Money and Credit Class 10 Social Science Important Questions
Objective Type Questions
Question. Sunil works in a private company, Anil works as a daily wage earner. Both want a credit of ₹ 30,000. The Bank is more likely to give credit to whom?
(a) Anil as he is more needy.
(b) Sunil as he has regular employment.
(c) Neither Sunil nor Anil will be provided credit from bank.
(d) Both Anil and Sunil will be provided credit from bank.
Answer : (b) Sunil as he has regular employment.
Question. Which of the following is not a formal source of credit from the given options?
(a) Banks
(b) Cooperative
(c) Employer
(d) All of these
Answer : (c) Employer
Question. Which among the following is not a feature of informal sources of credit?
(a) It is supervised by the Reserve Bank of India
(b) Rate of interest is not fixed
(c) Terms of credit are very flexible
(d) Traders, employers, friends, etc provides informal credit source.
Answer : (a) It is supervised by the Reserve Bank of India
Question. Which one of the following options describes ‘Collateral’?
(a) Double coincidence of wants
(b) Certain products for barter
(c) Trade in barter
(d) Asset as guarantee for loan
Answer : (d) Asset as guarantee for loan
Question. Which of the following is not included in the terms of credit in a bank loan?
(a) The rate of interest
(b) The lender’s land
(c) The borrower’s land
(d) The time period of the loan
Answer : (b) The lender’s land
Question. Raghav has surplus money so he open a bank account and deposits in it.Whenever, he needs money, he can go to his bank and withdraw from there. This kind of deposit’ with the banks is known as
(a) Fixed Deposit
(b) Term Deposit
(c) Demand Deposit
(d) Surplus Deposit
Answer : (c) Demand Deposit
Question. Read the given information carefully and select the most appropriate answer from the given options.
A shoemanufacturer,M.Salimhas to make a payment to the leather supplier and writes a cheque for a specific amount. This means that the shoe manufacturer instructs the bank to pay this amount to the leather supplier. The leather supplier takes this cheque and deposits it in his own bank account in the bank. The money is transferred from one bank to another account in a couple of days. The transaction is complete without any payment of cash. After the transaction between Salim and Prem ………. .
(a) Salim’s balance in his bank, account increases and Prem’s balance also increases
(b) Salim’s balance in his bank account decreases and Prem’s balance increases
(c) Salim’s balance in his bank account increases and Prem’s balance decreases
(d) Salim’s balance in his bank account decreases and Prem’s balance also decreases
Answer : (b) Salim’s balance in his bank account decreases and Prem’s balance increases
Question. Match the following:
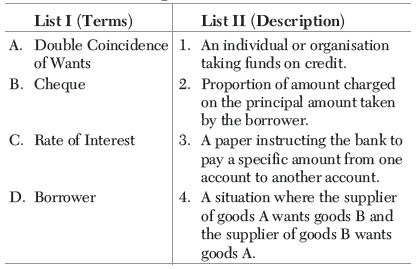
Codes
(a) A – 2, B – 3, C – 4, D – 1
(b) A – 4, B – 3, C – 2, D – 1
(c) A – 3, B – 4, C – 1, D – 2
(d) A – 1, B – 2, C – 4, D – 3
Answer : (b) A – 4, B – 3, C – 2, D – 1
Question. Assertion (A) Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits.
Reason (R) The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors is their main source of income.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Question. Assertion (A) Modern currency is used as a medium of exchange, however, it does not have a use of its own.
Reason (R) Modern currency is easy to carry.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer : (b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Question. Assertion (A) Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns and use this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
Reason (R) Collateral is given as the lender can sell the collateral to recover the loan amount if the borrower fails to repay the loan.
Codes
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Answer : (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain the main function of money.
Answer : The medium of exchange.
Question. Explain the main difficulty of Barter System.
Answer : The double coincidence of wants.
Question. Formal Loans : Bank, Informal Loans: ________ .
Answer : Money lenders.
Question. What is money ?
Answer : Money is anything which is generally acceptable as a medium of exchange.
Question. Highlight the inherent problem in double coincidence of wants.
Answer : The inherent problem in double coincidence of wants is that both parties must agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities.
Question. Recognize the situation when both the parties in a barter economy have to agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities? What is it called?
Answer : Double coincidence of wants.
Question. Give any two examples of informal sector of credit.
Answer : Credit from ‘Moneylender’ Credit from ‘Family member’
Question. How does money remove the difficulty of the double coincidence of wants ?
Answer : Money has removed the problem of double coincidence of wants by breaking a single exchange transaction for specific goods into two transactions of buying and selling by involving a medium of general acceptability, i.e., money. Everyone involved in a transaction may buy the good of his requirement from anybody who has got that thing. Now they don’t have to look for a person who desires to sell exactly what the other wishes to buy.
Question. Who issues currency in India?
Answer : The Reserve Bank of India.
Question. What is demand deposit ?
Answer : Demand deposits are the deposits with the bank which are withdrawable by cheque. Since such deposits can be withdrawn by cheque on demand, that is why they are called demand deposits.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What do you understand by double coincidence of wants ?
Answer : Double coincidence of wants is a difficult situation involved in the barter system. Under the barter system, the transactions between two persons were executed through the mutual exchange of goods. For example, person A has got rice and wants a blanket while person B has blanket and wants rice. Both of them have the things which the other one wants. So the transaction here can take place easily. This is called double coincidence of wants, i.e., what a person desires to sell is exactly what the other wishes to buy.
Question. ‘‘Banks are efficient medium of exchange.’’ Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : We agree with the statement that banks are efficient medium of exchange.
(i) Demand deposits share the essential features of money.
(ii) The facility of cheque against demand deposit makes it possible to directly settle payment without use of cash.
(iii) Demand deposits are accepted widely as a medium of payment.
Question. “Focuses of currency have undergone several changes since early times.” Elucidate.
Answer : (i) Before the introduction of coins, a variety of objects were used as money.
(ii) For example, since the very early ages, Indians used grains and cattle as money.
(iii) Thereafter, the use of metallic coins–gold, silver, copper coins–a phase which continued well into the last century.
(iv) Modern forms of money include currency–paper notes and coins.
(v) Modern currency is not made of precious metal, it is without any use of its own.
Question. Explain any three loan activities of banks in India.
Answer : Activities of banks in India who are involved in providing loan : (i) Banks in India these days want 15% to 20% from loan seeker to pay for their other resources and give balance money as loan on interest. For example, if someone wants ` 1 lakh as loan for purchase of house, bank will pay around 80% of amount against hypothecation of property of equal amount.
(ii) Bank keeps a provision to pay the amount to loan seeker or depositor who might come for the money to the bank on any given day.
(iii) Bank uses the major portion of deposits to extend loan.
(iv) Difference between the interest rates, what bank pay to public for FD and what they charge from loan seeker is the main source of income of banks.
Question. ‘‘Credit can play a negative role.’’ Justify the statement with arguments.
Answer : Credit can play a negative role in the following ways
◆ In situations where credit is taken to repay the earlier loans then it will increase the burden of repayment.
◆ In high risk situations when the future is uncertain, there credit plays a negative role. For example, farmers taking credit before sowing but their harvest may not be good and they may not be able to repay their loans.
◆ Rural borrowers normally depend on informal sources of credit who charge a high rate of interest. This repayment of larger amounts may sometimes be larger then their income. In that case, credit plays a negative role.
Question. Explain the features of Self Help Groups.
Answer : The features of the Self Help Groups (SHGs) are
◆ SHGs typically consist of 15-20 members and each member is required to save and pool (collect) in their resources.
◆ The SHGs are constituted to provide loans to its members at a reasonable rate.
◆ After a year or two and with regular savings, the group is eligible to take loans from banks.
◆ SHGs seek loans from banks for its member collectively and meet the needs of buying assets, machinery, raw materials, construction or repair.
◆ SHGs also meet regularly to discuss and act on various social issues like dowry, domestic violence, child marriage, health, nutrition, etc.
Question. Why are service conditions of formal sector loans better than informal sector ? Explain.
Answer : Service conditions provided by formal sector loans are better than informal sector loans because
◆ Formal sources of credit provide cheap and affordable credit without any undue exploitation.
◆ People in rural areas take credit from moneylenders and traders (informal sector) who charge very high rate of interest.
◆ Informal sector exploit the borrowers leading to debt traps.
◆ Formal sector is mainly supervised by the Reserve Bank of India. So, every clause is in writing and clear to comprehend. Whereas, no external organisation supervises informal sector. So, there is no such written clause.
Question. Examine any three situations in which credit pushes the borrower into a debt-trap.
Answer : Three situations in which credit pushes the borrower into a debt-trap are
(i) When a borrower sells the agricultural produce to repay a loan but it may not be enough. Then more credit is taken to repay the entire amount which pushes the borrower into debt trap.
(ii) When borrowers depend on informal sources of credit who charge a high rate of interest. This increases the repayment amount and new loans have to be taken to repay the earlier ones.
(iii) In high risk situations, for example, farmers taking credit before sowing of crops. If harvest fails then fresh loans are taken to repay the existing loans leading to debt-trap.
Question. How do demand deposits have the essential features of money? Explain.
Answer : Demand deposits have the essential features of money in the following ways
◆ Demand deposits can be withdrawn from the bank whenever it is required.
◆ Demand deposits are widely accepted as a means of payment, along with the currency, thus they are considered as money.
◆ Demand deposits are also accepted widely as means of payment by way of a cheque instead of cash.
Question. Explain any three reasons for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas.
Answer : Banks and cooperatives are needed to increase their lending facilities in rural areas because
(i) People in rural areas take credit from moneylenders and traders who charge very high rate of interest. These people must be aware about the role of banks and cooperatives so that they can be provided by cheap credit facilities.
(ii) Rural people are exploited by using unfair means thus, leading them to debt traps. To reduce the dependence of informal sector in rural areas, there is need for setting up of more banks.
(iii)Formal sources of credit provide cheap and affordable credit in rural areas without any undue exploitation. These formal sources will serve as a building block for rural households. This will help the people to start up their small business or trade in certain goods.
Question. Explain the role of credit for economic development.
Answer : The role of credit for economic development is
◆ A country’s growth and economic development is greatly dependent on cheap and affordable credit system. Different kinds of economic activities need credit like to set up business for investment purpose, and also buying new house, cars and so on.
◆ Mostly manufacturing units need a huge amount of money to buy raw materials for their production process. Thus, credit here helps to make such manufacturing works easy.
◆ Cheap, affordable and fast credit system helps farmers to buy new and advanced technology for agricultural practices, e.g. tractors, threshers, fertilisers, new and advanced seeds (HYVs) and so on.
Question. Explain any three reasons for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas.
Answer : Banks and cooperatives water should be there landing facility in rural area for the following reason.
The the section of the society can get a greater share of formal credit and prosper.
The depends on money lenders and traders who charge extra ordinary high rate decrease.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. In what ways does the Reserve Bank of India supervise the functioning of banks ? Why is this necessary ?
OR How does Reserve Bank of India play crucial role in controlling the formal sector loans.
Answer : Reserve Bank of India (RBI) supervises the functioning of the banks in the following manner :
(i) First of all RBI determines the necessary reserve ratios for the banks such as Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) to be maintained by them. The reserves are maintained by the banks to deal with the liquidity crunch if that may ever arise. These reserves are calculated on the basis of the deposits with the banks.
(ii) The banks have to periodically submit reports with RBI regarding the credit portfolio. They have to ensure that they do not breach any of the instructions given by RBI on the management of credit portfolio. This helps the RBI to contain any risk situations that may emerge due the lending practices of the banks. (iii) RBI also ensures that the banks are not being partial in providing loans : It means that RBI ensures that the banks are lending not only to the big businessmens or companies but also taking care of the weaker sections of the society like small farmers and agricultural labourers in rural areas and small businessmen, labourers, small artisans etc. in urban areas. Lending to such weaker sections may be included in priority sector lending of the banks. (iv) The RBI may supervise the expansion pattern of the banks in order to ensure that the banks are not only opening their branches in urban areas only but also expanding their facilities in rural and remote areas like hilly areas of the country.
Question. ‘‘Self Help Groups’ help borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral.’’ Examine the statement.
OR How is the concept of Self Help Groups important for poor people ? Give your view point.
Answer : ‘‘Self Help Groups’’ help borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral. We explain the system of working by ‘‘Self Help Groups’’. (i) In a self help group most of the important decisions regarding the savings and loan activities are taken by the group members. (ii) Group members are well known to each other. They belong to the same society. (iii) Also, it is the group which is responsible for the repayment of the loan. (iv) Any case of non-repayment of loan by any member is followed up seriously by other members in the group. (v) Due to this feature, banks are willing to lend to the poor woman when organised in SHGS, even though they have no collateral as such.
Question. Raman is a leading businessman of the city. He wants to expand his business. Why do you think he will get loan from banks ?
Answer : Following are the various reasons which indicate that there is a great possibility of Raman getting loans from formal sources like bank :
(i) As Raman is a leading businessman of the city, he may be rich. The richer sections of the society are comparatively better educated and they can understand very well the formal procedures of getting credit from the formal sources of credit. (ii) The richer sections of the society have proper documents, guarantees or collateral which they can offer to the bank or any other institution. Poor sections generally lack all such things. (iii) The richer sections of the society have better repayment capacity. So, their chances of back tracking on the repayment are lesser. In the case of poor sections such chances of failure of repayments may be higher.
(iv) The richer sections of society have regular interactions with the formal sector institutions in terms of deposits and withdrawals. Such kind of interaction increases the trust of the formal sector in richer sections of the society. So, the above mentioned are some of the reasons which indicate that Raman may get loan from a bank easily.
Question. Why are banks necessary for a country ?
Answer : Banks provide a “Yeoman Services” to a country. The modernisation of any economy has been possible with the development of banking system of that country. Following are the reasons which justify the necessity of banks for a country :
(i) Banks mobilise the dormant savings of the country. The surplus money which the people have and don’t need in the near future is accepted by the banks as deposits.
(ii) These deposits of the public provide safety to their funds and income in the form of interest.
(iii) People can withdraw this money whenever they are in need. So these deposits give liquidity to the depositors.
(iv) Banks provide loans to the needy borrowers.
(v) Banks provide loans to the people out of the money deposited by the depositors. This way the banks acts the role of financial intermediary.
(vi) Most of the credit issued by the banks is used for productive purposes which increase the production and employment opportunities in the economy.
(vii) Banks provide such kind of credit services not only to general people, but participate in government loans as well. So this way banks help the government in the development of infrastructural facilities.
Question. Name two formal and two informal sources of credit in India. State advantages of formal and informal sources of credit.
Answer : Two formal sources of credit are bank and cooperatives and two informal sources of credit are moneylenders and traders. The advantages of formal sources of credit are
◆ It provides loans at a fixed rate and terms.
◆ It gives loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries and small borrowers etc.
◆ Cost of borrowing is less and hence promote borrowing and more economic growth.
◆ There is no exploitation as in the case with the informal sectors.
The advantages of informal sources of credit are
◆ There is no external control over the lending practices.
◆ It is suitable for poor households as they didn’t have to follow a certain kind of procedure which is required in formal sources of credit.
Question. Which government body supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans in India? Explain its functioning.
OR
Describe the functions of the Reserve Bank of India.
OR
Describe the significiance of the Reserve Bank of India.
Answer : The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans in India.
Functions or significance of Reserve Bank of India are
◆ The RBI monitors that the banks actually maintain the cash balance and do not give all the deposits as loans
◆ The RBI ensures that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and rich traders, but also to small cultivators, small scale industries, small borrowers, etc.
◆ Periodically, banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom, etc.
◆ The rate of interest charged on loans given by the banks is decided by the Reserve bank.
◆ In this way, the RBI keeps a check on all the activities of banks and checks the flow of credit also.
Question. Mohan works at a construction site in a sub-urban area while Sudhir is a marketing manager in a company. Both want credit to buy a home. Create a list of arguments explaining who has more possibility of getting a home loan from formal sector.
Answer : Sudhir has more possibility of getting a home loan from the formal sector due to the following arguments
◆ Formal sector consists of banks and cooperatives. Banks require proper documentation and collateral. In the above case, Sudhir will be able to provide the necessary documents like salary slip, employment record and other documents that are needed by the banks.
◆ Banks also require collateral security which can be provided by Sudhir since his economic condition is better. Even if he is not able to provide collateral security then bank can retain the ownership papers of the house as collateral security.
◆ Since Sudhir has a regular source of income, he is in a better position to repay the loan amount in future. But Mohan will not be able to provide proper documents or collateral security so he has to depend on informal sector for credit needs.
Question. Manav needs a loan to set up a small business. On what basis will Manav decide whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender ? Discuss.
Answer : In order to decide whether to take loan from a bank or moneylender, Manav has to give attention to the following factors :
(i) Availability of banks in the area : Only when banks are available in the area, Manav can take loan from it. Otherwise he will have to resort to a moneylender.
(ii) Availability of necessary documents and collateral : If Manav has got necessary documents and collateral, only then he can take loan from the bank. Otherwise he will have to go to moneylender. Moneylenders may sometimes lend without collateral and documents if they know the borrower personally.
(iii) Rate of Interest : If Manav does not want to pay higher rate of interest then he will have to take loan from the bank because the moneylenders charge very high rate of interest.
(iv) Other terms and conditions : Other terms and conditions like time of loan, mode of repayment etc. are some other factors which he may have to consider before taking loans because banks may not be very flexible in terms and conditions while moneylenders may be.
Question. What are Self Help Groups ? How do they work ? Explain.
Answer : Self Help Groups are the organisations of the rural poor, people of same socio-economic background to pool their savings and provide loans to their members. Work of self-help groups :
(i) Generally self help groups consist of 15 – 20 members.
(ii) Members belong to one neighbourhood. (iii) They meet regularly. (iv) Their savings varies form ` 25 to ` 100 or more. (v) Only members can take loans from the group itself. (vi) The group charges interest less then the moneylenders. (vii) All the important decisions regarding savings and loans are taken by the members of the group. (viii) The group is collectively responsible for the repayment of the loan. (ix) The regular meeting of the group provides a platform to discuss and act as a variety of social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence etc.
Case Based Questions
Question. Read the following case and answer the questions that follow
Source A Informal Credit
Compared to the formal lenders, most of the informal lenders charge a much higher interest on loans. Thus, the cost to the borrower of informal loans is much higher. Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan.
(i) To what extent, do you agree that credit from informal sector is not good for borrowers?
Answer : Yes, credit from informal sector is not good for the borrowers as the rate of interest charged by the informal lenders is so high that a larger part of income of the borrowers goes to interest payment which results in debt-trap or more poverty.
Source B Currency
Unlike the things that were used as money earlier, modern currency is not made of precious metal such as gold, silver and copper. And unlike grain and cattle, they are neither of everyday use. The modern currency is without any use of its own.
(ii) Why modern currency is not like the earlier forms of currency like grain or cattle?
Answer : Modern form of currency is unlike earlier forms of currency as Grain and cattle even when they were not used as currency had value of its own. On the other hand, modern currency if not authorised by Reserve Bank of India, becomes an ordinary piece of paper as it has no value of its own.
Source C Loan Activities of Bank
There is an interesting mechanism at work here. Banks keep only a small proportion of their deposits as cash with themselves. For example, banks in India these days hold about 15 per cent of their deposits as cash.
(iii) In the above lines, which function of the bank is highlighted?
Answer : The function of giving loans is highlighted here. Banks after keeping 15% of their deposits as cash, extend the rest of the deposits to people as loans.

