Question: Answer the following questions:
(A) In the following reactions, name the reactants which undergo oxidation and reduction:
(i) CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(g)
(ii) CuO(s) + Zn(s) → ZnO(s) + Cu(s)
(B) Also state one industrial application of reduction.
Answer: (A) Explanation: The substance which gains oxygen get oxidised and the one which losses oxygen gets reduced.
Here in equations:
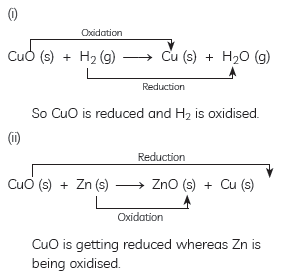
(B) One industrial application of reduction:
In industries, metallic ores are reduced to obtain the metal from them. For example Calcium carbonate is reduced in industries to get CaO and CO2.
Question: Which among the following changes are exothermic or endothermic in nature?
(A) Decomposition of ferrous sulphate
(B) Dilution of sulphuric acid
(C) Dissolution of sodium hydroxide in water
(D) Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water
Answer: (A) The decomposition of ferrous sulphate absorbs heat during reaction. Therefore, it is an example of endothermic reaction.
(B) When we dissolve sulphuric acid in water, a large amount of heat is liberated, so it is an exothermic reaction.
(C) When we dissolve sodium hydroxide in water, a large amount of heat is liberated, so it is an exothermic reaction.
(D) The mixing of ammonium chloride in water absorbs heat from the reaction mixture.
Therefore, it is an example of endothermic reaction.
Question: A chemical compound ‘X‘ is used in the soap and glass industry. It is prepared from brine.
(A) Write the chemical name, common name and chemical formula of ‘X‘.
(B) Write the equation involved in its preparation.
(C) What happens when it is treated with water containing Ca or Mg salts?
Answer: (A) Chemical name of compound ‘X‘–Sodium carbonate common name of compound
‘X‘—washing soda Chemical formula of compound
‘X‘ = Na2CO3. 10H2O
(B) Na2CO3 + 10H2O → Na2CO3.10H2O
Question:P, Q and R are 3 elements which undergo chemical reactions according to the following equations:
(i) P2O3 + 2Q → Q2O3 + 2P
(ii) 3RSO4 + 2Q → Q2(SO4)3 + 3R
(iii) 3RO + 2P → P2O3 + 3R
Answer the following:
(A) Which element is most reactive?
(B) Which element is least reactive?
(C) State the type of reaction listed above.
Answer: Element Q displaces P and R from their compounds in reaction ‘a’ and reaction ‘b’ respectively.
So element Q is more reactive than P and R. Also element P displaces element R in reaction ‘c’. So we can say that
(A) Q is the most reactive element
(B) R is the least reactive element.
(C) The above reactions are displacement reactions.
Question: A solution of potassium chloride when mixed with silver nitrate solution forms an insoluble white substance. Write the chemical reaction
involved and also mention the type of the chemical reaction.
Answer: When a solution of potassium chloride is mixed with silver nitrate solution, we get a precipitate of silver chloride. Chlorides are usually soluble but one important exception to this rule is silver chloride.
The chemical reaction is:
KCl + AgNO3 → KNO3(aq) + AgCl(s)
This type of chemical reaction is called a double displacement reaction.
Question: Why do we store silver chloride in dark coloured bottles?
Answer: We store silver chloride in dark coloured bottles to prevent the breakdown of the salt into its elements (photo decomposition). When silver chloride is exposed to light, it breaks down into elemental silver and chlorine gas.
2AgCl(s) Sunlight → 2Ag(s) + Cl2(g)
Silver chloride Silver Chloride
(grey) (white)
In order to prevent the decomposition of silver chloride to silver, we store them in dark coloured bottles which block the light.
Question:A silver article generally turns black when kept in the open for a few days. The article when rubbed with toothpaste again starts shining.
(A) Why do silver articles turn black when kept in the open for a few days? Name
the phenomenon involved.
(B) Name the black substance formed and give its chemical formula.
Answer: (A) The metal surface of silver articles reacts with atmospheric sulphur compounds like hydrogen sulphide and forms black layer of sulphides. This phenomenon is called as corrosion or tarnishing of silver.
(B) The black substance that is formed by the reaction of hydrogen sulphide and
atmospheric oxygen is silver sulphide (Ag2S).
4Ag + O2 + 2H2S → 2Ag2S + 2H2O
Question: (A) Design an activity to demonstrate the decomposition reaction of lead nitrate.
(B) Draw labelled diagram of the experimental set-up. List two main observations.
(C) Write balanced chemical equation for the reaction stating the physical state of the reactant and the products.
Answer: (A) Take a small amount of lead nitrate powder in a boiling tube.
Hold the boiling tube with a pair of tongs and heat it over the flame first gently and then strongly.
(B) Labeled diagram of the experimental setup:
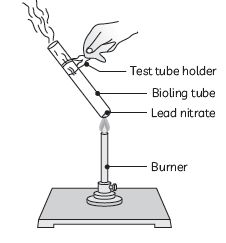
Two main observations:
(1) We observe emission of brown fumes of a gas which is nitrogen dioxide.
(2) The white colour of lead nitrate changes to yellow colour as lead oxide is formed.
(3) Balanced equation:
2Pb(NO3)2(s) → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
Question: (A) Classify the following reactions into different types:
(i) AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq)
(ii) CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
(iii) 2KClO3(s) → 2KCl(aq) + 3O2(g)
(iv) Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
(B) Translate the following statement into a balanced chemical equation:
‘‘Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and barium sulphate.’’
Answer: (A) Type of reactions are:
(i) Double Displacement reaction.
(ii) Combination reaction
(iii) Decomposition reaction
(iv) Displacement reaction
(B) The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between barium chloride and aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and barium sulphate.
3BaCl2(aq) + Al2(SO4)3(aq) → 3BaSO4(s) + 2AlCl3(aq)
Question: (A) What is a double displacement reaction? Explain with an example.
(B) A small amount of quick lime is added to water in a beaker.
(i) Name and define the type of reaction that has taken place.
(ii) Write balanced chemical equation for the above reaction and the chemical name of the product formed.
(iii) List two main observations of this reaction.
Answer: (A) Those reactions in which two compounds react by an exchange of ions to form two new compounds are called double displacement reactions.
Example: When we mix sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed by the reaction of SO42– and Ba2+.
The other product formed is sodium chloride which remains in the solution..
The equation for the reaction taking place is:
Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(s)
+ 2NaCl(aq)
(B) (i) Type of chemical reaction taking place when water is added to quick lime or calcium oxide is combination reaction.
Combination reactions are those reactions in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
(ii) Equation of the reaction taking place is:
CaO(s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + Heat
Product formed is calcium hydroxide or slaked lime.
(iii) Two observations are:
(1) The reaction of quicklime with water is very vigorous.
(2) It is an exothermic reaction as a large amount of heat is produced.
Question:(A) Arrange the following metals in the increasing order of their reactivities:
(B) List two observations you would record in your notebook 30 minutes after adding iron filings to copper sulphate solution.
Answer: (A) Metals arranged in increasing order of reactivity: Cu<Fe< Zn<Al
(B) When iron filings are added to copper sulphate solution we will observe:
(1) Colour of the solution changes from blue to green.
(2) Deposition of brown colour on iron filings.
Question: 2 g of silver chloride is taken in a china dish and the china dish is placed in sunlight for sometime. What will be your observation in this case? Write the chemical reaction involved in the form of a balanced chemical equation.
Identify the type of chemical reaction.
Answer: When 2 g of silver chloride is taken in a china dish and the china dish is placed in sunlight for sometime, we will observe that silver chloride turns grey.
This is because of the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine by sunlight.
The balanced chemical reaction involved is:
2AgCl(s) Sunlight → 2Ag(s) + Cl2(g)
Question: On adding a drop of barium chloride solution to an aqueous solution of sodium sulphite, white precipitate is obtained.
(A) Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(B) What other name can be given to this precipitation reaction?
(C) On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to the reaction mixture, white precipitate disappears. Why?
Answer: (A) Balanced chemical equation:
Na2SO3(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO3(s)
Sodium Barium Barium
sulphite chloride sulphite
+ 2NaCl(aq)
Sodium
chloride
(B) This reaction is also known as double displacement reaction.
(C) BaSO3 is a salt of a weak acid (H2SO3).
Therefore, a dilute acid such as HCl decomposes barium sulphite to produce sulphur dioxide gas, which has the smell of burning sulphur.
BaSO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → BaCl2 + H2O + SO2(g) White ppt.
BaCl2 is soluble in water; hence, white precipitate disappears.
Question: You are provided with two containers made up of copper and aluminium. You are also provided with solutions of dilute HCl, dilute HNO3, ZnCl2 and H2O. In which of the containers can these solutions be kept?
Answer: (A) Reactions of Copper with:
(1) Dilute HCI: Copper exhibits no reaction with HCl, so it can be stored in the copper container.
(2) Dilute HNO3: Nitric acid acts as a strong oxidizing agent and reacts with copper vessel. With dilute nitric acid, copper metal forms copper nitrate with nitric oxide and water, so dilute nitric acid cannot be stored in the copper container.
Cu(s) + 8HNO3(dil) → 3Cu(NO3)2(aq)
+ 2NO(g) + 4H2O(l)
(3) ZnCl2: Since Cu metal is less reactive than Zn, it cannot displace Zn from its compounds and there will be no reaction. Hence, zinc chloride can be stored in the copper container.
(4) H2O: There is no reaction between water and copper metal at room temperature, so water can be stored in a copper container.
(B) Reactions of Aluminium with:
(1) Dilute HCI: Al reacts with dilute HCI and forms aluminium chloride with hydrogen gas evolved, so it cannot be stored in the aluminium container.
2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2
(2) Dilute HNO3: Nitric acid is an oxidizing agent and in its presence, aluminium metal gets oxidized to form a layer of Al2O3, and forms a protective layer of oxide, so it will not react further. Hence, dilute nitric acid can be stored in the aluminium container.
(3) ZnCl2: Aluminium, being more reactive than zinc, can displace zinc ion from the solution. It readily reacts with zinc chloride and forms aluminium chloride with zinc metal.
2Al + 3ZnCl2 → 2AlCl3 + 3Zn
Hence, it cannot be stored in the aluminium container.
(4) H2O: At room temperature, there will be no reaction between aluminium metal and hot or cold water, so it can be stored in the aluminium container.
Aluminium is attacked by steam to form aluminium oxide and hydrogen.
2Al(s) + 3H2O(g) → Al2Cl3(s) + 3H2(g)
(B) Calcium oxide reacts with water to give lime water.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2
(C) Sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to give sodium chloride and water.
NaOH(s) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
(D) Dil. hydrochloric acid is added to copper oxide to give green coloured copper chloride and water.
CuO + 2HCl(dil.) → CuCl2 + H2O
(E) Solution of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water reacts to give insoluble barium sulphate and solution of sodium chloride.
BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4 → BaSO4
+ 2NaCl(aq)