Class 12 HOTs Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question. The terminal structure of stamen is called
(a) pollen
(b) filament
(c) anther
(d) All of these
Answer
C
Question. Cleistogamous flowers are strictly autogamous because they remain
(a) always open
(b) always close
(c) always fragrance
(d) are brighty coloured
Answer
C
Question. Identify A to F in the diagram given below.
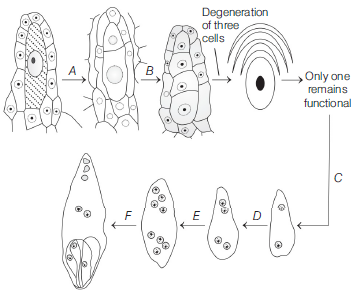
(a) A–Mitosis, B–Meiosis-I, C–Meiosis-II, D–Mitosis, E–Meiosis, F–Meiosis
(b) A–Meiosis-I, B– Meiosis-II, C–Mitosis, D–Mitosis, E–Mitosis, F–Embryo sac
(c) A–Embryo, B–Meiosis-I, C–Meiosis-II, D–Mitosis, E–Mitosis, F–Mitosis
(d) A–Mitosis, B–Mitosis, C–Mitosis, D–Meiosis, E–Meiosis, F–Meiosis
Answer
B
Question. In embryo sac, the number of synergid® egg cell® central cell® antipodal cell follows the order
(a) 1–1–2–3
(b) 2–1–3–2
(c) 2–1–1–3
(d) 3–2–1–2
Answer
C
Question. Two nuclei within a single cell is
(a) antipodal cell
(b) chalazal cell
(c) central cell
(d) synergid cell
Answer
C
Question. Egg apparatus consists of
(a) 2 synergids + 2 eggs
(b) 2 synergids + 2 eggs
(c) 2 synergids + 1 egg
(d) 2 synergids + 4 eggs
Answer
C
Question. In an embryo sac of anatropous ovule, cells present at chalazal end are called
(a) nucellar cells
(b) synergids
(c) antipodal cells
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. In an angiospermic anatropous ovule, the embryo sac contains certain cells at the micropylar end. These are called
(a) synergids
(b) antipodal cells
(c) nucellar cells
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Geitonogamy involves CBSE-AIPMT 2014, 10, 1994
(a) fertilisation of a flower by the pollen from another flower of the same plant
(b) fertilisation of a flower by the pollen from the same flower
(c) fertilisation of a flower by the pollen from a flower of another plant in the same population
(d) fertilisation of a flower by the pollen from a flower of another plant belonging to a distant population
Answer
A
Question. Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to stigma of another flower of different plant is called
(a) geitonogamy
(b) xenogamy
(c) chasmogamy
(d) cleistogamy
Answer
B
Question. The feathery long stigma is found in
(a) rice
(b) maize
(c) sugarcane
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Ovules contain many embryo in
(a) Citrus
(b) apple
(c) mango
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Occurrence of more than one embryo is called
(a) polyembryony
(b) embryony
(c) parthenogenesis
(d) fertilisation
Answer
A
Question. Flowers, which have single ovule in the ovary and are packed into inflorescence are usually pollinated by
(a) water
(b) bee
(c) wind
(d) bat
Answer
C
Question. What type of pollination takes place in Vallisneria?
(a) Pollination occurs in submerged condition by water
(b) Flowers emerge above surface of water and pollination occurs by insects
(c) Flowers emerge above water surface and pollen is carried by wind
(d) Male flowers are carried by water currents to female flowers at the surface of water
Answer
D
Question. Pollen grain of water pollinated plants are coated by covering to prevent it from wetting
(a) mucilage
(b) cuticle
(c) exine
(d) intine
Answer
A
Question. Continued self-pollination results in
(a) inbreeding depression
(b) out breeding depression
(c) hybrid vigour
(d) better result in offspring
Answer
A
Question. Device to discourage self-pollination or increase cross-pollination is
(a) pollen release and stigma receptivity are not synchronised
(b) anther and stigma placed at different position
(c) same height of stamen and stigma
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. Identify A to G in following figure and answer accordingly.

(a) A–Ovary, B–Filament, C–Sepal, D–Petal, E–Style,F–Stigma, G–Anther
(b) A–Sepal, B–Ovary, C–Petal, D–Filament, E–Anther,F–Stigma, G–Style
(c) A–Ovary, B–Sepal, C–Filament, D–Petal, E–Anther,F–Stigma, G–Style
(d) A–Petal, B–Anther, C–Stigma, D–Style, E–Filament,F–Sepal, G–Ovary
Answer
C
Question. Find odd one out.
(a) Stamen
(b) Stigma
(c) Style
(d) Ovary
Answer
A
Question. Autogamy stands for
(a) pollination in same flower
(b) pollination between different plants
(c) pollination in two flowers of same plant
(d) division in embryo
Answer
A
Question. If stem has 2n =10 number of chromosomes then find out
A – number of chromosome in endosperm.
B – number of chromosome in egg cell.
C – number of chromosome in polar nuclei, respectively.
(a) 15, 15, 20
(b) 10, 15, 20
(c) 15, 5, 10
(d) 10, 5, 15
Answer
C
Question. If endosperm has 36 number of chromosomes then find out the chromosome number of male and female gamete.
(a) 18, 18
(b) 17, 18
(c) 20, 20
(d) 12, 12
Answer
D
Question. Even in the absence of pollinating agents seed-setting is assured in
(a) Commelina
(b) Zostera
(c) Salvia
(d) Fig
Answer
A
Question. Identify A to D in the following diagram.
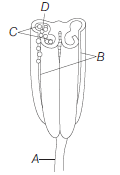
(a) A – Filament (stalk) , B – Pollen sac,C – Pollen grain, D – Line of dehiscence
(b) A – Filament (stalk), B – Pollen sac,C – Line of dehiscence, D – Pollen grain
(c) A – Line of dehiscence, B – Filament (stalk) ,C – Pollen sac, D – Pollen grains
(d) A – Filament (stalk), B – Line of dehiscence,C – Pollen sac, D – Pollen grains
Answer
D
Question. Male gametophyte in angiosperms produces
(a) two sperms and a vegetative cell
(b) single sperm and a vegetative cell
(c) single sperm and two vegetative cell
(d) three sperms
Answer
A
Question. Pollen tablets are available in the market for
(a) in vitro fertilisation
(b) breeding programmes
(c) supplementing food
(d) ex situ conservation
Answer
C
Question. In a fertilised embryo sac, the haploid, diploid and triploid structures are
(a) synergid, zygote and primary endosperm nucleus
(b) synergid, antipodal and polar nuclei
(c) antipodal, synergid and primary endosperm nucleus
(d) synergid, polar nuclei and zygote
Answer
A
Question. The outermost and innermost wall layers of microsporangium in an anther are respectively.
(a) Endothecium and tapetum
(b) Epidermis and endodermis
(c) Epidermis and middle layer
(d) Epidermis and tapetum
Answer
D
Question. A particular species of plant produces light, non-sticky pollen in large numbers and its stigmas are long and feathery. These modifications facilitate pollination by
(a) insects
(b) water
(c) wind
(d) animals
Answer
C
Question. Advantage of cleistogamy is
(a) higher genetic variability
(b) more vigorous offspring
(c) no dependence on pollinators
(d) vivipary
Answer
C
Question. The lengthwise running groove on anther which separate theca is called
(a) rupture line
(b) line of dehiscence
(c) suture of anther
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Number of microsporangia in an angiospermic anther is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
D
Question. Identify the labelling of given diagrams.
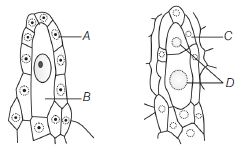
(a) A–MMC, B–Megaspore dyad, C–Nucellus, D–Nucleus
(b) A–Nucellus, B–Megaspore dyad, C–Nucellus,D–MMC
(c) A–Nucellus, B–MMC, C–Nucellus, D–Megaspore dyad
(d) A–MMC, B–Nucellus, C–Megaspore dyad, D–Nucleus
Answer
C
Question. Identify A to E in the diagram given below.
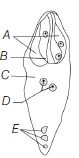
(a) A–Antipodal, B–2 polar nuclei, C–Central cell, D–Egg, E–Synergids
(b) A–Antipodal, B–Central cell, C–2 polar nuclei, D–Egg, E–Synergids
(c) A–2 polar nuclei, B–Central cell, C–Antipodal cell, D–Egg, E–Synergids
(d) A–Synergids, B–Egg, C–Central cell, D–2 polar nuclei, E–Antipodal cell
Answer
D
Question. Microsporangium develops into
(a) pollens
(b) microgametes
(c) megagametes
(d) pollen sac
Answer
D
Question. Identify A to E in the following diagram.
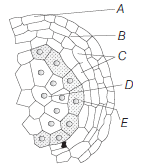
(a) A–Tapetum, B–Microspore mother cell, C–Middle layer, D–Endothecium, E–Epidermis
(b) A–Epidermis, B–Middle layer, C–Microspore mother cell, D–Tapetum, E–Endothecium
(c) A–Middle layer, B–Epidermis, C–Tapetum, D–Microspore mother cell, E–Endothecium
(d) A–Epidermis, B–Endothecium, C–Middle layer, D–Microspore mother cell, E–Tapetum
Answer
D
Question. Identify A to E inQuestion. the following diagram.
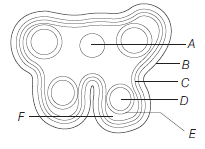
(a) A–Epidermis, B–Endodermis, C–Connective,
D–Sporogenous tissue, E–Middle layers, F–Tapetum
(b) A–Endodermis, B–Connective, C–Epidermis,
D–Tapetum, E–Sporogenous tissue, F–Middle layers
(c) A–Tapetum, B–Middle layers, C–Sporogenous tissue,
D–Connective, E–Endodermis, F–Epidermis
(d) A–Connective, B–Epidermis, C–Endothecium,
D–Sporogenous tissue, E–Tapetum, F–Middle layers
Answer
D
Question. Identify the structures marked A to F in the given diagram.
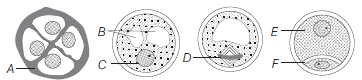
(a) A–Asymmetric nucleus, B–Nucleus, C–Generative cell, D–Vegetative cell, E–Pollen, F–Pollen tetrad
(b) A–Pollen tetrad, B–Pollen, C–Generative cell, D–Vegetative cell, E–Asymmetric spindle, F–Nucleus
(c) A–Pollen tetrad, B–Vacuole, C–Nucleus, D–Asymmetric spindle, E–Vegetative cell, F–Generative cell
(d) A–Vacuole, B–Nucleus, C–Pollen tetrad, D–Vegetative cell, E–Asymmetric spindle, F–Generative cell
Answer
C
Question. When the pollen grain is mature, it contains two cells,the … A … and … B ….
(a) A–generative cell, B–spore mother cell
(b) A–vegetative cell, B–spore mother cell
(c) A–spore mother cell, B–male gamete
(d) A–vegetative cell, B–generative cell
Answer
D
Question. The outermost wall layer of microsporangium in anther is
(a) endothecium
(b) tapetum
(c) middle layer
(d) epidermis
Answer
D
Question. Which is the most common type of embryo sac in angiosperms? NEET (Odisha) 2019
(a) Tetrasporic with one mitotic stage of divisions
(b) Monosporic with three sequential mitotic divisions
(c) Monosporic with two sequential mitotic divisions
(d) Bisporic with two sequential mitotic divisions
Answer
B
Question. Single megasporic development is called
(a) single sporic
(b) unisporic
(c) monosporic
(d) disporic
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following perform microsporogenesis?
(a) Microspore mother cell
(b) Pollen mother cell
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. The process of formation of microspores from pollen mother cell through … A… is called … B… .
Microspores are arranged in … C … . As the anthers matures and dehydrate, microspores develop into the …D… .
Fill in the blanks A to D.
(a) A–pollen grains, B–microspore tetrad, C–microsporogenesis, D–meiosis
(b) A–microspore tetrad, B–microsporogenesis, C–meiosis, D–pollen grains
(c) A–microsporogenesis, B–microspore tetrad, C–pollen grain, D–meiosis
(d) A–meiosis, B–microsporogenesis, C–microspore tetrad, D–pollen grains
Answer
D
Question. Microspore tetrad (pollen grains) is the result of
(a) mitotic cell division
(b) meiotic cell division
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Identify the type of flower A and B.
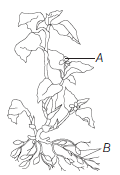
(a) A–Cleistogamous; B–Chasmogamous
(b) A–Homogamous; B–Heterogamous
(c) A–Chasmogamous; B–Cleistogamous
(d) A–Heterogamous; B–Homogamous
Answer
C
Question. In chasmogamy pollination takes place in
(a) open flower
(b) closed flower
(c) large flower
(d) geitonogamy flower
Answer
A
Question. Dehiscence of anther in mesophytes is caused by
(a) hydration of anthers
(b) dehydration of anthers
(c) mechanical injury
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. In the given fertilised embryo sac, identify A to E.
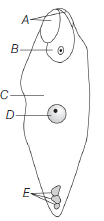
(a) A–Degenerating antipodal cell, B–Primary endosperm nucleus, C–Primary endosperm cell, D–Synergid cell, E–Zygote
(b) A–Synergid cell, B–Antipodal cell, C–Zygote, D–Endosperm cell, E–Chalazal cell
(c) A–Degenerating synergids, B–Zygote, C–Primary endosperm cell, D–Primary endosperm nucleus, E–Degenerating antipodal cell
(d) A–Zygote, B–Synergid, C–Primary endosperm cell, D–Primary endosperm nucleus, E–Degenerating antipodal cell
Answer
C
Question. Identify the different stages in embryogenesis in the given diagram A, B, C, D, E, F and G.
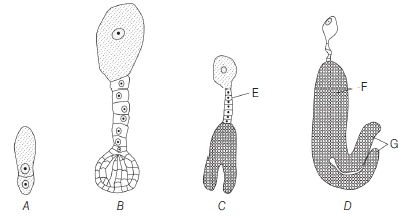
(a) A–2-celled stage, B–Heart-shaped embryo, C–Globular embryo, D–Mature embryo, E–Radicle, F–Suspensor, G–Cotyledon
(b) A–2-celled stage, B–Mature embryo, C–Heart-shaped embryo, D–Globular embryo, E–Cotyledon, F–Radicle, G–Suspensor
(c) A–2-celled stage, B–Globular embryo, C–Heart-shaped embryo, D–Mature embryo, E–Suspensor, F–Radicle, G–Cotyledon
(d) A–Mature embryo, B–Heart-shaped embryo, C–Globular embryo, D–2-celled stage, E–Suspensor, F–Cotyledon, G–Radicle
Answer
C
Question. Pollens have two prominant walls which are …A… and …B… . Here A and B refers to
(a) A–intine, B–protein coat
(b) A–exine, B–intine
(c) A–sporopollenin, B–intine
(d) A–sporopollenin, B–exine
Answer
B
Question. Patterns and designs of exine of pollen grains are the characteristic features of
(a) species of plant
(b) genus of plants
(c) order of plants
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The stalk which joins ovule and placenta is called
(a) funicle
(b) hilum
(c) chalaza
(d) micropyle
Answer
A
Question. Which is most crucial for seed storage?
(a) Dehydration and dormancy
(b) Endosperm and water
(c) Least amount of development
(d) Endosperm in large quantity
Answer
A
Question. Thalamus contributes in the fruit formation in
(a) apple
(b) strawberry
(c) cashewnut
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. The ovule of an angiosperm is technically equivalent to NEET 2016
(a) megasporangium
(b) megasporophyll
(c) megaspore mother cell
(d) megaspore
Answer
A
Question. An ovule is a
(a) differentiated megasporangium
(b) dedifferentiated megasporangium
(c) integumented megasporangium
(d) redifferentiated megasporangium
Answer
C
Question. Hardest substance in plant kingdom is JIPMER 2019
(a) saple
(b) corolla
(c) sporopollenin
(d) anther
Answer
C
Question. How many nuclei are found in female gametophyte?
(a) 8
(b) 7
(c) 6
(d) 5
Answer
A
Question. The phenomenon observed in some plants where in parts of the sexual apparatus is used for forming embryos without fertilisation is called
(a) parthenocarpy
(b) apomixis
(c) vegetative propagation
(d) sexual reproduction
Answer
B
Question. In a flower, if the megaspore mother cell forms megaspores without undergoing meiosis and if one of the megaspores develops into an embryo sac, its nuclei would be
(a) haploid
(b) diploid
(c) a few haploid and a few diploid
(d) with varying ploidy
Answer
B
Question. The phenomenon wherein, the ovary develops into a fruit without fertilisation is called
(a) parthenocarpy
(b) apomixis
(c) asexual reproduction
(d) sexual reproduction
Answer
A
Question. I. Antipodal cell II. Egg cell
III. Synergid cell IV. Polar nuclei
V. Male gamete VI. Nucellar cell VII. Central cell
Out of the seven names given above, find out haploid cells.
(a) I, II, IV and V
(b) II, IV, VI and VII
(c) I, II, III and V
(d) II, IV, III and I
Answer
C
Question. What is the fate of the male gametes discharged in the synergid?
(a) All fuse with the egg
(b) One fuses with the egg, other(s) fuse(s) with synergid nucleus
(c) One fuses with the egg and other fuses with central cell nuclei
(d) One fuses with the egg other(s) degenerate(s) in the synergid
Answer
C
Question. How many cells are found in female gametophyte?
(a) 6
(b) 8
(c) 7
(d) 5
Answer
C
Question. Identify the parts labelled as A to D in structure of seed given below.
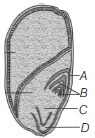
(a) A–Coleoptile, B–Plumule, C–Radicle, D–Coleorhiza
(b) A–Plumule, B–Coleoptile, C–Coleorhiza, D–Radicle
(c) A–Coleorhiza, B–Radicle, C–Plumule, D–Coleoptile
(d) A–Radicle, B–Plumule, C–Coleoptile, D–Coleorhiza
Answer
A
Question. A typical dicotyledonous embryo consist of an …A…axis an d …B… cotyledons.
The portion of embryonal axis above the level of cotyledons is …C… which terminates with the …D… or stem tip.
A, B, C and D in the above statement are
(a) A–plumule, B–epicotyl, C–cotyledons, D–embryonal
(b) A–embryonal, B–two, C–epicotyl, D–plumule
(c) A–embryonal, B–epicotyl, C–cotyledons, D–plumule
(d) A–embryonal, B–plumule, C–cotyledons, D–epicotyl
Answer
B
Question. The sporopollenin is non-degradable because
(a) it can withstand strong acids
(b) it is resistant at very high temperature
(c) no enzyme degrade it
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following has proved helpful in preserving pollen as fossils?
(a) Oil content
(b) Cellulosic intine
(c) Pollenkitt
(d) Sporopollenin
Answer
D
Question. The functions of germ pore is/are
(a) emergence of radicle
(b) absorption of water for seed germination
(c) initiation of pollen tube
(d) All of the above
Answer
C
Question. During microsporogenesis, meiosis occurs in
(a) endothecium
(b) microspore mother cells
(c) microspore tetrads
(d) pollen grains
Answer
B
Question. From among the sets of terms given below, identify those that are associated with the gynoecium.
(a) Stigma, ovule, embryo sac, placenta
(b) Thalamus, pistil, style, ovule
(c) Ovule, ovary, embryo sac, tapetum
(d) Ovule, stamen, ovary, embryo sac
Answer
A
Question. To achieve 3-celled stage in angiosperms, which cell of the pollen grain divides to form two male gametes ?
(a) Vegetative cell NEET 2018
(b) Generative cell
(c) Microspore mother cell
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Starting from the innermost part, the correct sequence of parts in an ovule are
(a) egg, nucellus, embryo sac, integument
(b) egg, embryo sac, nucellus, integument
(c) embryo sac, nucellus, integument, egg
(d) egg, integument, embryo sac, nucellus
Answer
B
Question. From the statements given below choose the option that are true for a typical female gametophyte.
I. It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity.
II. It is free-nuclear during the development.
III. It is situated inside the integument, but outside thenuc ellus.
IV. It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end.
(a) I and IV
(b) II and III
(c) I and II
(d) II and IV
Answer
C
Question. 60% of the angiosperms shed their pollens at the
(a) 2-celled stage
(b) 3-celled stage
(c) 4-celled stage
(d) 1-celled stage
Answer
A
