Lifelines of National Economy Notes for Class 10 Social Science
Following are Lifelines of National Economy Notes for Class 10 Social Science. These revision notes have been prepared by expert teachers of Class 10 Social Science as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books released for the current academic year. Students should go through Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy concepts and notes as these will help you to revise all important topics and help you to score more marks. We have provided Class 10 Social Science notes for all chapters in your book. You can access it all free and download Pdf.
Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Notes Class 10 Social Science

Six types of Roads according to their capacity:-
- Golden quadrilateral:- Links Delhi, Kolkata, Mumbai, Chennai
- National highways:- Link extreme parts of the country.
- State highways:- Link state capital with district head quarters.
- District roads:- Connect district headquarters with other places of district.
- Other roads:- Rural roads, which link villages importance
- Border roads:- Link places of strategic more than border in northeast and northern border areas.
Advantages of Roadways over Railways
- Construction cost is much lower
- Can be laid any where such as on slopes, mountains
- Economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distance
- Provides door to door service, thus cost of loading and unloading is much lower
- Feeder to other models of transport as they provide a link between railway stations, air and sea ports.



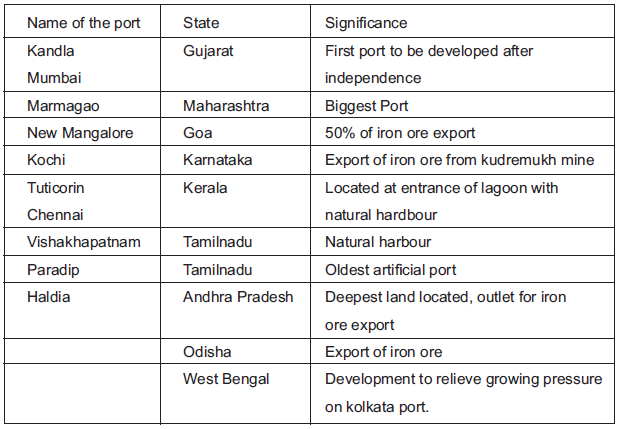
Major Sea Ports and their states
Airways
- Fastest, Most comfortable and prestigious mode of transport.
- Can cover difficult terrains like high mountains, dreary deserts, dense forest and long oceanic stretches.
- Provides help during natural disasters like floods and earthquakes.
* Not within the reach of the common people.
* Gets affected by weather conditions.
Tourism as a Trade
Significance :-
* Promotes national integration
* Provides support to local handicrafts
* Helps in development of International understanding about our culture and heritage.
Types of Tourism
* Heritage tourism
* Eco tourism
* Adventure tourism
* Cultural tourism
* Medical tourism
* Business tourism
Key points:
1. Life lines of a country-Modern means of communication and transport which brings people together and helps in local, national and international trade.
2. Means of Transport-Means of transports which make possible the movement of goods, services and humans/animals from one place to another place.
3. Means of communication-Methods through which information, news, dialogue etc. communicated from one place and person to another place and person are called means of communication. Such as newspaper, radio, T.V. telephone, mobile phone, e-mail etc.
4. Golden Quadrilateral-The six lane superhighways which being implemented by National highway Authority of India(NHAI) and connects Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai (the four metro cities)
5. National Highways-Four to six lane highways which connects or link extreme parts of the country and maintained by Central Public Works Department (CPWD)
6. Border Roads-Border Roads Organisation a Government of India undertaking constructs and maintains roads in the bordering areas of the country. These roads are border roads and improve the accessibility in areas of difficult terrain.
7. Trade-Exchange of goods and services among different peoples, states and countries referred to as trade.
8. International Trade-Trade between two and more countries is called International trade. 95% of country’s trade volume is moved by sea.
9. Balance of Trade-The balance of trade of a country is the difference between it’s export and import.
10. Rail Transport-A major means of transport in India. The Indian Railways is now reorganised in 16 zones in 2003.
11. Gauge or track-It is the distance between the two tracks of rail.
12. Port -The manmade place or facility near the sea cost where ships, boats and barges can be docked to load unload people, things etc. Fuel and other needs can also be taken here. A port is different than a harbour.
13. Tidal port – A port in which the water level within the port is subject to change with the ocean tides. These ports are found in coastal region. e.g. Kandla.
14. New forms of Tourism-Heritage tourism, eco tourism, adventure tourism, cultural tourism, medical tourism and business tourism. Over 2.6 million foreign tourists visit India every year.
Very Short Answer type Questions
Question. What do you understand by the road density?
Ans. The length of road per hundred sq. km. of area is known as density of roads.
Question. Between which two place national waterways no.1 is navigable? How long it is ?
Ans. Between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km long).
Question. Which measures were taken to facilitate quick delivery of mails in large towns and cities?
Ans. Six mail channels have been introduced. They are called Rajdhani channel, Metro channel, Green channel, Business channel, Bulk mail channel and Periodical channel.
Question. In which area of India the air transport has been provided to common people as a special provision?
Ans. In North eastern states.
Question. When and where did the first train start running in India?
Ans. On 16 April,1853 between Mumbai to Thane(34 km.)
Question. Which is the oldest artificial port in India?
Ans. Chennai
Question. Mention the two components of international trade.
Ans. Exports and Imports
Question. Apart from Hindi list out 2 language in which the largest no of newspaper are published.
Ans. English and Urdu
Question. Which two stations are linked by North-South corridor?
Ans. Srinagar with Kanyakumari.
Question. What does pipeline transport mean?
Ans. A new means of transport. A new arrival on the transportation map of India. Through which water is transported to houses and farms, and crude oil, petrol products and natural gas transported to gas refineries and thermal power stations.
Question. Which two stations are linked by East-West corridor?
Ans. Silchar (Assam) to Porbandar(Gujarat)
Question. Where is the head quarter of Northern Railways situated?
Ans. Delhi
Question. What is the total length of India’s coast line?
Ans. 7516.6 km
Question. Name two inland waterways of India?
Ans. (i) On river Ganga-between Allahabad and Haldia.
(ii) On river Brahmaputra-between Sadiya and Dhubri.
Question. Which is the longest gas pipeline?
Ans. Hajira-Vijaypur-Jagdishpur
Question. Give two examples of first class mail.
Ans. Cards and Envelops
Question. When did the airways nationalised in India?
Ans. In 1953.
Question. Which is the longest national highway?
Ans. NH-7 Connecting Varanshi and Kanyakumari
Question. Which state has highest and lowest road density respectively?
Ans. Highest-Kerala, lowest-Jammu and Kashmir
Question. Which is the busiest railway junction in Northern India?
Ans. Mughalsarai
Question. Which authority certifies both Indian foreign films?
Ans. Central board of film certification
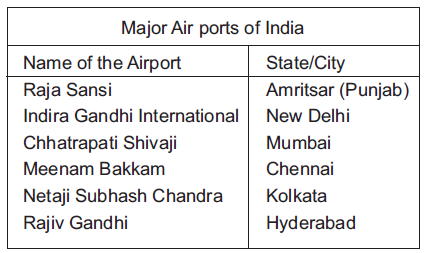
Question. Which two cities are connect through NH-1?
Ans. Delhi and Amritsar
Question. What is the total no of railway zones in India.
Ans. 16
Question. Which sea port is the major port in context to the export of Iron ore?
Ans. Marmagao.
Question. Which is the first port developed after the independence.
Ans. Kandla Port.
LONG/SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS -:
Question. Classify the Indian roads on the basis of their capacity?
Ans. (i) Golden Quadrilateral superhighways-It is a superhighway of six lanes.
(ii) National Highways-Links extreme parts of the country.
(iii) State Highways-Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters.
(iv) District Roads-These roads connect the district headquarters with other places of the district.
(v) Border Roads-Border Roads Organisation construct and maintains roads in the bordering area of the country. These roads have improved accessibility in areas of difficult terrain and have helped in the economic development of these areas.
Question. Write any three features of Golden Quadrilateral super highways?
Ans. (i) It’s a six lane super highways.
(ii) It links the mega cities of India i.e. Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai and Delhi.
(iii) It reduces the time and distance between the mega cities of India.
(iv) It is under the NHAI.
(v) it’s a major road development project of our country.
Question. Which means of Transport is being used mostly in the North-Eastern states of India? Why this means of transport is used in these states give four reasons?
Ans. Though the air travel has made transportation in north-eastern states easier with the presence of big rivers, dissected relief, dense forests and frequent floods and international frontiers, etc. but it is not in the reach of the common man, as it is expensive. Therefore mostly inland waterways are being used as the most common means of transport in the north-eastern states of India. The reason behind are-
(i) Waterways are the cheapest means of transport.
(ii) They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
(iii) It is fuel-efficient and environment friendly mode of transport.
(iv) Road and Rail transport are not very much developed in northeastern states.
(v) Here rivers make harbours and ports for the inland navigation waterways.
Question. ‘Road transport is more important than the Rail transport’. Why?
Ans. (i) Road transport was started before the rail transport.
(ii) Construction and management is easy thus can built and maintained easily.
(iii) Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railway lines.
(iv) Can be constructed on mountains, and difficult terrains.
(v) It also provide door- to- door service, thus the cost of loading and unloading is much lower.
(vi) Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide a link between railway stations, air and sea ports.
Question. Describe the advantages of Pipeline Transport?
Ans. (i) Pipeline transport network is used to transport water to cities and industries, crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil and natural gas fields to refineries, fertilizer factories and big thermal power plants.
(ii) Initial cost of laying pipelines is high but subsequent running costs are minimal.
(iii) It rules out trans-shipment losses or delays.
(iv) Pipelines make transport fast, safe and easy.
(v) It saves time and reduce pressure on rail transport.
Question. Explain the importance of Air transport ?
Ans. (i) It is fastest among all. Take lesser time to reach one place to another.
(ii) It is a most comfortable.
(iii) It’s prestigious mode of transport.
(iv) It can cover very difficult terrains like high mountains, dreary deserts, dense forests and also long oceanic stretches with great ease.
(v) On the border, to maintain the force and to provide them food and ration at earliest.
Question. Describe any three advantages of Mass communication?
Ans. (i) Mass communication provides entertainment.
(ii) Creates awareness among people about various National programme and policies.
(iii) It spreads knowledge.
(iv) It broadcasts a variety of programmes from entertainment, educational to sports, etc.
(v) Doordarshan, the national television channel of India is the medium of national message and is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world.
Question. “The progress of international trade of a country indicates the economic prosperity of that country.”Prove this statement with five logics.
Ans. Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to it’s economic prosperity. It is, therefore, considered the economic barometer for a country. Following facts justifies and prove this-
(i) Due to the progress of the international trade the living standard of the people of a country prospers.
(ii) Developed nations get foreign exchange by selling their high quality goods to other countries.
(iii) Developed countries produce/manufacture goods more than their requirements and exports in foreign countries.
(iv) Developing countries depends on developed countries in many ways.
(v) Under developed countries depends on other countries and have to give a big part of their income to developed countries.
(vi) It increases employment opportunities.
(vii) Much needed foreign currency stock increases.
Question. Write the reasons behind the unequal distribution of Rail network in India?
Ans. (i) It is difficult to lay railway lines on mountainous region and it is expensive too.
(ii) The northern plains with their vast level land provides favourable condition for Rail construction. Here construction is easy and construction cost is low.
(iii) High population density and rich agricultural resources provide the most favourable condition for the growth.
(iv) Due to sparse population and lack of economic activities it was difficult to lay railway lines on the sandy plains of western Rajasthan and in the hilly terrains of the peninsular region.
(v) Due to administrative reasons and Government policies also the development of Railways effected.
Question. Write the name of any three Railway zones and their headquarters?
Ans. (i) Northern Railway Zone-New Delhi
(ii) Western Railway zone-Mumbai
(iii) Southern Railway zone-Chennai
Question. How is the tourism is helpful in the development of economy as a trade or industry?
Ans. (i) Tourism in India has grown substantially over the last three decades.
(ii) More than 15 million(150 lakhs)people are directly engaged in this industry.
(iii) Tourism also promotes national integration.
(iv) It also helps in the development of international understanding about our culture and heritage.
(v) It also provide support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
(vi) It contributes significantly in earning foreign exchange.
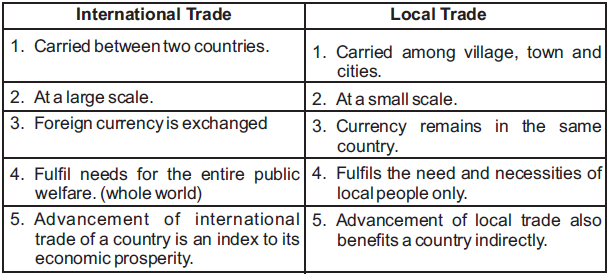
Question. Differentiates between the International and local trade?
Ans.
Question. What are the major challenges of road transport?
Ans. (i) Almost half of the roads are unmetalled roads and go out of use in the rainy season.
(ii) Roads are insufficient in compare to transport and commuters.
(iii) Roads are narrow and crowded due to the increasing number of vehicles.
(iv) It leads to traffic jams and road rage.
(v) Even National highways are insufficient.
Question. Why the transport and means of communication are called the lifelines of an economy?
Ans. i) The trade, transport and communication are complementary to each other.
ii) Connects the far reaching areas of the country and the world
iii) Encourage the national and international tourism.
iv) Brings foreign exchange.
v) Life gets comfortable and easy.
vi) The whole country unites in emergency.



