Metals and Non-Metals Class 10 Science Important Questions
Please refer to Metals and Non-Metals Class 10 Science Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metalsin NCERT Book for Class 10 Science have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 10 Science for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals
All Metals and Non-Metals Class 10 Science Important Questions provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of Standard 10 Science. Please learn them and let us know if you have any questions.
Very Short Answer type Questions
Question. A green layer is gradually formed on a copper plate left exposed to air for a week in a bathroom. What could this green substance be?
Answer : It is due to the formation of basic copper carbonate [CuC03.Cu(0H)2].
Question. Which of the following two metals will melt at body temperature (37 °C) ?
Gallium, Magnesium, Caesium, Aluminium
Answer : Gallium and Caesium
Question. Name a non-metal which is lustrous and a metal which is non-lustrous.
Answer : Iodine is a non-metal which is lustrous, lead is a non-lustrous metal
Question. Which one of the following metals does not react with oxygen even at high temperatures ?
(a) Calcium (b) Gold (c) Sodium
Answer : (b) Gold does not react with oxygen even at high temperatures.
Question. Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state.
Answer : (i) Gold (ii) Silver
Question. Why does calcium float in water?
Answer : It is because hydrogen gas is formed which sticks to surface of calcium, therefore it floats.
Question. What is the valency of phosphorus with atomic number 15?
Answer : Phosphorus has valency 3.
Question. Metals generally occur in solid state. Name and write symbol of a metal that exists in liquid state at room temperature.
Answer : Mercury(Hg) exists in liquid state at room temperature.
Question. Which gas is liberated when a metal reacts with an acid? How will you test the presence of this gas?
Answer : Hydrogen gas is formed. Bring a burning matchstick near to it, H2 will burn explosively with ‘pop’ sound.
Question. A green layer is gradually formed on a copper plate left exposed to air for a week in a bathroom. What could this green substance be ?
Answer : It is due to the formation of basic copper carbonate [CuCO3.Cu(OH)2].
Question. From amongst the metals sodium, calcium, aluminium, copper and magnesium, name the metal (a) which reacts with water only on boiling, and
(b) another which does not react even with steam.
Answer : (a) Magnesium reacts with water only on boiling.
(b) Copper does not react even with steam.
Question. What is the valency of silicon with atomic number 14?
Answer : Its valency is equal to 4.
Question. Name any one metal which reacts neither with cold water nor with hot water, but reacts with heated steam to produce hydrogen gas.
Answer : Iron; 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
Question. What is the valency of an element with atomic number 35?
Answer : Its valency is 1.
Question. Mention the names of the metals for the following:
(i) Two metals which are alloyed with iron to make stainless steel.
(ii) Two metals which are used to make jewellary.
Answer : (i) Nickel and chromium.
(ii) Gold and platinum.
Question. Arrange the following metals in the decreasing order of reactivity: Na, K, Cu, Ag.
Answer : K > Na > Cu > Ag
Question. The way, metals like sodium, magnesium and iron react with air and water is an indication of their relative positions in the ‘reactivity series’. Is this statement true ? Justify your answer with examples.
Answer :Yes, sodium reacts explosively even with cold water, it is most reactive. Magnesium reacts with hot water, it is less reactive than Na. Iron reacts only with steam which shows it is least reactive among the three.
Question. Name the metal which reacts with a very dilute HNO3 to evolve hydrogen gas.
Answer : Magnesium
Question. A non-metal X exists in two different forms Y and Z. Y is the hardest natural substance, whereas Z is a good conductor of electricity. Identify X, Y and Z.
Answer : ‘X’ is carbon, ‘Y’ is diamond as it is the hardest natural substance and ‘Z’ is graphite as it is good conductor of electricity.
Question. Write one example of each of
(i) a metal which is so soft that, it can be cut with knife and a non-metal which is the hardest sustance.
(ii) a metal and a non-metal which exist as liquid at room temperature.
Answer : (i) Sodium, carbon (diamond).
(ii) Mercury is liquid metal, bromine is liquid non-metal.
Question. X + YSO4——-> XSO4+ Y
Y + XSO4 ——–> No reaction
Out of the two elements, ‘X’ and ‘Y’, which is more reactive and why?
Answer : ‘X’ is more reactive than ‘Y’ because it displaces ‘Y’ from its salt solution.
Question. Give reason for the following:
(a) School bells are made up of metals.
(b) Electric wires are made up of copper.
Answer : (a) It is because metals are sonorous, i.e. they produce sound when struk with a hard substance.
(b) It-is because copper is good conductor of electricity.
Question. Name the following:
(a) A metal, which is preserved in kerosene.
(b) A lustrous coloured non-metal.
(c) A metal, which can melt while kept on palm.
(d) A metal, which is a poor conductor of heat.
Answer : (a) Sodium is preserved in kerosene. (b) Iodine is lustrous coloured non-metal. (c) Gallium. (d) Lead.
Question. What is an alloy? State the constituents of solder. Which property of solder makes it suitable for welding electrical wires?
Answer : Alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals. One of them can be a non-metal also. Solder consists of lead and tin. It has low melting point which makes it suitable for welding electrical wires.
Question. Explain why calcium metal after reacting with water starts floating on its * surface. Write the chemical equation for the reaction. Name one more metal that starts floating after some time when immersed in water.
Answer : Calcium starts floating because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of metal.
Ca(s) + 2H2O(I) Ca(OH)2 + H2(g)
Magnesium reacts with hot water and starts floating due to the bubbles of hydrogen gas sticking to its surface.
Question. An element forms an oxide, A2O3 which is acidic in nature. Identify A as a metal or nonmetal.
Answer : ‘A’ is non-metal as non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature.
Question. Give reason for the following:
(a) Aluminium oxide is considered as an amphoteric oxide.
(b) Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state.
Answer : (a) It is because it reacts with acids as well as bases to produce salts and water.’Al’ is less electropositive metal. So, it forms amphoteric oxide which can react with acid as well as base.
(b) Ionic compounds can conduct electricity in molten state because ions ’ become free to move in molten state.
Question. Write two differences between calcination and roasting.
Answer :

Question. When a metal X is treated with cold water, it gives a base Y with molecular formula XOH
(Molecular mass = 40) and liberates a gas Z which easily catches fire. Identify X, Y and Z.
Answer :

Short Answer type Questions
Question: Give reason for the following:
(a) Aluminium oxide is considered as an amphoteric oxide.
(b) Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state.
Answer: (a) Aluminium oxide reacts with both acidic and basic substances to give neutralization reaction and hence cannot be called a true acid as well as base. Hence it is called Amphoteric oxide.
Al2 O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O » Neutralisation Reaction with hydrochloric acid (behaves like a base)
Al2 O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O » Neutralisation reaction with Sodium hydro oxide (behaves like an acid)
(b) Ionic compounds are bound to each other with strong attraction force. Hence they are in solid form and their ions are not mobile. When in molten state the ions become mobile and act as carriers for charge and hence conduct electricity.
Question: Element ‘M’ forms a chloride with the formula MCl2 which is sold with high melting point. To which group of the Periodic table does the element ‘M’ belong?
Answer: Element M should belong to group 2 of the periodic table. Reason: Since the chloride formula formed by the metal is of the form MCl2, the valency of the metal is +2. Also, it is high melting solid so it has to be an ionic compound and so metal should be definitely from 1st or 2nd group. But since metals of group 1 can show only +1 valency, the metal cannot be from group 1 then it is definitely from group 2. Ex: Ca, Mg etc. are 2nd group metals and satisfy this situation.

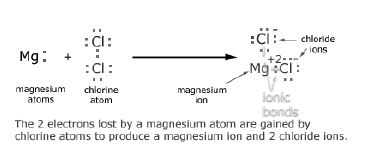
Question: A. Show on a diagram the transfer of electrons between the atoms in the formation of MgO. Write symbols of cation and anion present in MgO.
Answer: Cation present in MgO >>> Mg2+ Anion present in MgO >>> O2–

Question: B. Name the solvent in which ionic compounds are generally soluble.
Answer: Ionic compounds are soluble in polar solvents like water.
Question: C. Why are aqueous solutions of ionic compounds able to conduct electricity?
Answer: Aqueous solution of ionic compounds contains ions in mobile form which carry charge and hence help in conduction of electricity.
Question: Show the electronic transfer in the formation of MgCl2 form its elements.
Answer: Mg >> Electronic configuration= 2,8,2 Stable form>> 2,8 hence valency= +2 Cl>> Electronic configuration= 2,8,7 Stable form>> 2,8,8 hence valency= -1
Formation of MgCl2
Formation of magnesium ion by donating an electron
Mg(2,8) → Mg+2 + 2e-
Formation of chlorine ion by accepting an electron
Cl(2,8,7) + e- → Cl-
When 2 free chlorine atoms accept the electrons given by single magnesium ion the compound MgCl2 is formed.
Question: Reema’s maid fainted in her house. Reema took her maid to doctor. After check-up Doctor fond she suffered from anaemia Doctor advised her to take vegetables and fruits rich in iron. Doctor gave her some folic acid tablets which contain iron (II) sulphate. Reema helped her maid financially also.
(a) What values are possessed by Reema?
(b) Deficiency of which metal cause anaemia?
(c) What is a formula of folic acid?
Answer: (a) Reema has good human values. She is a person who likes to help poor.
(b) Deficiency of metal iron in our blood causes anaemia.
(c)c19H19N7o6 is the formula of folic acid.
Question: With the help of a suitable example, explain how ionic compounds are
formed State any three general properties of ionic compounds.
Answer: Let us take the example of an ionic compound MgCl2.it consists of cation Mg2+ and anion Cl–. Mg in its pure form consists two extra electrons on of the other hand chlorine is sort of one electron to complete its octet. Hence one magnesium and two chlorine come together to transfer electrons between them and form the ionic compound. Formation of all ionic compounds take place in similar fashion.

Three general properties of ionic compounds are as follows:
1) Soluble in polar solvents and insoluble in organic solvents.
2) Good conductor in molten form but non-conductor in solid forms.
3) Generally found in crystalline solid forms due to strong force of interaction.
Question: (a) Write the electron dot structures for potassium and chlorine.
(b) Show the formation of KCl by the transfer of electrons.
(c) Name the ions present in the compound, KCl.
Answer.

Question: A metal ‘X’ loses two electrons and a non-metal ‘Y’ gains one electron. Show the electron dot structure of compound formed between them. Is it ionic or covalent? Does it have high melting point or low? Will it conduct electricity in solid state or in aqueous solution and why? Will it be soluble in water?
Answer: Since X loses two electrons, its valence becomes +2 and it forms the ion of the form X2+. Similarly, valency of Y is -1 and its ionic form is Y-.

Formation of compound with X and Y Since compound is formed by ions it is ionic. Ionic compounds are High melting points, are soluble in aqueous solutions because of mobile ions and are soluble in water.
Question: State three reasons for the following facts
(i) Sulphur is a non-metal
(ii)Magnesium is a metal
One of the reasons must be supported with a chemical equation.
Answer.

Question: What is cinnabar? How is metal extracted from cinnabar? Explain briefly.
Answer. Cinnabar is HgS.
Mercury is obtained by roasting cinnabar. HgO formed is thermally unstable and gives mercury.

Question: A metal ‘X’ acquires a green colour coating on its surface on exposure to air.
(i) Identify the metal ‘X’ and name the process responsible for this change.
(ii) Name and write chemical formula of the green coating formed on the metal.
(iii) List two important methods to prevent the process.
Answer. (i) Metal is copper. The process is corrosion.
(ii) Basic copper carbonate [CuCO3.Cu(0H)2].
(iii)
• It should be coated with tin
• It should be mixed with other metals to form alloys
Question: (a)State the electron-dot structure for calcium and sulphur.
(b) Show the formation of CaS by the transfer of electrons.
(c) Name the ions present in this compound CaS. Atomic number of Ca = 20, O = 16.
Answer.

Question: You are given samples of three metals. Sodium, magnesium and copper. Suggest any two activities to arrange them in order of decreasing activity.
Answer. Activity 1: Sodium reacts with cold water vigorously to form sodium hydroxide
and hydrogen gas
2Na(s) + 2H2O (I) → 2AaOH (aq) + H2 (g)
cold
Magnesium does not react with cold water but with hot water to form magnesium ! hydroxide and
hydrogen gas.
Mg (s) + 2H2O → Mg(OH)2 (aq) + H2(g)
Hence sodium is more reactive than magnesium.
Mg (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → MgSO4(aq) + Cu (s)
Cu (s) + MgSO4 (aq) → No reaction
Question: (a) Explain the formation of ionic compound CaO with electron dot structure. Atomic number of calcium and oxygen are 20 and 8 respectively.
(b) Name the constituent metals of bronze.
Answer.

Question: (a) Show on a diagram the transfer of electrons between the atoms in the formation of MgO. Write symbols of cation and anion present in MgO.

(b) Name the solvent in which ionic compounds are generally soluble.
(c) Why are aqueous solutions of ionic compounds able to conduct electricity?
Answer. (b) Ionic compounds are soluble in water.
(c) It is because aqueous solutions consist of ions which can move freely in them and carry current.
Question: Write balanced equations for the reaction of:
(i) aluminium when heated in air. Write the name of the product.
(ii) iron with steam. Name the product obtained.
(iii) calcium with water. Why does calcium start floating in water?
Answer.

The product formed is aluminium oxide.
(ii) 3Fe + 4H2O (steam) Fe3,O4 + 4H2
The product obtained is iron(II) iron (III) oxide.
(iii) Ca + 2H2O Ca(OH)2 + H2
The bubbles of hydrogen stick to the surface of metal that is why it floats.
Question: You are provided with magnesium ribbon and sulpher powder. Explain with the help of an
activity that metal oxides are basic and non-metal oxide are acidic in nature.
Answer.
Aim: To test the nature of oxides formed by metals and non-metals. Materials Required: Sulphur powder, Mg ribbon, water, blue litmus paper, red litmus paper.
Procedure:
1. Take magnesium ribbon with a pair of tongs and burn it in flame in the presence of air.
2 .Collect the product formed and dissolve it in warm water.
3. Add red litmus paper into it.
4. Observe the change in colour and decide the nature of the oxide formed.
5. Burn sulphur in a deflagrating spoon in the presence of air and dissolve the oxide formed in water.
6. Dip blue litmus paper into the solution and observe the changein the colour and decide the nature of the oxide formed.
Observation: The oxide formed by metal turns red litmus blue whereas oxide of non-metal turns
blue litmus red.
Chemical Reaction:

Conclusion: Most of the metallic oxides are basic in nature whereas most of the non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature.
Question: (a) Show the formation of Na2O by the transfer of electrons between the combining atoms.
(b) Why are ionic compounds usually hard?
(c) How is it that ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity but they do so when in molten state?
Answer.

(b) It is due to strong force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
(c) In solid state, ions are not free to move whereas in molten state ions are free to move, therefore, they conduct electricity in molten state.
Question: An ore on heating in air produces sulphur dioxide. Which process would you suggest for its concentration? Describe briefly any two steps involved in the conversion of this concentrated ore into related metal.
Answer. It is concentrated by froth-floatation process.
(i) Roasting: The concentrated sulphide ore is heated strongly in the presence of oxygen to convert it into its oxide.
2ZnS(s) + 3O2 (g) → 2ZnO(s) + 2SO2 (g)
(ii) Reduction : This oxide of metal is reduced with suitable reducing agent to get free metal.

Question: Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(b) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium carbonate.
(c) Carbon dioxide is passed through lime water.
Answer.

Question: What are amphoteric oxides? Choose the amphoteric oxides from amongst the following oxides:
Na2O, ZnO, Al2O3, CO2, H2O
Answer. Those oxides which reacts with acids as well as bases to produce salts and water are called amphoteric oxides, e.g. Na2O, ZnO, are amphoteric oxides among given oxides.
Question: Write the names and symbols of two most reactive metals. Explain by drawing electronic structure how any one of the two metals react with a halogen. State any four physical properties of the compound formed.
Answer. K(Potassium) and Na(Sodium) are the two most reactive metals. K’ and Na‘ are electronic structures as they have one valence electron

where ‘F’ is a halogen.
Four physical properties of the compounds formed by these elements and halogens are:
(i) They have high melting point.
(ii)They are soluble in water.
(iii) They conduct electricity in molten state not in solid state.
(iv) They are solid and somewhat hard.
Question: Give reasons for the following observations:
(i) Ionic compounds in general have high melting and boiling points.
(ii) Highly reactive metals cannot be obtained from their oxides by heating them with carbon.
(iii) Copper vessels get a green coat when left exposed to air in the rainy season.
Answer. (i) Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points due to strong force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
(ii) It is because these metals themselves are strong reducing agents. Therefore, cannot be reduced by reducing agent like carbon.
(iii) Copper vessels react with CO2, O2 and moisture to form green-coloured basic copper carbonate [CuCO3.Cu(OH)2].
Question: State reasons for the following observations:
(i) The shining surface of some metals becomes dull when exposed to air for a long time.
(ii) Zinc fails to evolve hydrogen gas on reacting with dilute nitric acid.
(iii) Metal sulphides occur mainly in rocks but metal halides occur mostly in sea and lake waters.
Answer. (i) It is because metal reacts with substances present in atmosphere to form surface compounds which make it dull.
(ii) It is because dil. HNO3 is an oxidising agent therefore zinc gives NO and not H2 with dil. HNO3.
(iii) It is because sea water contains sodium chloride due to which metal halides are formed, whereas sulphur is found below rocks. Therefore, metal – sulphides are formed in rocks.
Question: State reasons for the following:
(i) Electric wires are covered with rubber like material.
(ii) From dilute hydrochloric acid, zinc can liberate hydrogen gas but copper cannot.
(iii) Sulphide ore of a metal is first converted to its oxide to extract the metal from it.
Answer. (i) It is because rubber is an insulator and does not allow current to flow through it.
(ii) Zinc is more reactive than hydrogen. Therefore, it can displace hydrogen from dilute HCl whereas copper cannot, because it is less reactive than hydrogen. ,
(iii) It is because it is easier to reduce oxide ore as compared to sulphide ore.
Long Answer Type Question [5 Marks]
Question: (a) Write electron dot diagram for chlorine (At No. 17) and calcium (At No. 20). Show the formation of calcium chloride by transfer of electrons.
(b) Identify the nature of above compound’and explain three physical properties of such compound. Answer.
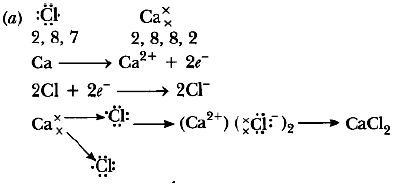
(b) It is ionic compound.
Physical properties
1. It is hard and solid.
2. It has high melting and boiling point.
3. It soluble in water.
Question: (a) Define activity series of metals. Arrange the metals gold, copper, iron and magnesium in order of their increase in reactivity.
(b) What will you observe when:
(i) Some zinc pieces are put in copper sulphate solution.
(ii) Some silver pieces are put into green coloured ferrous sulphate solution.
Answer. (a) The series of metals in which metals are arranged in decreasing order of their reactivity.
Au < Cu < Fe < Mg is increasing order of reactivity.
(b) (i) The blue solution will become colourless and reddish brown copper metal will be deposited.
Question: (a) In the formation of compound between two atoms A and B, A loses two electrons and B gains one electron.
(i) What is the nature of bond between A and B?
(ii) Suggest the formula of the compound formed between A and B.
(b) On similar lines explain the formation of MgCl2 molecule.
(c) Common salt conducts electricity only in the molten state. Why?
(d) Why is melting point of NaCl high?
Answer.

Question: Give reasons for the following:
(i) Silver and copper lose their shine when they are exposed to air. Name the substance formed on their surface in each case.
(ii) Tarnished copper vessels are cleaned with tamarind juice.
(iii) Aluminium is more reactive than iron yet there is less corrosion of aluminium as
compared to iron when both are exposed to air.
Answer. (i) These metals get corroded. Silver forms black Ag2S (silver sulphide) and copper form greenish layer of basic copper carbonate CuCO3. Cu(OH)2 .
(ii) Tamarind contains acid which reacts with basic copper carbonate and product gets dissolved and removed from copper vessel.
(in) Aluminium forms oxide layer on its surface which does not further react with air.
Question: (a) Explain with an example how the metal (X) which is low in reactivity series and metal
(Y) which is high in the reactivity series are obtained from their compounds by reduction process.
(b) Write the electronic configurations of sodium and chlorine. Show the formation of sodium chloride from sodium and chlorine by the transfer of electrons.
(c) List any two observations when a highly reactive metal is dropped in water.
Answer. (a) ‘X’ is obtained by chemical reduction.
‘Y’ is obtained by electrolytic reduction.

(c) (i) Metal will catch fire.
(ii) Alkali solution is formed which turns red litmus blue.
Question: (a) Write the electron dot structures of sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
(b) Show the formation of Na2O and MgO by transfer of electrons. Name the ions present in these compound.
(c) List three properties of ionic compounds.
Answer.

(i) They are solids having high melting point.
(ii) They are soluble in water.
(iii) They conduct electricity in molten state as well as in aqueous solution.
Question: A metal (E) is stored under kerosene. When a small piece of it is left open in the air, it catches fire. When the product formed is dissolved in water, it turns red litmus to blue.
(i) Name the metal (E).
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction when it is exposed to air and when the product is dissolved in water.
(iii) Explain the process by which the metal is obtained from its molten chloride.
Answer. (i) ‘E’ is sodium which catches fire in presence of moisture.
(ii) 4Na + O2 → 2NaO
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
(iii) Electrolytic reduction: Electric current is passed through molten NaCl. Sodium is formed at cathode and chlorine gas is liberated at anode.

Question: (a) How can the metals at the top of the reactivity series be extracted from their ores?
Explain with an example.
(b) Name any one alloy made from
(i) a metal and a non-metal, and
(ii) two metals.
Answer. (a) These metals are extracted by electrolytic reduction, e.g. aluminium is obtained from bauxite by electrolytic reduction.
(b) (i) Steel is made up of iron and carbon.
(ii) Brass is made up of copper and zinc.
Question: With the help of a suitable example, explain how ionic compounds are formed. State any three general properties of ionic compounds.
Answer. Ionic compounds are formed by transfer of electrons from metal to non-metals, e.g.

General Properties:
(i) They are the solids having high melting point.
(ii) They are soluble in water.
(iii) They conduct electricity in molten state as well as in aqueous solution.
Question: No reaction takes place when granules of a solid ‘A’ are mixed with a powder of solid ‘B\ However when the mixture is heated, a reaction starts with evolution of much heat. Product ‘C’ of the reaction settles down as a liquid metal and solid product ‘D’ keeps floating over the liquid ‘C\ This reaction is sometimes used for making metals for ready use in odd places.
(i) Based on this information, make assumptions about ‘A’ and ‘B’ and corresponding deductions about ‘C’ and ‘D’ and write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
Include in the chemical equation about physical states of the reactants and products, need of heating for starting the reaction and the reaction being exothermic.
(ii) Name two types of chemical reactions to which this reaction can belong.
Answer. (i) ‘A’ is aluminum, ‘B’ is ferric oxide [Iron(III) oxide],
(ii) This reaction is displacement reaction because AT is displacing ‘Fe’. It is also a redox reaction because AT is reducing agent and Fe2O3is oxidising agent.
Question: (a) The reaction of metal (X) with ferric oxide is highly exothermic. Metal
(X) is obtained from its oxides by electrolytic reduction. Identify (X) and write its reaction with ferric oxide.
(b) Give reason to justify that aluminium oxide is an amphoteric oxide. Also, give another example of amphoteric oxide.
(c) Mention constituent metals present in bronze.
Answer. (a) ‘X’ is ‘Al’

Question: (a) Distinguish between ionic and covalent compounds under the following properties:
(i) Strength of forces between constituent elements.
(ii) Solubility of compounds in water.
(iii) Electrical conduction in substances.
(b) Explain how the following metals are obtained from their compounds by the reduction process:
(i) Metal M which is in the middle of the reactivity series.
(ii) Metal N which is high up in the reactivity series.
Give one example of each type.
Answer.

(b) (i) Metal M which is in the middle of the reactivity series is reduced by aluminium, e.g.
3MnO2(s) + 4Al(s) ——–> 2Al2O3(s) + 3Mn(l)
(ii) Metal N will be obtained by electrolytic reduction, e.g. A1 is obtained by electrolytic reduction.

