Electrochemistry Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions
Please refer to Electrochemistry Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 3 Electrochemistry in NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry
All Electrochemistry Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of Standard 12 Chemistry. Please learn them and let us know if you have any questions.
Very Short Answer Questions :
Question. E0cell of the following reaction is 0.59 V.
A(s) + B2+ (aq) <———> A2+ (aq) + B (s)
Calculate its equilibrium constant.
Answer:For the given reaction, n=2
nFEo=2.303 RT log K
n=2 , Eo= 0.59V
log K = nEo/0.0591
log k = 2
K=100
Question. A solution of copper sulphate is electrolysed between platinum electrodes using a current Of 5.0 A for 20 min. What mass of copper will be deposited at the cathode.
[ Atomic mass of Cu=63.5 u ]
Answer:Charge (C) = Current (A) × time (s)
= 5A x 20×60 = 6000C
Cu +2 + 2e– → Cu
Means I mol copper formed when 2 mol of electrons passes through the sample.
So charge on two moles electrons = 2×96500 C
So 2×96500 C charge deposit Cu = 63.5 g Cu

charge deposited = 1.974 g of Cu
Question. Give the units of equivalent conductivity and molar conductivity. How equivalent conductivity And molar conductivity of Al2(SO4)3 are related?
Answer:Molar conductance= S cm2mol-1
Equivalent conductance = S cm2eq-1
M. cond. = 6×Eq. cond.
Question. The conductivity of 0.001028 M of acetic acid is 4.95×10-5 S cm-1 . Calculate its dissociation constant if molar conductance for acetic acid is 390.5 S cm2 mol-1.
Answer:
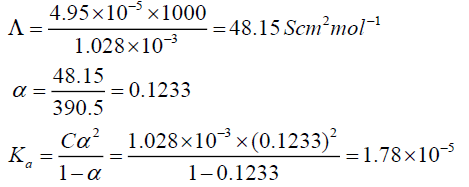
Question. What is galvanic cell ? Explain the working of a galvanic cell by taking the example of Zn/CuSO4 reaction. ?
Answer:The devices in which electrical energy is produced from chemical reactions are called Galvanic cells.The arrangement consists of two beakers one contain copper sulphate
solution and other contain zinc sulphate solution.a zinc rod is dipped in zinc sulphate solution while a copper rod is dipped in copper sulphate solution.both solutions are in contact by means of salt bridge.when electric current flows through the circuit following obsevations are made :
1.Zinc rod loses its weight
2.The concentration of Zn+2 in the zinc sulphate solution increases
3.Copper gets deposited on the electrode.
4.The concentration of Cu+2 in copper sulphate solution decreases.
5.Electric current follows from copper to zinc.
Question. A cell in which following reaction occurs.
Al + Fe2+ (0.02 M) —————-→ Al3+ (0.01 M) + Fe
Find the following
a) Show the cell representation for the above reaction
b) Find EOcell
c) Find Ecell
d) Find the change in gibbs free energy for the above reaction.
[Given:- EO(Al3+/Al)= – 1.66 V, EO(Fe2+/Fe)= -0.44 V]
Answer:
a) Al(s) | Al3+ (0.01 M) || Fe2+ (0.02 M) |Fe(s)
b) EOCELL = 1.22 V
c) Ecell = 1.209 V
d) ΔG= -700.01 KJ
:E0 cell= E0cathode – E0 anode =-.44+1.66=1.22 V
: Ecell = E0cell-(0.0591/n) log [{Al3+ (0.01M)}2/ {Fe2+ (0.02 M)}3 ]
n=6
: ΔG= -nFE cell
N=6 , F=96500 C.
Question. Determine the value of equilibrium constant (Kc) and ΔG° for the following reactions :
Ni(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Ni2+(aq) + 2Ag(s), E° = 1.05 V (1 F = 96500 C mol–1)
Answer :

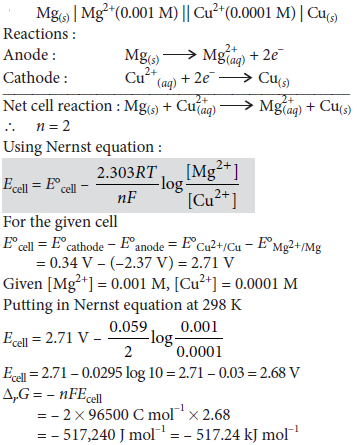
Question. Calculate e.m.f and ΔG for the following cell
Mg(s) | Mg2+ (0.001 M) || Cu2+ (0.0001 M) | Cu(s)
E°(Mg2+/Mg) = – 2.37 V, E°(Cu2+/Cu) = − 0.33 V
Answer :
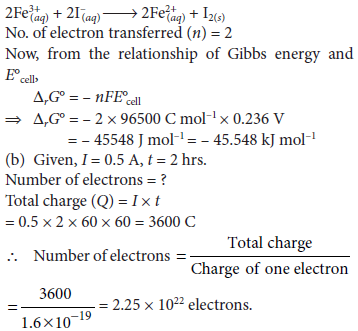
Question. (a) The cell in which the following reaction occurs :
2Fe3+(aq) + 2I–(aq) → 2Fe2+(aq) + I2(s)
has E°cell = 0.236 V at 298 K. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy of the cell reaction.
(Given : 1 F = 96,500 C mol–1)
(b) How many electrons flow through a metallic wire if a current of 0.5 A is passed for 2 hours? (Given : 1 F = 96,500 C mol–1)
Answer : (a) Given cell reaction is
Question. (i) Formulate the electrochemical cell representing the reaction ;
2Cr(s) + 3Fe2+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3Fe(s)
(ii) Calculate E°cell.
(iii) Calculate Ecell at 25°C if
[Cr3+] = 0.1 M and [Fe2+] = 0.01 M
Given :
E°Cr3+/Cr = – 0.1 74 V, E°Fe2+/Fe = − 0.44V
Answer :
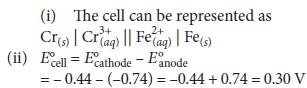
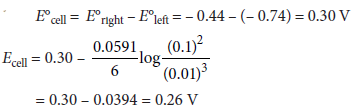
Question. Write the name of the cell which is generally used in hearing aids. Write the reactions taking place at the anode and the cathode of this cell.
Answer : (i) The cell can be represented as


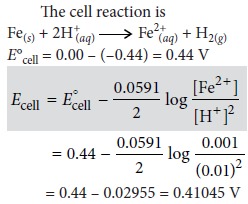
Question. Calculate emf of the following cell at 25°C:
Fe | Fe2+(0.001 M)||H+(0.01 M)|H2(g)(1 bar)|Pt(s)
E°(Fe2+|Fe) = –0.44 V, E°(H+|H2) = 0.00 V
Answer :
Question. Formulate the galvanic cell in which the following reaction takes place :
Zn(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
State :
(i) Which one of its electrodes is negatively charged.
(ii) The reaction taking place at each of its electrode.
(iii) The carriers of current within this cell.
Answer : The cell reaction is
Zn(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
The cell is represented as
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Ag2+(aq) | Ag(s)
(i) Anode i.e., zinc electrode will be negatively charged.
(ii) At anode :
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e– (oxidation)
At cathode :
Ag+(aq)+ e– → Ag(s) (Reduction)
(iii) Ions are the carriers of current within the cell.
Question. Write the name of the cell which is generally used in inverters. Write the reactions taking place at the anode and the cathode of this cell.
Answer : The cell which is generally used in inverters is secondary cell i.e., lead storage battery.
Question. Calculate e.m.f. of the following cell at 298 K 2Cr(s) + 3Fe2+(0.1M) → 2Cr3+(0.01M) + 3Fe(s)
Given : E°(Cr3+|Cr) = –0.74 V, E°(Fe2+|Fe) = –0.44 V
Answer :

Short Answer Questions :
Question. Define the following term : Limiting molar conductivity
Answer : The limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte is defined as its molar conductivity when the concentration of the electrolyte in the solution approaches zero.
Conductivity of an electrolyte decreases with dilution because the number of current carrying particles .e., ions present per cm3 of the solution becomes less and less on dilution.
Question. Silver is uniformly electrodeposited on a metallic vessel of surface area of 900 cm2 by assing a current of 0.5 ampere for 2 hours. Calculate the thickness of silver deposited.
Given : the density of silver is 10.5 g cm–3 and atomic mass of Ag = 108 amu.
Answer : Calculation of mass of Ag deposited
The electrode reaction is Ag+ + e– → Ag
The quantity of electricity passed = Current × Time = 0.5 (amp) × 2 × 60 × 60 (sec) = 3600 C
From the electrode reaction, it is clear that 96500 C of electricity deposit Ag = 108 g
3600 C of electricity will deposit Ag
= 108/96500 × 3600 = 4.03 g
Calculation of thickness :
Let the thickness of deposit be x cm
Mass = volume × density = Area × thickness × density
[∴ volume = area × thickness]
∴ 4.03 g = 900 (cm2) × x (cm) × 10.5 (g cm–3)
∴ x = 4.03/900 x 10.5 cm = 4.26 × 10–4 cm.
Question. Write two advantages of H2 — O2 fuel cell over ordinary cell.
Answer : (i) It is pollution free.
(ii) It has high effciency of 70 – 75% and its rate can be controlled.
Question. State and explain Kohlrausch’s law.
Answer : Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions : It states that limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte.
If λ°Na+ and λ°Cl– are limiting molar conductivities of the sodium and chloride ions respectively then the limiting molar conductivity for sodium chloride is given by
Λ°m(NaCl) = λ°Na+ λ°Cl–
Kohlrausch’s law helps in the calculation of degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte like acetic acid.
The degree of dissociation a is given by
α = Λm /Λ°m
where Λm is the molar conductivity and Λ°m is the limiting molar conductivity.
Question. Define conductivity and molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Discuss their variation with concentration.
Answer : The reciprocal of resistivity is known as specific conductance or simply conductivity. It is denoted by k (kappa).
k = 1/p or k = G X l/a
Hence, conductivity of a solution is defined as the conductance of a conductor of 1 cm length and having 1 sq. cm as the area of cross section. Alternatively, it may be defined as conductance of one centimetre cube of the solution of the electrolyte. Molar conductivity of a solution at a dilution V is the conductance of all the ions produced from 1 mole of the electrolyte dissolved in V cm3 of the solution. It is represented by Λm.
Λm = kV
Variation of conductivity and molar conductivity with concentration : Conductivity always decreases with decrease in concentration, for both weak and strong electrolytes. Because the number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.

Molar conductivity increases with decrease in concentration. Because that total volume, V, of solution containing one mole of electrolyte also increases. It has been found that decrease in k on dilution of a solution is more than compensated by increase in its volume.
Question. The resistance of a conductivity cell when filled with 0.05 M solution of an electrolyte X is 100 ohms at 40°C. The same conductivity cell filled with 0.01 M solution of electrolyte Y has a resistance of 50 ohms. Te conductivity of 0.05 M solution of electrolyte X is 1.0 × 10–4 S cm–1. Calculate
(i) Cell constant
(ii) Conductivity of 0.01 M Y solution
(iii) Molar conductivity of 0.01 M Y solution
Answer :

Question. What type of a battery is lead storage battery?
Write the anode and cathode reactions and the overall cell reaction occurring in the operation of a lead storage battery.
Answer : Lead storage battery is a secondary cell.
Cell reactions during operation

Question. Define the term degree of dissociation. Write an expression that relates the molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte to its degree of dissociation.
Answer : The fraction of the total number of molecules present in solution as ions is known as degree of dissociation.
Molar conductivity (Λm) = aλ°m
where λ°m is the molar conductivity at infinite dilution.
Question. How many coulombs are required to reduce 1 mole Cr2O72– to Cr3+?
Answer : The given reaction is
Cr2O72– + 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
one mole Cr2O72– requires 6 mol of electrons for reduction. Hence, quantity of electricity required
= 6 mol × 96500 C mol–1= 5.79 × 105 coulomb
Question. Mention the reactions occurring at (i) anode, (ii) cathode, during working of a mercury cell. Why does the voltage of a mercury cell remain constant during its operation?
Answer : Mercury Cell : It is a miniature cell which finds a frequent use these days to supply energy for watches, video cameras, hearing aids and other compact devices. In mercury cell the anode is zinc-mercury amalgam, and the cathode is a paste of mercury (II) oxide and carbon, electrolyte is a moist paste of KOH – ZnO.
The cell reactions are as follows :
Anode :

The cell potential remains constant during its life as the overall reaction does not involve any ion in solution whose concentration can change during its use.
Question. Express the relation between conductivity and molar conductivity of a solution held in a cell?
Answer : Λm M = k X 1000/M in CGS units
Λm = k X 10−3/M in SI units
where k is the conductivity, M is the molar concentration and Λm is molar conductivity.
Question. Write the reactions taking place at cathode and anode in lead storage battery when the battery is in use. What happens on charging the battery?
Answer : The lead storage battery is most important secondary cell. The cell reactions when the battery is in use :
At anode:

Question. Name the type of cell which was used in Apollo space programme for providing electrical power.
Answer : H2 — O2 fuel cell was used in Appollo space programme.
Question. (a) Define molar conductivity of a solution and explain how molar conductivity changes with change in concentration of solution for a weak and a strong electrolyte.
(b) The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is 1500 W. What is the cell constant if the conductivity of 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is 0.146 × 10–3 S cm–1?
Answer : (a) Molar Conductivity : Molar conductivity of a solution at a dilution V is the conductance of all the ions produced from one mole of the electrolyte dissolved in V cm3 of the solution when the electrodes are one cm apart and the area of the electrodes is so large that the whole solution is contained between them.
Λm = kV
It units is S cm2 mol–1
Strong electrolyte : The molar conductivity of strong electrolyte decreases slightly with the increase in concentration. This increase is due to increase in attraction as a result of greater number of ions per unit volume. With dilution the ions are far apart, interionic attractions become weaker and conductance increases.
Weak electrolyte : When the concentration of weak electrolyte becomes very low, its degree of ionisation rises sharply. There is sharp increase in the number of ions in the solution. Hence the molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte rises steeply at low concentration.

(b) Here, conductivity (k) = 0.146 × 10–3 S cm–1,
resistance (R) = 1500 Ω
Cell constant = Conductivity/Conductance
= Conductivity × Resistance
= k × R ∴ conductance = 1/resistance
= 0.146 × 10–3 × 1500 = 0.219 cm–1
Question. (a) State Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions. Write an expression for the molar conductivity of acetic acid at infinite dilution according to Kohlrausch’s law.
(b) Calculate L°m for acetic acid.
Given that
∧°m(HCl) = 426 S cm2 mol–1
∧°m(NaCl) = 126 S cm2 mol–1
∧°m(CH3COONa) = 91 S cm2 mol–1
Answer : Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions : It states that limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte.
If λ°Na+ and λ°Cl– are limiting molar conductivities of the sodium and chloride ions respectively then the limiting molar conductivity for sodium chloride is given by
Λ°m(NaCl) = λ°Na+ λ°Cl–
Kohlrausch’s law helps in the calculation of degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte like acetic acid.
The degree of dissociation a is given by
α = Λm /Λ°m
where Λm is the molar conductivity and Λ°m is the limiting molar conductivity.

Question. Write the anode and cathode reactions and the overall reaction occurring in a lead storage battery.
Answer : Lead storage battery is a secondary cell.
Cell reactions during operation

Question. What is a nickel-cadmium cell? State its one merit and one demerit over lead storage cell.
Write the overall reaction that occurs during discharging of this cell.
Answer : Nickel cadmium cell is a secondary battery which consists of a cadmium anode, nickel hydroxide as cathode and sodium or potassium hydroxide acts as electrolyte.
Merit : It has longer life than lead storage battery.
Demerit : It is more expensive than lead storage battery.
The following reaction takes place during discharging :
Cd(s) + 2Ni(OH)3(s) → CdO(s) + 2Ni(OH)2(s) + H2O(l)
Question. A solution of CuSO4 is electrolysed for 10 minutes with a current of 1.5 amperes. What is the mass of copper deposited at the cathode?
Answer :

Question. State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
Answer : The limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte is defined as its molar conductivity when the concentration of the electrolyte in the solution approaches zero.
Conductivity of an electrolyte decreases with dilution because the number of current carrying particles .e., ions present per cm3 of the solution becomes less and less on dilution.
Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions : It states that limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte.
If λ°Na+ and λ°Cl– are limiting molar conductivities of the sodium and chloride ions respectively then the limiting molar conductivity for sodium chloride is given by
Λ°m(NaCl) = λ°Na+ λ°Cl–
Kohlrausch’s law helps in the calculation of degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte like acetic acid.
The degree of dissociation a is given by
α = Λm /Λ°m
where Λm is the molar conductivity and Λ°m is the limiting molar conductivity.
Question. What type of battery is mercury cell? Why is it more advantageous than dry cell?
Answer : Mercury cell is a primary battery. Hence, it can be used only once and cannot be recharged.
Advantage : The cell potential remains constant during its life time. Hence, it is useful for devices requiring constant current e.g., hearing aids and watches.
Question. Express the relation between the conductivity and the molar conductivity of a solution.
Answer : Λm M = k X 1000/M in CGS units
Λm = k X 10−3/M in SI units
where k is the conductivity, M is the molar concentration and Λm is molar conductivity.
