Class 12 VBQs Biology Organisms and Populations
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name the interaction that exists between cuscuta and shoe-flower plant.
Answer : Parasitism.
Question. Name the type of interaction that exists between barnacles and whale.
OR
Name the interaction between a whale and the barnacles growing on its back.
Answer : Commensalism.
Question. Name the type of interaction seen between fig and wasps.
Answer : Mutualism.
Question. State Gause’s competitive exclusion principle.
Answer : According to this principle, the two closely related species competing for the same but limited resources cannot co-exist continuously for a long time . Eventually the competitively inferior one will be eliminated.
Question. How are closely related species of warblers able to co-exist in a competitive environment ?
Answer : They can co–exist due to behavioural differences in their foraging activities.
Question. Pollinating species of wasps shows mutualism with specific fig plants. Mention the benefits the female wasps derive from the fig trees from such an interaction.
Answer : The female wasp uses the fruit not only as an oviposition (egg-laying) site but uses the developing seeds within the fruit for nourishing its larvae. The wasp pollinates the fig inflorescence while searching for suitable egg-laying sites. In return for the favour of pollination, the fig offers the wasp some of its developing seeds as food for the developing wasp larvae.
Question. In a pond there were 200 frogs. 40 more frogs were born in a year. Calculate the birth rate of the population.
Answer : Birth rate = 0.2 frogs/yr or 20%.
Short Answer Type Questions
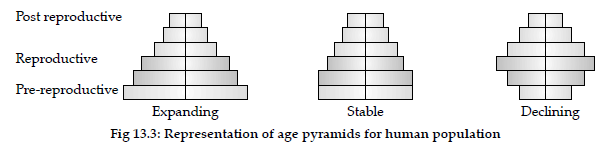
Question. Draw labelled diagrams of stable and declining age pyramids of human population.
Answer :
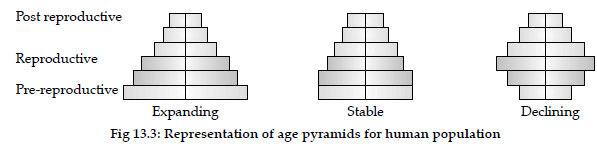
Question. Construct an age pyramid which reflects a stable growth status of human population.
Answer :
Question. Explain Verhulst – Pearl Logistic Growth of a population.
Answer : A population growing in a habitat with limited resources show initially a lag phase, followed by phases of acceleration and deceleration, finally an asymptote when the population density reaches the carrying capacity.
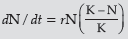
Question. Apart from being part of the food chain, predators play other important roles. Mention any two such roles supported by examples.
OR
Explain the role played by predators in a community.
Answer : (i) Predators act as conduits for energy transfer across trophic levels.
(ii) They keep prey population under control.
(iii) They help in maintaining species diversity in a community by reducing intensity of competition among competing prey species.
(iv) An efficient predator may cause extinction of prey species.
Question. Explain brood parasitism with the help of an example.
Answer : Koel is a parasitic bird (which has lost the instinct to make its own nest to lay eggs). It has evolved the technique of laying eggs in the nest of a crow.
Its eggs bear resemblances to those of crow.
Detailed Answer :
Brood parasitism is a condition where a bird lays eggs in the nests of other bird and let the other bird incubate them. A classical example of this can be seen in koel. Koel lays egg in the nest of crow and during the period of evolution, eggs of koel have begun to resemble with the eggs of crow in colour, shape and size.
Question. Koel is clever enough to lay eggs in a crow’s nest.
Write the reason for this peculiar behaviour. Name the type of interaction.
Answer : So that the crow can incubate the Koel’s eggs.
Interaction – Brood parasitism.
Question. Predation is usually referred to as a detrimental association. State any three positive roles that a predator plays in an ecosystem.
Answer : Positive roles that predator plays in an ecosystem:
(i) Predator acts as conduits for energy transfer across trophic levels.
(ii) Predators keep prey populations under control.
(iii) Predators also help in maintaining ecological balance species diversity in a community, by reducing the intensity of competition among competing prey species.
Question. Highlight the differences between the population interactions given below. Give an example of each.
(i) Parasitism
(ii) Amensalism
(iii) Mutualism
Answer : Parasitism : Only one species benefits e.g., Cuscuta / Tape worm
Amensalism : One species is harmed whereas the other is unaffected e.g., Penicillium growing on bacterial culture / Trichoderma – biological control agent and plant pathogen
Mutualism : Both species are benefitted E. g., lichens exhibit mutualistic relationship with fungus that absorbs water and nutrients from soil and photosynthesizing algae / cyanobacteria.
Question. Explain parasitism and co-evolution with the help of one example of each.
Answer : Mode of interaction between two species in which one species (parasite) depends on the other species (host) for food and shelter / one organism is benefitted, the other is harmed.
e.g. Human liver fluke / Malarial parasite / Cuscuta.
Co-evolution is the relationship between two interacting organisms where both organisms failed to survive in the absence of the other.
e.g. Fig and Fig wasp / Ophrys and bumble bee.
Detailed Answer:
Parasitism is an interaction between two species in which one species (parasite) derives benefit while the other species (host) is harmed. For example, ticks and lice (parasites) present on the human body represent this interaction where the parasites receive benefit (as they derive nourishment by feeding on the blood of humans). On the other hand, these parasites reduce host fitness and cause harm to the human body.
Co-evolution is an interaction between two living organism where both are equally benefitted and no one is harmed. For example, wasp pollinating fig inflorescence. The fig species is pollinated only by its ‘partner’ wasp species and no other species. The female wasp pollinates the fig inflorescence while searching for suitable egg-laying sites in fruits, whereas the fig offers the wasp some developing seeds as food for the wasp larvae.
Question. Study the graph given below and answer the question that follow :
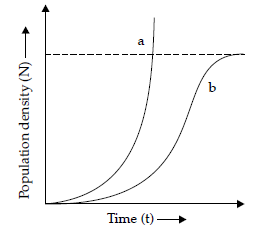
(i) Write the status of food and space in the curves (a) and (b).
(ii) In the absence of predators, which one of the two curves would appropriately depict the prey population ?
(iii) Time has been shown on X-axis and there is a parallel dotted line above it. Give the significance of this dotted line.
Answer : (i) a – Unlimited food and space.
b – Limited food and space.
(ii) Curve a.
(iii) Carrying capacity / a given habitat has enough resources to support maximum possible number – beyond which no further growth is possible.
Question. Name the type of interaction seen in each of the following examples :
(i) Ascaris worms living in the intestine of human
(ii) Wasp pollinating fig inflorescence
(iii) Clown fish living among the tentacles of seaanemone
(iv) Mycorrhizae living on the roots of higher plants
(v) Orchid growing on a branch of a mango tree
(vi) Disappearance of smaller barnacles when Balanus dominated in the coast of Scotland.
Answer : (i) Parasitism
(ii) Mutualism
(iii) Commensalism
(iv) Mutualism
(v) Commensalism
(vi) Competition
Question. Draw and explain a logistic curve for a population of density (N) at time (t) whose intrinsic rate of natural increase is (r) and carrying capacity is (K).
Answer : A population growing in a habitat with limited resources show initially a lag phase, this is followed by phases of acceleration and deceleration and finally an asymptote when the population density reaches carrying capacity (K). A plot of N in relation to time (t) result in a sigmoid curve (Verhulst – Pearl Logistic Growth).
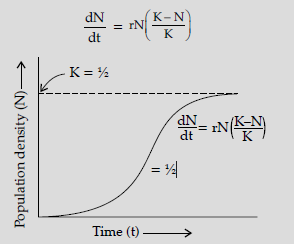
Question. Co-evolution is a spectacular example of mutualism between an animal and a plant. Describe coevolution with the help of an example.
Answer : Co-evolution is the mutual relationship between two interacting organisms where both the organisms are unable to survive in the absence of the other. The co-evolution of fig and wasp as a pollinator is highly linked with one another. Fig and wasp is a good example of mutualism and coevolution between a plant species and an animal species.
The female wasp uses the fruit and fig for oviposition / egg laying uses seeds within the fruit (developing seeds) for nourishing its larvae. In return the wasp pollinates the fig inflorescence. The given fig species can be pollinated only by its ‘partner’ wasp species and no other species.
Question. What is Predation ? Explain with the help of suitable examples why is it required in a community with rich biodiversity?
Answer : Organism of higher trophic level (predator) feeds on organism of lower trophic level (prey) is called the predation.
Importance of predation :
(i) It helps in transfer of energy from one trophic level to the next.
(ii) It keeps the prey population under control.
(iii) It helps in biological control, helps maintain species diversity.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (i) Represent diagrammatically three kinds of agepyramids for human populations.
(ii) How does an age pyramid for human population at given point of time helps the policy-makers in planning for future.
Answer : (i)
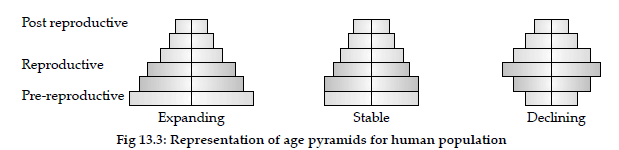
(ii) Planning of health / education / transport / infra-structure / finance / food / employment can depend on the age-pyramid analysis of a population / any other relevant point.
Detailed Answer :
(i) Same as above
(ii) Age pyramid for human population can help the policy makers to prepare future planning for–stress of family planning measures, help elderly people to live comfortably, planning more schools, technical institutes with digital facilities for education and more job opportunities for future.
Question. (i) What is population density ? Why are ecologists interested in measuring it ?
(ii) Write the different ways of measuring population density. Explain any two with the help of specific examples.
Answer : (i) The population density is the number of individuals of a population found per unit area at a given time.
Whatever ecological process we wish to investigate in a population (competition / pesticide applicable) we always evaluate in terms of any change in population size (numbers / biomass).
(ii) Number of organism
Biomass of organism
Example : Three ways of measuring population density of a habitat
(a) Per cent cover for trees with larger canopy.
(b) Number of fishes caught per trap.
(c) Pug marks or faecal pellets for tiger census.
Question. (i) List the different attributes that a population has and not an individual organism.
(ii) What is population density ? Explain any three different ways the population density can be measured, with the help of an example each.
Answer : (i) Following are the attributes that a population has but an individual organism does not have :
(a) Birth rate : Per capita births.
(b) Death rate : Per capita deaths.
(c) Sex ratio : Ratio of number of males to females in a population.
(ii) Population density : It means number of individuals present per unit area. Population density can be measured by determining the population size. The different methods to study population size are as follows :
(a) Quadrat method : It is a method that involves the use of square of particular dimensions to measure the number of organisms e.g. The number of parthenium plants in a given area can be measured using the quadrat method.
(b) Direct observation : It involves the counting of organisms in a given area e.g. In order to determine the number of bacteria growing in a petridish, their colonies are counted.
(c) Indirect method : In this method, there is no need to count the organisms individually e.g. number of fishes caught per trap gives the measure of their total density in a given water body.
Question. (i) Explain the equation.
Nt + 1 = Nt + [(B + I) – (D + E)]
on the basis of the flow chart given below :

(ii) Mention the different ways by which the population density of different species can be measured.
Answer : (i) In the given equation, N is the population density at time t and its density at time t + 1 is
Nt + 1 = Nt + [(B + I) – (D + E)]
The above equation shows that population density increases if the number of births plus the number of immigrants (B + I) is more than the number of deaths plus the number of emigrants (D + E), otherwise it will decrease.
Under normal conditions, births and deaths are the most important factors. The other two factors are important only under special conditions. For instance, if a new habitat is just being colonized, immigration may contribute more significantly to population growth than birth rates.
(ii) Population density of a species is the number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume e.g. number of animals per square kilometer, number of trees per hectare, number of phytoplanktons per cubic liter of water.
Population density (PD) can be calculated as P.D. = N/S
where, N = Number of individuals in a region.
S = Number of unit areas in a region or total unit land area of the region.
Population of an area is described on the basis of three parameters.
(a) Number and kind of individuals of a species.
(b) A given space or an area.
(c) Time.
Population density reflects the success of a species in a given area.
