Class 12 VBQs Biology Ecosystem
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. ‘Man is a primary as well as the secondary consumer’. Justify this statement.
Answer : The man is a primary consumer when he eats plants or their products and is a secondary consumer when he eats animals. Man is in fact omnivore because he eats both plants as well as animals.
Question. ‘It is possible that a species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.’ Explain with the help of one example.
Answer : Yes, it is possible because the trophic level of a species represents the functional role of the organism in energy flow, which is determined by the food it takes. For example, sparrow is an omnivore. When it eats seeds, fruits or any other plant product, it occupies the primary trophic level.
whereas, when it eats worms and any other insects, It occupies the secondary trophic level. Thus, it occupies more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem.
Question.

Identify the type of the given ecological pyramid and give one example each of pyramid of number and pyramid of biomass in such cases.
Answer : Inverted pyramid
Inverted pyramid of biomass in a lake –
Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Fishes.
Inverted pyramid of number – tree →insects → Birds.
Question. Mr. Galgotia eats curd/yoghurt. In this case, which trophic level will he occupy ?
Answer : He would occupy third trophic level in this case.
Short Answer Type Questions
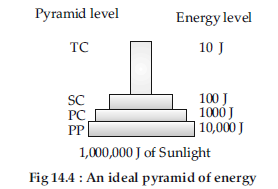
Question. Why is the pyramid of energy always upright? Explain.
OR
It is stated that the pyramid of energy is always upright. Justify.
Answer : The pyramid of energy is always upright because there is a gradual decrease in the energy contents in successive trophic levels from producers to consumers of various order. According to Lindeman’s 10% law, only 10% of the total energy is available to the next higher trophic level.
Question. Why are herbivores considered similar to predators in ecological context ? Explain.
Answer : The herbivores are considered like predators in ecological context because they feed on plants for as the predators feed on their prey for their food requirement.
Question. State the difference between the first trophic levels of detritus food chain and grazing food chain.
Answer : In detritus food chain, the detrivores and decomposers constitute the first trophic level whereas in grazing food chain the producers i.e. the autotrophic green and photosynthetic plants constitute the first trophic level.
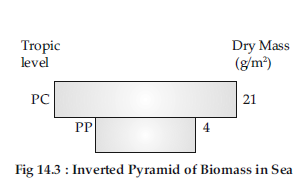
Question. Draw a pyramid of biomass and pyramid of energy in sea. Give your comments on the type of pyramids drawn.
Answer :
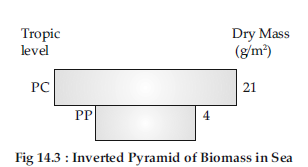
The pyramid of biomass in sea is inverted.
The pyramid of energy in sea is upright.
Question. “In a food-chain, a trophic level represents a functional level, not a species.” Explain.
Answer : Position of a species in any trophic level is determined by the function performed by that mode of nutrition of species in a particular food chain / A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem (in different food chains) at the given time.
If the function of the mode of nutrition of species changes its position shall change in the trophic levels, same species can be at primary consumer level in one food chain and at secondary consumer level in another food chain in the same ecosystem at the given time.
Similar value points explained with the help of a suitable example.
Detailed Answer :
The organisms can be divided on the basis of their feeding relationships. On the basis of sources of their nutrition, organisms occupy a specific position in the food chain called their trophic level. More than one species of organisms can occupy the same trophic level in a food chain, for example in a grassland ecosystem, rabbits and butterflies occupy the same trophic level, while both are different species. Thus, in a food chain, a trophic level represents a functional level, not a species.
Question. What is ecological succession ? Where and why would the rate of succession be faster in newly created pond or a forest destroyed by a forest fire?
Answer : Gradual / predictable change in the species composition of given area. Rate of succession would be faster in a forest destroyed by a forest fire. Such disturbances create new conditions that encourage some species and discourage or eliminate other species / since after a forest fire some soil is already present, so, succession is faster than primary succession.
Question. Construct labelled grazing and detritus food chains with minimum three trophic levels each.
Answer : Grazing food chain :
Autotrophs →Herbivores→Primary carnivores→secondary carnivores.
Detritus food chain :
Decay and → decomposer → soil animal organism which consume other soil organisms.
excretory materials from the grazing food chain.
Question. Name the pioneer species on a bare rock. How do they help in establishing the next type of vegetation ? Mention the type of climax community that will ultimately get established.
Answer : The pioneer species on a bare rock are usually lichen, mosses and annual grass stage and bluegreen algae. In primary succession on rocks, lichens are able to secrete acids to dissolve rocks, helping in weathering and soil formation. It paves way to some very small plants like bryophytes, which are able to take hold in the small amount of soil. They are with time, succeeded by bigger plants.
Several hard and light demanding trees grow in the area occupied by shrubs. Slowly environment becomes more moist and shadier so that plants of climax community can spread in this area. The type of climax community that will ultimately get established are shrubs and trees.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. It is often said that the pyramid of energy is always upright. On the other hand, the pyramid of biomass can be both upright and inverted. Explain with the help of examples and sketches.
Answer :

The pyramid of energy represents the total amount of energy consumed by each trophic level in a given food chain. An energy pyramid is always upright because the total amount of energy available for utilisation in the top levels is less than the energy available in the lower levels. This happens because according to the 10% law of energy flow, only 10% of the total energy is transferred from one trophic level to another.
The pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation of total amount of living matter present at each trophic level of an ecosystem. The pyramid of biomass can be both upright and inverted.

The pyramid of biomass is upright in grasslands and forest ecosystems because the amount of biomass present at the producer level is higher than at the top carnivore level.

The pyramid of biomass is inverted in a pond ecosystem as the biomass of fishes exceeds the biomass of zooplankton (upon which they feed).
Question. (i) Construct a pyramid of numbers considering a big banyan tree supporting a population of insects, small birds and their predators.
(ii) Differentiate, giving reason, between the pyramid of biomass of the above situation and the pyramid of numbers that you have drawn.
Answer : (i)

This is a spindle-shaped Pyramid.
In the above pyramid, the population of insects is more than the tree, therefore, the size of pyramid increases, but the number of small birds is lesser than the insects. The pyramid size becomes narrow.
Further, big birds are lesser than small birds. So the size of pyramid becomes narrower.
(ii) Actually, the pyramids of numbers do not give a true picture of the food chain, as they are not very functional. They do not indicate the relative effect of the geometric food chain and size. Here, the size of the pyramid becomes variable.
The pyramid of biomass of the given situation will be :

The pyramid of biomass in this ecosystem is upright because the biomass decreases at each trophic level.
Question. Explain how xerarch succession progresses from xeric to mesic condition and forms a stable climax community. You may use a flow chart.
Answer : Xerarch succession : Xerarch succession takes place in dry areas and the series progress from xeric to mesic condition.
In primary succession on rocks, the pioneer species i.e. lichens secrete acids to dissolve rock, helping in weathering and soil formation. These later pave way to some very small plants like bryophytes which are able to take hold in the small amount of soil. They are with time, succeeded by bigger plants and after several more stages ultimately a stable climax forest community is formed.
The climax community remains stable as long as the environment remains unchanged. With time the xerophytic habitat gets converted into a mesophytic one.
The stages in xerarch succession are as follows :
Lichens (Pioneer community)
↓
Bryophytes (mosses) (Serial communities)
↓
Herbaceous plants
↓
Shrubs (bushes)
↓
Trees (Climax community)
In secondary succession, the species that invade depends on the condition of the soil, availability of water, the environment and also on the seeds or other propagules present. Since soil is already there, the rate of succession is much faster and hence, climax is also reached more quickly. Primary succession is a slow process, taking about thousands of years for the climax to be reached. Another important fact is to understand that all succession, whether taking place in water or on land, proceed to a similar climax community, the mesic.
Question. What is an ecological pyramid ? Compare the pyramids of energy, biomass and numbers.
Answer : Graphical representation of the relationship among the organisms at different trophic level

Question. What does an ecological pyramid indicate ? Explain the three different type of upright pyramids in nature with the help of an example each.
Answer : It indicates food / energy relationship between organisms at different trophic levels
(i) Pyramid of Number = example : grassland ecosystem.
OR
Producers are more number than herbivores carnivores.
(ii) Pyramid of Biomass = example : forest / tree ecosystem.
OR
Producers have more biomass than herbivores / carnivores.
OR
Pyramid of biomass shows a sharp decrease in biomass in higher trophic levels.
(iii) Pyramid of energy = example : grassland ecosystem.
OR
Producers have more energy than herbivores / carnivores
Detailed Answer :
Ecological pyramids are the representation of a food chain in the form of a pyramid.
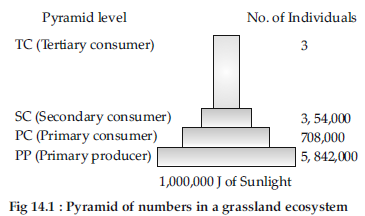
(i) Pyramid of Number : It represents the relationship between producers and consumers in an ecosystem in the form of a pyramid in terms of their numbers.
E.g. Grassland Ecosystem
(ii) Pyramid of Biomass : It shows a sharp decrease in biomass at higher trophic levels.
For diagram:

(iii) Inverted Pyramid of Biomass : Small standing crop of phytoplankton supports large standing crop of zooplankton.
(iv) Pyramid of Energy : Primary producers convert only 1%of the energy in the sunlight available to them into NPP. For diagram:
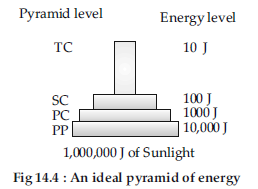
Question. (a) What is a trophic level in a ecosystem ? What is ‘standing crop’ with reference to it ?
(b) Explain the role of the ‘first trophic level’ in an ecosystem.
(c) How is the detritus food chain connected with the grazing food chain in a natural ecosystem ?
Answer : (a) Specific place of an organism in a food chain, mass of living material (biomass) at each trophic level at a particular time.
(b) First trophic level has producers / autotrophs, which trap solar energy / to produce food (photosynthesis).
(c) Organisms of the Detritus food chain (DFC) are the prey to the Grazing food chain (GFC) organism, the dead remains of GFC are decomposed into simple inorganic materials which are absorbed by DFC organisms.
Detailed Answer:
(a) A specific place of organisms in the food chain is known as their trophic level. Producers
belong to the first trophic level, herbivores to the second and carnivores to the third.
Each trophic level has a certain mass of living material at a particular time called as the standing crop. Standing crop is the quantity or total weight of dried biomass of the organism which is present in a specific location at a particular time. It is measured as the mass of living organisms (biomass) or the number in a unit area.
(b) The first trophic level is the producer. At this level, the organisms are autotrophic.
They prepare their own food with the help of sunlight. Producers have the ability to transform light energy into chemical energy so that it can be useful to other trophic levels and for the sustenance of the ecosystem.
In detritus food chain, energy comes from organic matter generated in trophic levels of the grazing food chain.
