Class 12 HOTs Biology Human Reproduction
Question. How many compartments (approximately) are there in each human testis?
(a) 250
(b) 300
(c) 350
(d) 400
Answer
A
Question. Compartments in mammalian testes are called
(a) testicular lobules
(b) seminiferous tubules
(c) Sertoli cells
(d) interstitial cells
Answer
A
Question. Testicular lobules contain
(a) 3-5 seminiferous tubules
(b) 2-6 seminiferous tubules
(c) 5-7 seminiferous tubules
(d) 1-3 seminiferous tubules
Answer
D
Question. The seminiferous tubules of the testis is lined on its inside by
(a) spermatocytes
(b) spermatogonia
(c) cells of Sertoli
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. ……… provide nutrition to the male germ cells.
(a) Interstitial cells
(b) Leydig cells
(c) Sertoli cells
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
C
Question. Pick the odd one out from each series given below and select the correct option.
I. Scrotum, rete testis, Fallopian tube, vas deferens.
II. Ovary, uterus, vagina, ejaculatory duct.
III. Acrosome, Graafian follicle, corpus luteum, cervix.
IV. Prostate, testis, seminal vesicles, Cowper’s gland.
I II III IV
(a) Vas deferens Vagina Cervix Cowper’s gland
(b) Rete testis Ovary Graafian Prostate follicle
(c) Scrotum Uterus Corpus Seminal luteum vesicles
(d) Fallopian Ejaculatory Acrosome Testis tube duct
Answer
D
Question. A sectional view of mammary gland shows
I. nipple and areola.
II. mammarylobes (alveolus) and duct.
III. ribs.
IV. ampulla and lactiferous duct.
Choose the correct option from the above.
(a) I, II, III and IV
(b) I, II and III
(c) III, IV and II
(d) I, IV and III
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following cells present in the mammalian testes forms the sperms?
(a) Leydig cells
(b) Spermatogonia
(c) Interstitial cells
(d) Sertoli cells
Answer
B
Question. Region outside the seminiferous tubules is called
(a) interdigital space
(b) interferous space
(c) interstitial space
(d) blind space
Answer
C
Question. The seminiferous tubules of the testis open into the vasa efferentia by
(a) vasa deferentia
(b) rete testis
(c) epididymis
(d) seminiferous tubules
Answer
B
Question. Select the correct sequence for transport of sperm cells in male reproductive system.
(a) Seminiferous tubules® Rete testis® Vasa efferentia ® Epididymis® Vas deferens® Ejaculatory duct® Urethra® Urethral meatus
(b) Seminiferous tubules® Vasa efferentia® Epididymis ® Inguinal canal® Urethra
(c) Testis® Epididymis® Vasa efferentia® Vas deferens® Ejaculatory duct® Inguinal canal® Urethra® Urethral meatus
(d) Testis® Epididymis® Vasa efferentia® Rete testis ® Inguinal canal® Urethra
Answer
A
Question. Choose the incorrect pair.
(a) Leydig cells — Secrete testicular hormone
(b) Vasa efferentia and epididymis — Accessory ducts
(c) Vas deferens — Loops over the urinary bladder
(d) Ejaculatory duct — Vasa efferentia and seminal vesicle
Answer
D
Question. Choose the correct option.
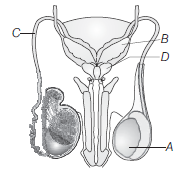
(a) A– Testis–possesses 3-4 testicular lobule
(b) B– Seminal vesicle–storage of sperm
(c) C– Vas deferens–helps in sperm transfer
(d) D– Prostate gland–secretes seminal fluid
Answer
C
Question. The shared terminal duct of the reproductive and urinary system in the human male is
(a) urethra
(b) ureter
(c) vas deferens
(d) vasa efferentia
Answer
A
Question. Identify A, B, C and D in the given diagram
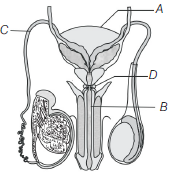
(a) A–Urinary bladder, B–Bulbourethral gland, C–Prostate gland, D–Seminal vesicles
(b) A–Urinary bladder, B–Urethra, C–Vas deferens, D–Bulbourethral gland
(c) A–Prostate gland, B–Seminal vesicles, C–Urinary bladder, D–Bulbourethral gland
(d) A–Bulbourethral gland, B–Urinary bladder, C–Seminal vesicles, D–Prostate gland
Answer
B
Question. Identify the accessory glands found in males.
(a) Seminal vesicles
(b) Prostate gland
(c) Bulbourethral gland
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. The given diagram refers to TS of testis showing sectional view of a few seminiferous tubules. Identify the parts labelled A-D and select the correct option.
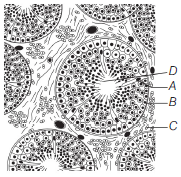
(a) A–Sertoli cells, B–Spermatozoa, C–Interstitial cells, D–Sperms
(b) A–Sertoli cells, B–Secondary spermatocyte, C–Interstitial cells, D–Spermatozoa
(c) A–Interstitial cells, B–Spermatogonia, C–Sertoli cells, D–Sperms
(d) A–Sertoli cells, B–Spermatogonia, C–Interstitial cells, D–Spermatozoa
Answer
D
Question. The given digaram shows LS of testis showing various parts. Identify the parts labelled (A-G) from the list given below.
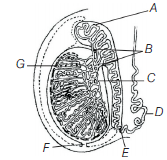
I. Caput epididymis
II. Cauda epididymis
III. Vas deferens
IV. Vasa efferentia
V. Corpus epididymis
VI. Seminiferous tubules
VII. Tunica vaginalis
VIII. Tunica albuginea
IX. Tunica vasculosa
X. Rete testis

Answer
C
Question. The ovaries are located one on each side of the…A….
Each ovary is about 2-4 cm in length connected to the …B… wall by …C… . Each ovary is covered by a thin epithelium which encloses the ovarian stroma.
Stroma is divided into two zones …D… and …E… .
Fill the suitable choices for A-E.
(a) A–inner medulla, B–peripheral cortex, C–ligaments, D–pelvic wall, E-lower abdomen
(b) A–lower abdomen B–pelvic, C–ligaments, D–peripheral cortex, E–inner medulla
(c) A–pelvic wall, B–lower abdomen, C–ligaments, D–inner medulla, E–peripheral cortex
(d) A–inner medulla, B–peripheral cortex, C–lower abdomen, D–pelvic wall, E–ligaments
Answer
B
Question. The following diagram refers to female reproductive system of human. Identify A to E.
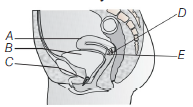
(a) A–Urethra, B–Urinary bladder, C–Uterus, D–Cervix, E–Vagina
(b) A–Urethra, B–Urinary bladder, C–Uterus, D–Vagina, E–Cervix
(c) A–Urethra, B–Urinary bladder, C–Uterus, D–Cervix, E–Vagina
(d) A–Uterus, B–Urinary bladder, C–Urethra, D–Cervix, E–Vagina
Answer
D
Question. Oviducts are also called
(a) Fallopian tubes
(b) uterus
(c) vagina
(d) ovary
Answer
A
Question. The main function of fimbriae of Fallopian tube is
(a) help in development of ovary
(b) help in collection of the ovum after ovulation
(c) help in development of ova
(d) help in fertilisation
Answer
B
Question. Choose the incorrect pair.
(a) Finger-like projections – Fimbriae
(b) Narrow part of oviduct – Ampulla
(c) Part of oviduct joining the uterus – Isthmus
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. The following diagram refers to the female reproductive system of humans. Identify A-F.
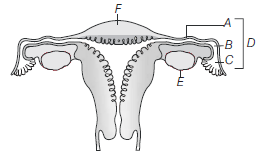
(a) A–Ampulla, B–Isthmus, C–Infundibulum, D–Fallopian tube, E–Ovary, F–Uterine fundus
(b) A–Isthmus, B–Infundibulum, C–Ampulla, D–Fallopian tube, E–Ovary, F–Uterine fundus
(c) A–Isthmus, B–Ampulla, C–Infundibulum, D–Fallopian tube, E–Ovary, F–Uterine fundus
(d) A–Ampulla, B–Infundibulum, C–Isthmus, D–Fallopian tube, E–Ovary, F–Uterine fundus
Answer
C
Question. Choose the incorrect pair.
(a) Cushion of fatty tissue covered by pubic hair –Mons pubis
(b) Membrane covering opening of vagina–Hymen
(c) Finger-like structure above the urethral opening –Clitoris
(d) Uterine layer exhibiting strong contraction during delivery–Endometrium
Answer
D
Question. The main tissue present in breast is ……… tissue.
(a) glandular
(b) squamous
(c) ciliated
(d) epithelium
Answer
A
Question. The reproductive cycle in the female primates such as monkeys, apes and human beings is called
(a) menstrual cycle
(b) oestrus cycle
(c) circadian cycle
(d) ovulatory cycle
Answer
A
Question. The first menstruation that begins at puberty is called
(a) menopause
(b) ovulation
(c) gametogenesis
(d) menarch
Answer
D
Question. Menstrual flow occurs due to the lack of
(a) progesterone
(b) FSH
(c) oxytocin
(d) vasopressin
Answer
A
Question. Given the diagrammatic sectional view of mammary gland. Identify A, B, C and D.
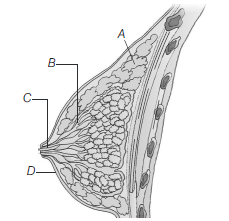
(a) A–Alveolus, B–Mammary duct, C–Lactiferous duct, D–Areola
(b) A–Alveolus, B–Lactiferous duct, C–Mammary duct, D–Areola
(c) A–Alveolus, B–Mammary duct, C–Lactiferous duct,D–Lactogenic spot
(d) A–Fat, B–Mammary duct, C–Lactiferous duct, D–Areola
Answer
D
Question. Several mammary ducts join to form a wider mammary ampulla, which is connected to
(a) lactiferous duct
(b) seminiferous duct
(c) seminiferous tubules
(d) nipple
Answer
A
Question. Number of chromosomes present in spermatogonium is
(a) 46
(b) 23
(c) 48
(d) 43
Answer
A
Question. Which cells come earliest in the sequence of sperm production?
(a) Spermatozoa
(b) Spermatocyte
(c) Spermatid
(d) Spermatogonia
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following undergoes meiosis-I division during spermatogenesis?
(a) Primary spermatocytes
(b) Secondary spermatocytes
(c) Sertoli cell
(d) Leydig cell
Answer
A
Question. Number of chromosomes present in secondary spermatocyte is JIPMER 2019
(a) 22
(b) 23
(c) 24
(d) 25
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following cells have haploid number of chromosome?
(a) Primary spermatocytes
(b) Secondary spermatocytes
(c) Spermatid
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. During spermatogenesis, which cells are the first to contain haploid number of chromosomes?
(a) Spermatogonium
(b) Primary spermatocyte
(c) Secondary spermatocyte
(d) Spermatid
Answer
C
Question. Find out spermatid and Sertoli cell in given below diagram.
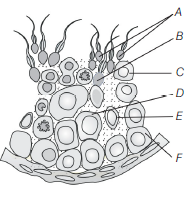
(a) D and E
(b) E and F
(c) A and C
(d) B and E
Answer
D
Question. Spermiogenesis is
(a) spermatids transformed into spermatozoa
(b) spermatozoa transformed into spermatids
(c) spermatozoa transformed to spermatocytes
(d) spermatid to secondary spermatocytes
Answer
A
Question. If the mammalian ovum fails to get fertilised, which one of the following is likely to happen?
(a) Corpus luteum will degenerate
(b) Oestrogen secretion further decreases
(c) Primary follicle starts developing
(d) Progesterone secretion rapidly increases
Answer
A
Question. Which of them is not a correct match?
(a) Proliferative phase–Rapid regeneration of myometrium and maturation of Graafian follicle
(b) Secretory phase–Development of corpus luteum and increased secretion of progesterone
(c) Menstruation–Breakdown of endometrium
(d) Ovulation–LH and FSH attain peak level and cause rupture of Graafian follicle
Answer
A
Question. Pouch in which testes are suspended outside the abdominal cavity, is
(a) tunica albuginea
(b) inguinal canal
(c) epididymis
(d) scrotum
Answer
D
Question. Function of scrotum is to maintain the
(a) temperature of testes
(b) body temperature
(c) level of growth hormone
(d) level of male hormone
Answer
A
Question. Approximate length and width of testis are
(a) 4-5 cm and 2-3 cm
(b) 5-6 cm and 3-4 cm
(c) 6-7 cm and 4-5 cm
(d) 7-8 cm and 8-9 cm
Answer
A
Question. Correct sequence of secretion of hormone from beginning of menstrual cycle to the end is
(a) FSH, progesterone, LH
(b) oestrogen, FSH and progesterone
(c) FSH, oestrogen, progesterone
(d) oestrogen, progesterone, FSH
Answer
C
Question. What is the correct sequence of sperm formation?
(a) Spermatid, Spermatocyte, Spermatogonia, Spermatozoa
(b) Spermatogonia, Spermatocyte, Spermatozoa, Spermatid
(c) Spermatogonia, Spermatozoa, Spermatocyte, Spermatid
(d) Spermatogonia, Spermatocyte, Spermatid, Spermatozoa
Answer
D
Question. The difference between spermiogenesis andsperm iation is
(a) in spermiogenesis, spermatozoa from Sertoli cells are released into the cavity of seminiferous tubules, while in spermiation, spermatozoa are formed
(b) in spermiogenesis, spermatozoa are formed, while in spermiation, spermatids are formed
(c) in spermiogenesis, spermatids are formed, while in spermiation, spermatozoa are formed
(d) in spermiogenesis, spermatozoa are formed, while in spermiation, spermatozoa are released through seminiferous tubules
Answer
D
Question. Spermatogenesis starts at puberty due to significant increase in the secretion of
(a) GnRH
(b) prolactin
(c) testosterone
(d) oestrogen
Answer
A
Question. GnRH, a hypothalamic hormone, needed in reproduction, acts on
(a) anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of LH and oxytocin
(b) anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of LH and FSH
(c) posterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of oxytocin and FSH
(d) posterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of LH and relaxin
Answer
B
Question. Give the name of two hormones A and B in the figure given below.
(a) FSH and GH
(b) LH and androgens
(c) GH and LH
(d) GH and lactin
Answer
B
Question. Choose the incorrect pair.
(a) Antrum – Fluid-filled cavity in primary follicle
(b) Tertiary follicle – Primary oocyte completes its Ist meiotic division inside it
(c) Secondary oocyte – Haploid cell formed after Ist meiotic division
(d) Graafian follicle – Mature tertiary follicle which ruptures during ovulation
Answer
A
Question. Human Fallopian tube is about
(a) 8-9 cm long
(b) 9-10 cm long
(c) 10-12 cm long
(d) 12-17 cm long
Answer
C
Question. Funnel-shaped part of oviduct closer to the ovary is called
(a) fimbriae
(b) infundibulum
(c) ampulla
(d) isthmus
Answer
B
Question. Fimbriae are associated with which organ?
(a) Fallopian tube
(b) Uterus JIPMER 2018
(c) Vagina
(d) Ovary
Answer
A
Question. The new membrane formed by follicular cells in secondary oocyte is called
(a) zona granulosa
(b) zona pellucida
(c) plasma membrane
(d) tertiary membrane
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following layers in an antral follicle is acellular?
(a) Granulosa
(b) Theca interna
(c) Stroma
(d) Zona pellucida
Answer
D
Question. At which stage of the development, ovum is released from the ovary of the human female?
(a) Primary oocyte
(b) Oogonium
(c) Secondary oocyte
(d) Ootid
Answer
C
Question. Consider the figure given below.
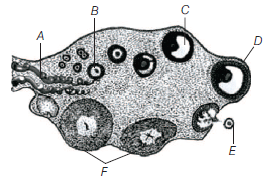
Select the option which correctly identifies the parts labelled as C, D and F.
Answer
D
Question. Identify A, B and C in the figure given below.
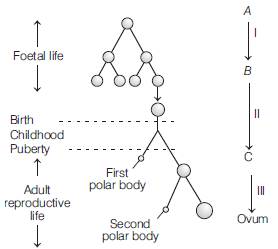
(a) A–Secondary oocyte, B–Oogonia, C–Primary oocyte
(b) A–Oogonia, B–Primary oocyte, C–Secondary oocyte
(c) A–Secondary oocyte, B–Primary oocyte, C–Oogonia
(d) A–Oogonia, B–Secondary oocyte, C–Primary oocyte
Answer
B
Question. Mark the wrong item in each series and select the correct option.
I. Spermatocyte, polar body, spermatid, spermatogonium
II. Endometrium, corpus luteum, acrosome, Graafian follicle
III. Vas deferens, Fallopian tube, epididymis, Cowper’s gland
IV. Testes, prostate, seminal vesicles, Cowper’s gland
I II III IV
(a) Spermatid Endometrium Epididymis Prostate
(b) Polar body Acrosome Fallopian tube Testes
(c) Spermatocyte Corpus luteum Vas deferens Cowper’s gland
(d) Spermatogonium Graafian follicle Cowper’s gland Seminal vesicles
Answer
B
Question. Level of LH is maximum
(a) just before ovulation
(b) just after ovulation
(c) at the time of ovulation
(d) during menstrual bleeding phase
Answer
C
Question. When does ovulation occur in a healthy menstruating female?
(a) 9-14 days
(b) 14-16 days
(c) 16-28 days
(d) 20-26 days
Answer
B
Question. Cleavage is the rapid mitotic division occurring on the way through isthmus to oviduct. It occurs in
(a) gametes
(b) zygote
(c) sperm
(d) ova
Answer
B
Question. Cleavage forms 2-4-8-16 cells. These cells are called
(a) blastocysts
(b) blastomeres
(c) morula
(d) trophoblast
Answer
B
