Production and Costs Class 12 Economics Important Questions
Please refer to Production and Costs Class 12 Economics Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 3 Production and Costs in NCERT Book for Class 12 Economics have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 12 Economics for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 12 Economics Chapter 3 Production and Costs
All Production and Costs Class 12 Economics Important Questions provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of Standard 12 Economics. Please learn them and let us know if you have any questions.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is the relation between average and marginal product when average product is falling?
Answer : MP falls but it falls at faster rate than AP
Question. What do you mean by fixed factors of production? Give example.
Answer : These factors of production which cannot be varied in short period e.g. machine, land.
Question. How does fall in total product affects marginal product?
Answer : When total product falls, marginal product becomes negative.
Question. Define explicit costs.
Answer : Those monetary payments by producer on factor and non factor payments is called explicit cost. Which are not owned by himself.
Question. What do you mean by implicit costs?
Answer : Implicit cost is the cost of self owned resources of producer.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Distinguish between change in quantity supplied and change in supply.
Answer :
| Change in quantity supplied | Change in supply |
| 1. It refers the change in supply due to change in price of the good. | 1. It refer’s the change in supply due to the change in the determinents of supply other |
| 2. Determinents of supply other than price remains unchanged. | 2. Price of the good remains unchanged. |
| 3. Law of supply apply. | 3. Law of supply does not apply. |
| 4. There is upward and downward movement along with supply curve in this situation. | 4. supply curve shifted to leftward or rightward under this condition. |
Question. Explain how changes in prices of other products influence the supply of a given product.
Answer : The supply of a good is inversly influenced with the change in price of other product which can explain as fallows.
A. Rise in price of other product :– When there is rise in the price of other product the production of these product become more profitable due to unchanged cost in comparison of the production of given produce. As a result the producer will produce more quantity of other product so the supply of given good will decrease.
B. Fall in the price of other product :– When there is fall in the price of other product the production of these product become less profitable due to unchanged cost in comparison of the production of given product. As a result producer will produce less quantity of other product so the factors of production shifted for the production of given good. It cause an increase in supply of given good.
Question. Explain the law of variable proporation with the help of diagram schedule.
OR
What is the likely behaviour of total product/marginal product when only one input is increased for increasing production? Use diagram/ schedule.
Answer : Law of variable proportion state the inpact of change in unit of a variable factor on the physical output. When more and more unit of a variable factor combined with fixed factor physical product passes though following phases.
Behaviour of TP
(i) TP increases at an increasing rate
(ii) TP increases at diminishing rate
(iii) TP falls
Behaviour of MP
(i) MP increases and becomes maximum.
(ii) MP decreases and becomes zero.
(iii) MP becomes negative.
| Machine | Unit of labour | TPP | MPP |
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 1 | 2 | 7 | 4 |
| 1 | 3 | 12 | 5 |
| 1 | 4 | 16 | 4 |
| 1 | 5 | 19 | 3 |
| 1 | 6 | 21 | 2 |
| 1 | 7 | 22 | 1 |
| 1 | 8 | 22 | 0 |
| 1 | 9 | 21 | -1 |
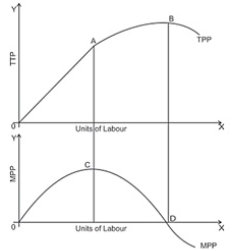
1. First Phase :– TPP increases with increasing rate upto A point. MPP also increase and becomes maximum of point C.
2. Second Phase :– TPP increases with diminishing rate and it is maximum on point B.
MPP start to decline and becomes zero at D point.
3. Third Phase :– TPP starts to decline and MPP becomes negative.
• Important instruction for giving the answer of above question.
• Do not use diagram for the explaination of this question if it is instructed to use schedule and do not use schedule if the explaination of this question asked with the help of diagram.
• Do not explain the behaviour of marginal product with the help of schedule and diagram. If there is instruction to explain only the behaviour of total product.
• Do not explain the behaviour of total product with help of schedule and diagram if there is instruction to explain only the behaviour of marginal product.
Question. What do you understand by returns to factor? Why do diminishing returns to a factor operate?
Answer : Returns to a factor relates to the behavior of total output as one variable input say labour is varied. It is a short run concept. There are three aspects of returns to a factor.
1. Increasing Returns to a factor,
2. Constant Returns to a Factor, and
3. Diminishing Returns to a Factor.
Diminishing returns to a factor may occur due to following reasons:-
1. Fixity of the factor: As more and more units of the variable factor continue to be combined with the fixed factor, the later gets over-utilized.
2. Imperfect Substitution among Factor: Beyond a certain limit, factors of production can not be substitute for one another e.g. more and more of labour cannot be continuously used in place of additional capital.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. All the inputs used in production of a good are increased simultaneously and in the same proportion. What are its possible effects on Total Product? Explain with the help of a numerical example.
Answer : The behaviour of total output in the long run time period is technically termed as Returns to Scale.
There are three possibilities:
1. Increasing Returns to Scale (IRS):- It occurs when a given proportionate increase in all factor inputs (in some constant ratio) causes proportionately greater increase in output.
For example: Suppose there are only two inputs, labour (L) and Capital (K). Suppose 1K + IL produce 100 units and 2K + 2Lproduce 250 units. Input rises by 100% while the output rises by 150%.
2. Constant Returns to Scale (CRS):- It occurs when a given proportionate increase in all factor inputs causes proportionately equal increase in output. At this stage, economies of scale are counter balanced by diseconomies of scale. For example, suppose 1K+1L produce 100 units and 2K+2L produce 200 units, both inputs and TP rise in the same proportion.
3. Diminishing Returns to Scale (DRS):- It occurs when a given proportionate increase in
all factor inputs causes proportionately lesser increase in output.
For example, Suppose 1K+1L produce 100 units and 2K+2L produce 190 units, inputs rise by 100% while the output rise by 90%.
Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question. Why is total variable cost curve parallel to total cost curve?
Answer : Total cost is the sum of total fixed cost and total variable cost. TFC remains constant
at all levels of output.
Question. Why is total fixed cost curve parallel to ox-axis.
Answer : TFC remains constant at all levels of output.
Question. What behaviour of per unit price will cause the equality of average and marginal
revenue.
Answer : Per unit price remains constant.
Question. What is the price elasticity of supply associated when the supply curve passing
through to intersect to x-axis?
Answer : Inelastic.
Question. What is the price elasticity of supply associated with when a supply curve passes
through the origin at 40° angle?
Answer : Equal to unity elastic.
Question. What effect does an increase in price of competitive good have on the supply of a commodity?
Answer : Supply of the commodity will fall.
