Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Set B
Please see below Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Set B with solutions. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Sample Papers with solutions designed by Chemistry teachers for Class 12 based on the latest examination pattern issued by CBSE. We have provided the following sample paper for Class 12 Chemistry with answers. You will be able to understand the type of questions which can come in the upcoming exams.
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry Set B
Topic-1
Principles and Methods of Extraction
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. Zone refining is based on the principle that
(a) impurities of low boiling metals can be separated by distillation.
(b) impurities are more soluble in molten metal than in solid metal.
(c) different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent.
(d) vapours of volatile compound can be decomposed in pure metal.
Answer
B
Question. Electrolytic refining is used to purify which of the following metals?
(a) Cu and Zn
(b) Ge and Si
(c) Zr and Ti
(d) Zn and Hg
Answer
A
Question. Number of elements are available in the Earth’s crust but most abundant elements are :
(a) Al and Fe.
(b) Al and Cu.
(c) Fe and Cu.
(d) Cu and Ag.
Answer
A
Question. Brine electrolysed by using inert electrodes. The reaction at anode is :

Answer
A
Question. Which of the following reactions is an example of auto-reduction?
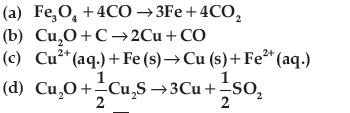
Answer
D
B. Match the following :
Question. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct code :
Column I Column II
(A) Coloured bands (1) Zone refining
(B) Impure metal to (2) Fractional distillation
volatile complex
(C) Purification of (3) Mond Process
Ge and Si
(D) Purification of mercury (4) Chromatography
(5) Liquation
Code :
(a) A (1) B (2) C (4) D (5)
(b) A (4) B (3) C (1) D (2)
(c) A (3) B (4) C (2) D (1)
(d) A (5) B (4) C (3) D (2)
Answer
B
C. Answer the following:
Question. Write the chemical reaction which takes place in Mond’s process for refining of nickel.
Answer.
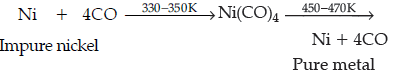
Question. Name the method used for refining of copper metal.
Answer. Electrolytic refining.
Question. What is the role of collectors in froth floatation process ?
Answer. Collectors such as pine oils, fatty acids, xanthates etc, enhance non-wettability of ore particles. They stick to the surface of mineral particles and allow them to float.
Question. Name the method used for the vapour phase refining of impure titanium and nickel metals.
Answer. Van Arkel method for refining impure titanium.
Mond’s process for refining impure nickel.
Question. What is the role of graphite in the electrometallurgy of aluminium ?
Answer. Graphite acts as an anode in the electrometallurgy of Aluminium.
Question. Name the method that is used for refining of nickel.
Answer. Mond process.
Question. State the principle of the method of zone refining of metals.
Answer. Zone refining is based on the principle that the impurities are more soluble in (the melt) than in the solid state of the metal.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain the principle of the method of electrolytic refining of metals. Give one example.
Answer. In this method, the impure metal is made to act as anode. A strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode. They are put in a suitable electrolytic bath containing soluble salt of the same metal. Pure metal gets deposited at the cathode and impurities remain in the solution.
For Example : Electrorefining of Cu, Ag, Au.
Question. How do we separate two sulphide ores by froth flotation method? Explain with an example.
Answer. The separation of two sulphide ores can be done by adjusting the proportions of oil to water or can be also done by using depressants. In the case of an ore containing ZnS and PbS, the depressant used is NaCN. It forms complex with ZnS and prevents it from coming with froth but PbS remains with froth.
Question. Outline the principles behind the refining of metals by the following methods :
(i) Zone refining method
(ii) Chromatographic method
Answer. (i) Impurities are more soluble in molten state than in solid state of the metal.
(ii) Different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent.
Question. Write the principle behind the froth flotation process. What is the role of collectors in this process ?
Answer. This method is based upon the preferential wetting of mineral / ore particles by oil and gangue by water.
Collectors enhance non-wettability of the mineral / ore particles to float.
Question. Write the principle behind the following methods of refining :
(i) Hydraulic washing
(ii) Vapour phase refining
Answer. (i) Hydraulic washing : This is based on the differences in gravities of the ore and the gangue particles.
(ii) Vapour phase refining : In this method, the metal forms a volatile compound which on further heating at higher temperature decomposes to pure metal.
Question. Give reasons for the following :
(i) Alumina is dissolved in cryolite for electrolysis instead of being electrolysed directly.
(ii) Zinc oxide can be reduced to metal by heating with carbon but Cr2O3 cannot be reduced by heating with carbon.
Answer. (i) Cryolite performs two functions in the electrolysis of alumina.
(a) It lowers the melting point of the mixture to about 1250 K.
(b) It improves the electrical conductivity of the metal.
(ii) The choice of a reducing agent in a particular case depends on thermodynamic factor. For a reaction to be feasible, the reaction of metal oxide with the reducing agent should have negative ΔG°.
Therefore, that reducing agent is suitable for which
ΔG° for the reduction is negative. Thus,
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
ΔrG° = – ve (Feasible)
Cr2O3 + 3C → 2Cr + 3CO
ΔrG° = +ve (Not feasible)
Question. What should be the considerations during the extraction of metals by electrochemical method?
Answer. The following factors should be kept in mind to ensure proper precautions :
(i) Reactivity of the metal.
(ii Suitability of the electrode.
Question. Describe the role of the following :
(i) SiO2 in the extraction of copper from copper matte.
(ii) NaCN in froth flotation process.
Answer. (i) It acts as flux to remove iron oxide as silicate
(slag). FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3 (Slag).
(ii) NaCN acts as the depressant. It selectively depress the flotation property of ZnS particles and hence PbS particles go into froth when air is blown in.
Question. Give two requirements for vapour phase refining.
Answer. The two requirements for vapour phase refining are given below :
(a) The metal should form a volatile compound with available reagent.
(b) The volatile compound should be unstable and easily decomposable so that the recovery is easy.
Question. Explain the role of the following :
(i) Iodine in the refining of titanium.
(ii) NaCN in the extraction of silver from silver ore.
Answer. (i) Iodine in the refining of titanium :
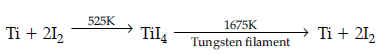
(ii) NaCN is used to convert silver into cyanide complex.

Question. Write the principles of the following methods :
(i) Froth flotation method
(ii) Electrolytic refining
Answer. (i) Froth flotation method : This is based upon the preferential wetting of mineral/ore particles by oil while the gangue particles by water.
(ii) Electrolytic refining : Electrolytic refining is based on the principle of deposition of pure metal on cathode.
Question. What criterion is followed for the selection of the stationary phase in chromatography?
Answer. The stationary phase is selected in such a way that the components of the sample have different solubility in the phase. Hence, different components have different rates of movement through the stationary phase and as a result, can be separated from each other.
Question. Giving examples, differentiate between calcination and roasting.
Answer. Calcination : Calcination involves heating of the concentrated ore in absence of air to remove water or CO2 from hydrated oxides or carbonates respectively below its melting point. Whereas roasting is carried out by heating the ore strongly in the presence of excess of air. It oxidises the impurities of P, As, S, etc, and converts sulphide ores into metal oxides.
Example for calcination :
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Limestone
MgCO3 → MgO + CO2
Magnesite
CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 → 2CuO + H2O + CO2
Malachite
Examples for roasting :
S + O2 → SO2 ↑
4As+3O2 → 2As2O3 ↑
P4 + 5O2 → 2P2O5 ↑
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. (i) Write the principle of electrolytic refining.
(ii) Why does copper obtained in the extraction from copper pyrites have a blistered appearance?
(iii) What is the role of depressants in the froth flotation process?
Answer. (i) On passing current through the electrolytic cell, the pure metal gets deposited on the cathode.
(ii) Evolution of SO2 gas
(iii) It selectively prevents one of the sulphide ores from coming to the froth.
Question. (i) Write the principle involved in the following:
(a) Zone refining of metals
(b) Electrolytic refining
(ii) Name the metal refining by each of the following processes:
(a) Mond Process
(b) van Arkel Method
Answer.
(b) The more basic/reactive ones go the anode mud.
(ii) (a) Ni (b) Ti/Zr
Question. (i) What is the principle behind ‘Zone refining’ of metal ? Name an element which is refined by this method.
(ii) Write the name of the metal refined by each of the following processes:
(a) Distillation
(b) Liquation
Answer. (i) Impurities are more soluble in the molten state than in the solid state of the metal.
Example: Ge/Si/ B (any other)
(ii) (a) Zn/Hg
(b) Sn
Question. (i) Write the principle of vapour phase refining.
(ii) What is the role of depressant in froth flotation process?
(iii) Write the name of reducing agent to obtain iron from Fe2O3 at high temperature.
Answer.(i) Metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere. It is then decomposed at high temperature to give pure metal.
(ii) It selectively prevents one of the sulphide ores from coming to the froth.
(iii) Coke.
Question. Write the principle of the following :
(i) Zone refining
(ii) Froth floatation process
(iii) Chromatography
Answer. (i) Zone refining –Impurities are more soluble in the molten state than in the solid state of metal.
(ii) Mineral particles are wetted by oils forming froth while gangue particles are wetted by water and settle down.
(iii) Different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent.
Question. (i) Write the principle of vapour phase refining .
(ii) Write the role of dilute NaCN in the extraction of silver.
(iii) What is the role of collectors in the froth flotation process? Give an example of a collector.
Answer.(i) Metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere. It is then decomposed at high temperature to give pure metal.
(ii) It acts as a leaching agent/forms soluble complex with Ag.
(iii) Enhance non-wettability of mineral particles. For e.g. Pine oil, Fatty acids, xanthates (Any one).
Question. Write the chemical reactions involved in the process of extraction of Gold. Explain the role of dilute NaCN and Zn in the process.
Answer. 4Au(s) + 8CN–(aq) 2H2O(aq) + O2(g) → 4[Au(CN)2]–(aq) + 4OH–(aq)
2[Au(CN)2]–(aq) + Zn(s) → 2Au(s) +[Zn(CN)4]2–(aq)
(No marks will be deducted for not balancing)
NaCN leaches gold/NaCN acts as a leaching agent/ complexing agent Zn acts as reducing agent / Zn displaces gold.
Question. (i) Name the method of refining of metals such as Germanium.
(ii) In the extraction of Al, impure Al2O3 is dissolved in conc. NaOH to form sodium aluminate and leaving impurities behind. What is the name of this process?
(iii) What is the role of coke in the extraction of iron from its oxides?
Answer. (i) Zone refining.
(ii) Leaching / Bayer’s process.
(iii) Coke act as a reducing agent resulting in formation of CO.
Question. (i) Write the name of the method used for the refining of the following metals:
(a) Titanium
(b) Germanium
(c) Copper
(ii) Write the name of the method of concentration applied for the following ores:
(a) Zinc blende
(b) Haematite
(c) Bauxite
Answer. (i) (a) Vapour phase refining /van Arkel method ½
(b) Zone refining
(c) Electrolytic refining
(ii) (a) Froth floatation process
(b) Magnetic separation
(c) Leaching
Question. (i) Name the method of refining of nickel.
(ii) What is the role of cryolite in the extraction of aluminium ?
(iii) What is the role of limestone in the extraction of iron from its oxides ?
Answer. (i) Mond’s process.
(ii) Cryolite acts as a solvent. The melting point of alumina is very high. It is dissolved in cryolite which lowers the melting point and brings conductivity.
(iii) Limestone is decomposed to CaO, which removes the silica impurity of the ore as slag.
Question. Write the principle of the following methods:
(i) Vapour Phase refining
(ii) Zone refining
(iii) Chromatography
Answer. (i) Metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere. It is then decomposed at high temperature to give pure metal.
(ii) The impurities are more soluble in the molten state than in the solid state of metal.
(iii) Different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent.
Question. What chemical principle is involved in choosing a reducing agent for getting the metal from its oxide ore ? Consider the metal oxides, Al2O3 and FeO and justify the choice of reducing agent in each case.

OR
Account for the following facts :
(i) The reduction of a metal oxide is easier if the metal formed is in the liquid state at the temperature of reduction.
(ii) Limestone is used in the manufacture of pig iron from haematite.
(iii) Pine oil is used in the froth flotation process used to concentrate sulphide ores.
Answer. The feasibility of thermal reduction can be predicted on the basis of Ellingham diagram. Metals for which the standard free energy of formation (Δf G°) is more negative can reduce those metals for which Δf G° is less negative. At a given temperature, any metal will reduce the oxide of other metals which lie above it in the Ellingham diagram.
(i) Below the temperature approx. 1623 K,corresponding to the point of intersection of Al2O3 and MgO curves, Mg can reduce alumina.
(ii) At temperatures below 1073 K, the CO, CO2 line lies below Fe, FeO line, thus CO is a better reducing agent.
At temperatures above 1073 K, coke will reduce FeO and itself get oxidised to CO.
OR
(i) Entropy is higher when a metal is in the liquid state than when it is in the solid state. Thus TΔS increases, thus ΔG° becomes more negative and the reduction becomes easier. (ΔG = ΔH – TΔS)
(ii) Limestone provides the flux (CaO) which combines with the impurities (SiO2) to form slag (CaSiO3).
Thus it helps in the removal of impurities.
(iii) Pine oil (collector) enhances the non-wettability of the ore particles, which becomes lighter and hence rise to the surface along with the froth.
Question. (i) Write the principle involved in the ‘vapour phase refining’ of metals.
(ii) Write the name of the metal refined by each of the following processes:
(a) Mond process
(b) van Arkel method
(iii) What is the role of depressant in froth flotation process?
Answer. (i) Metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere. It is then decomposed at high temperature to give pure metal.
(ii) (a) Ni (b) Ti/Zr
(iii) It is used to separate two sulphide ores by preventing one to form froth.
Question. (i) Indicate the principle behind the method used for the refining of zinc.
(ii) What is the role of silica in the extraction of copper ?
(iii) Which form of the iron is the purest form of commercial iron ?
Answer. (i) Zinc is refined by electrolytic refining.
(a) This method is based upon the phenomenon of electrolysis.
(b) The crude metal is made anode whereas a thin sheet of pure metal is made cathode.
(c) Electrolyte is the solution of some salt of metal.
(ii) In the extraction of copper, silica (SiO2) acts as ‘flux’.It reacts with FeO and removes it as slag (FeSiO3).
FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3
(Flux) Slag
(iii) Wrought iron is the purest form of iron.
Question. (i) Write the principle of Zone refining .
(ii) What is the role of collectors in froth flotation process? Give an example of a collector.
(iii) Write the name of a reducing agent to obtain Fe from Fe2O3 at low temperature.
Answer.
(ii) Collectors enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles Ex. Pine oil /fatty acids.
(iii) Carbon monoxide (CO).
Question. Describe how the following steps can be carried out?
(a) Recovery of Gold from leached gold metal complex.
(b) Conversion of Zirconium iodide to pure Zirconium.
(c) Formation of slag in the extraction of copper.
(Write the chemical equations also for the reactions involved)
OR
Explain the use of the following:
(a) NaCN in Froth Floatation Method.
(b) Carbon monoxide in Mond process.
(c) Coke in the extraction of Zinc from Zinc Oxide
Answer. (a) Leached gold complex is treated with Zinc and gold is recovered by displacement method
2Au[(CN)2]–(aq) + Zn(s) → 2Au(s) +[Zn(CN)4]2–(aq)
b) Zirconium iodide is decomposed on a tungsten filament; electrically heated to 1800 K. Pure Zr metal is deposited on the filament.
ZrI4 → Zr + I2
(c) Silica is added to the ore and heated. It helps to slag off iron oxide as iron silicate
FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3 (slag)
OR
(a) NaCN is used as depressant to separate two sulphide ores ( ZnS and PbS) in Froth Floatation Method.
(b) Carbon monoxide forms a volatile complex of nickel, nickel tetracarbonyl.
(c) Coke is used as a reducing agent to reduce zinc oxide to zinc.
Long Answer Type Questions-II
Question. Explain the following :
(a) CO2 is a better reducing agent below 710 K whereas CO is a better reducing agent above 710 K.
(b) Generally, sulphide ores are converted into oxides before reduction.
(c) Silica is added to the sulphide ore of copper in the reverberatory furnace.
(d) Carbon and hydrogen are not used as reducing agents at high temperatures.
(e) Vapour phase refining method is used for the purification of Ti.
Answer. (a) Ellingham diagram which relates Gibbs free energy and temperature at below 710K.
ΔG(C, CO2 ) < ΔG(C, CO) . Thus, CO2 is a better reducing agent than CO while above 710K, CO becomes a very good reducing agent.
(b) Sulphide ores cannot be reduced easily but oxide ores can be easily reduced. So, sulphide ores are generally converted into oxides before reduction.
(c) Copper pyrites contain iron sulphide in addition to copper sulphide. In the reverberatory furnace, copper ore is roasted to give oxides. FeO is removed by adding silica from the matte containing Cu2S and FeS.
2FeS+ 3O2 → 2FeO + 2SO2
FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3
(Slag)
(d) At the high temperature carbon and hydrogen react with metals to form carbides and hydrides respectively. Hence, they are not used as reducing agents.
(e) Ti reacts with iodine to form TiI4 which is volatile and decomposes to give Ti at high temperature to give extra pure titanium.

Topic-2
Principles of Extraction of Aluminium, Copper, Zinc and Iron
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions (1 mark each)
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. In the extraction of copper from its sulphide ore, the metal is formed by the reduction of Cu2O with :
(a) FeS.
(b) CO.
(c) Cu2S.
(d) SO2.
Answer
C
Question. For the reduction of FeO at the temperature corresponding to point D, which of the following statements is correct?
(a) ΔG value for the overall reduction reaction with carbon monoxide is zero.
(b) ΔG value for the overall reduction reaction with a mixture of 1 mol carbon and 1 mol oxygen is positive.
(c) ΔG value for the overall reduction reaction with a mixture of 2 mol carbon and 1 mol oxygen will be positive.
(d) ΔG value for the overall reduction reaction with carbon monoxide is negative.
Answer
A
Question. Choose the correct option of temperature at which carbon reduces FeO to iron and produces CO.
(a) Below temperature at point A.
(b) Approximately at the temperature corresponding to point A.
(c) Above temperature at point A but below temperature at point D.
(d) Above temperature at point A.
Answer
D
Question. When copper ore is mixed with silica, in a reverberatory furnace copper matte is produced.
The copper matte contains _____________.
(a) sulphides of copper (II) and iron (II).
(b) sulphides of copper (II) and iron (III).
(c) sulphides of copper (I) and iron (II).
(d) sulphides of copper (I) and iron (III).
Answer
C
Question. Below point ‘A’ FeO can ______________.
(a) be reduced by carbon monoxide only.
(b) be reduced by both carbon monoxide and carbon.
(c) be reduced by carbon only.
(d) not be reduced by both carbon and carbon monoxide.
Answer
A
B. Match the following :
Question. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct code :
Column I Column II
(A) Sapphire (1) Al2O3
(B) Sphalerite (2) NaCN
(C) Depressant (3) Co
(D) Corundum (4) ZnS
(5) Fe2O3
Code :
(a) A (3) B (4) C (2) D (1)
(b) A (5) B (4) C (3) D (2)
(c) A (2) B (3) C (4) D (5)
(d) A (1) B (2) C (3) D (4)
Answer
A
C. Answer the following:
Question. What is the role of zinc metal in the extraction of silver ?
Answer. Zn acts as reducing agent.
Question. Which reducing agent is employed to get copper from the leached low grade copper ore ?
Answer. Hydrogen/Iron.
Short Answer Type Question
Question. The mixture of compounds A and B is passed through a column of Al2O3 by using alcohol as eluant. Compound A is eluted in preference to compound B. Which of the compounds A or B, is more readily adsorbed on the column?
Answer. The mixture of compounds A and B is passed through a column of Al2O3 by using alcohol as eluant. Compound A is eluted in preference to compound B since compound A is eluted in preference to compound B. Compound B is more readily adsorbed on the column.
Question. Name the principle ore of aluminium. Explain the significance of leaching in the extraction of aluminium.
Answer. Bauxite is the main ore of aluminium. It is concentrated by leaching.
Bauxite ore is treated with caustic soda at 473-523 K and 35-36 bar pressure. Al2O3 dissolves in concentrated solution leaving behind impurities.
Al2O3 + 2NaOH + 3H2O → 2Na[Al(OH)4](aq)
The aluminate in solution is neutralised by passing CO2 gas and hydrated Al2O3 is precipitated.
2Na [Al(OH)4](aq) + CO2(g) → Al2O3. xH2O(s) + 2NaHCO3(aq)
The sodium silicate remains in the solution and hydrated alumina is filtered, dried and heated to get back pure Al2O3.

Question. Wrought iron is the purest form of iron. Write a reaction used for the preparation of wrought iron from cast iron. How can the impurities of sulphur, silicon and phosphorus be removed from cast iron?
Answer. The required reaction is given below:
Fe2O3 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO
Limestone is added as flux and the impurities of sulphur, silicon and phosphorus change to their oxides and pass into slag.
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. Answer the following :
(i) What is the role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium ?
(ii) Differentiate between roasting and calcination.
(iii) What is meant by the term ‘chromatography’ ?
OR
Write the reactions taking place in different zones of the blast furnace to obtain Iron.
Answer. (i) It lowers the melting point of alumina / acts as a solvent.

(iii) It is a process of separation of different components of a mixture which are differently adsorbed on a suitable adsorbent.

Cast iron has lower carbon content (about 3%) than pig iron / cast iron is hard & brittle whereas pig iron is soft.
Question. Write the role of
(i) NaCN in the extraction of gold from its ore.
(ii) Cryolite in the extraction of aluminium from pure alumina.
(iii) CO in the purification of Nickel.
OR
Describe the role of
(i) NaCN in the extraction of gold from its ore.
(ii) Cryolite in the extraction of aluminium from pure alumina.
(iii) CO in the purification of Nickel.
Answer. (a) Gold is leached out in the form of a complex with dil. solution of NaCN in the presence of air/NaCN acts as leaching agent.
(b) It lowers the melting point of alumina and makes it a good conductor of electricity.
(c) CO forms a volatile complex with nickel which is further decomposed to give pure Ni metal.
Question. Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods :
(i) Distillation
(ii) Zone refining
(iii) Electrolysis
OR
Write down the reactions taking place in different zones in the blast furnace during the extraction of iron. How is pig iron different from cast iron ?
Answer. (i) The impurities are evaporated from volatile metals to obtain the pure metal as distillate.
(ii) This method is based on the principle that the impurities are more soluble in the molten state than in the solid state of the metal.
(iii) The impure metal is made to act as anode. A strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode. They are put in a suitable electrolytic bath containing soluble salt of the same metal.
The more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
OR

Cast iron has lower carbon content (about 3%) than pig iron / cast iron is hard & brittle whereas pig iron is soft.
Question. (i) Indicate the principle behind the method used for the refining of zinc.
(ii) What is the role of silica in the extraction of copper ?
(iii) Which form of the iron is the purest form of commercial iron ?
Answer. (i) Zinc is refined by electrolytic refining. In the method, the impure metal acts as anode. A strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode. These are put in suitable electrolytic bath containing soluble salt of the same metal. The more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
(ii) Roasting of copper pyrite (CuFeS2) gives FeO, Cu2O and SO2.
4CuFeS2(s) + 11O2(g) → 4FeO(s) + 2Cu2O(s) + 8SO2(g)
To remove FeO, SiO2 acts as flux and is added to form slag.
FeO(s) + SiO2(s) → FeSiO3(l)
(slag)
(iii) Wrought iron.
Question. (i) Write the principle of method used for the refining of germanium.
(ii) Out of PbS and PbCO3 (ores of lead), which one is concentrated by froth flotation process preferably?
(iii) What is the significance of leaching in the extraction of aluminium ?
Answer. (i) Zone refining : The impurities are more soluble in the molten state (melt) than in the solid state of the metal.
(ii) PbS
(iii) Impurities like SiO2 etc, are removed by using NaOH solution and pure alumina is obtained.
