Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper Term 2 Set F
Please see below Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper Term 2 Set F with solutions. We have provided Class 10 Social Science Sample Papers with solutions designed by Social Science teachers for Class 10 based on the latest examination pattern issued by CBSE. We have provided the following sample paper for Term 2 Class 10 Social Science with answers. You will be able to understand the type of questions which can come in the upcoming exams.
CBSE Sample Paper for Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Set F
Section A
1. When and why was the Cripps Mission sent to India? Point out any two main defects responsible for its failure.
Answer : The Cripps Mission was sent to India in March 1942 under the chairmanship of Sir Stafford Cripps to win the co-operation of the Indian people in the Second World War. In fact, the position of the British in 1942 had become very precarious because of Hitler’s attacks so they wanted to enlist the cooperation of the Indians.
Cripps Mission talks failed because of the following defects :
(i) He rejected the Congress proposal for the formation of a national government during the war.
(ii) He was not prepared to give any assurance of granting independence to India even after the war.
As such, his proposals were rejected both by the Congress and the Muslim League.
2. Why did Mahatma Gandhi perceive salt as a powerful symbol that unite the nation ?
Answer : Gandhiji perceived salt as a powerful symbol that united nation because,
(a) Salt was something consumed by the rich and the poor alike.
(b) It was the most essential items of food.
(c) The tax on salt and the government monopoly over its production revealed the most oppressive face of the British rule.
3. Study the table given below and answer the questions that follow :
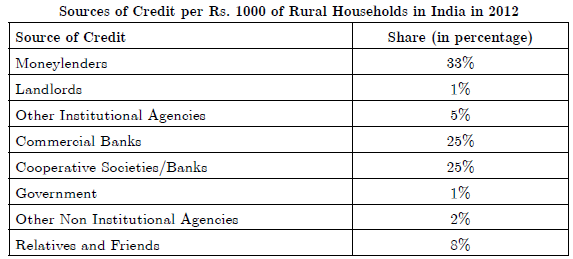
3.1. Which are the three major sources of credit for rural households in India ?
Answer : Moneylenders, Commercial Banks, and Cooperative Societies/Banks.
3.2. Moneylenders are the most dominant source of credit for rural households. Why ?
Answer : Moneylenders are the most dominant source of credit for rural households because they do not ask for a collateral and there is no need of complicated paper work or documentation for taking loan from them.
4. Why are MNCs keen on setting up offices and factories in developing countries ?
Answer : MNC are keen on setting up offices and factories in developing countries as they hope to get labour and other resources easily at cheaper rates. In such a situation the cost of production would be low and their changes of profit would greater.
5. Why is India preferred destination for setting of MNCs ?
Answer : India is preferred destination for setting up MNCs unit due to following reasons :
1. India has highly skilled engineers who can understand the technical aspects of production.
2. It has also educated English speaking youths who can provide customer care services.
3. India has cheap labour resources.
Section B
6. Name two major means of mass communication with two examples of each. Explain the main features of each type of communication.
Answer : Radio, television, newspapers, magazines, books and films are the main means of mass communication. The importance of radio and television as an effective means of communication in India is due to the factors as mentioned below :
(i) Radio and television provide entertainment to the people.
(ii) Programmes are broadcast in different languages for all types of people.
(iii) These create awareness among people about various national programmes and policies as debates are conducted an television and radio.
(iv) Doordarshan, the national television channel of India and one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world, broadcasts various types of programmes from entertainment, educational to sports.
OR
What are different classes of roadways ? Explain.
Answer : 1. Super highways : Golden Quadrilateral Super Highway is a major road development project linking Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai by sixlane super highways.
2. National highways : They link extreme parts of the country.
3. State highways : They link a state capital with different district headquarters.
4. District roads : They connect the district headquarters with other places of the district.
5. Other roads : In this category comes those roads which link rural areas and villages with towns.
6. Border roads : These roads are made near the international boundaries for easy transport of troops and goods.
7. Suggest three legal ways to reform political parties. Will legal solutions to political problems leave a healthy impact on political parties ?
Answer : (i) A law should be made to regulate the internal affairs of the political parties. It should maintain register of its members. It should follow its constitution. It should hold open elections to the highest post within the party.
(ii) A law should be made so that parties distribute one-third of contesting seats to women. Women should be given quota in the party’s decision-making body.
(iii) To check use of money for wrong, the state should fund money to the parties to meet election expenses. It can be given in form of kind or cash and there should be proper scrutiny of the expenses.
No, legal solution to every political problem will not work always. Over-regulation can be counter-productive. This will force parties to find ways to cheat the law. Also, they will not agree to pass a law that they do not like.
8. Do democracies lead to a just distribution of goods and opportunities ? Justify your answer by three suitable arguments.
Answer : No. Reasons in support of my answer are as under :
(i) Although individuals have political equality, we find growing economic inequalities. A small number of ultra-rich enjoy a highly disproportionate share of wealth and incomes.
(ii) The income of those at the bottom of the society is declining so much so that it becomes difficult to meet their basic needs, such as food, clothing, housing etc.
(iii) Although the poor constitute a large proportion of voters, yet democratically elected governments do not provide them opportunities on equal footing.
Section C
9. How did Gandhiji bring the masses into the National Movement ?
Answer : 1. Gandhiji’s simple saintly life and his style of convincing the masses in local languages made him extremely popular as a leader.
2. His undisputed leadership and magnetic personality helped to coordinate and unite the movement.
3. His policy of non-violent Satyagraha brought millions into the struggle. For example, the Champaran Satyagraha brought the peasants into the struggle.
4. He launched three powerful mass movements Non-Cooperation Movement, Civil Disobedience and Quit India. They influenced millions of Indians belonging to all sections of the society to show bravery, self-confidence and to take up revolutionary passive resistance against the British rule.
5. His new method of agitation like hartals, boycott, civil disobedience, non-payment of taxes, etc., appealed to the masses.
6. Under his guidance, Indians withstood brutal repression and willingly accepted imprisonment, lathi charges and bullets for the sake of freedom.
7. Through his programmes of social reform, charkha, cottage industries and his fight against untouchability; the Harijans and depressed classes joined the freedom struggle and these efforts provided millions with employment.
8. His deep commitment to Hindu-Muslim unity and his secular ideals persuaded every community to unite for the noble cause of freedom.
9. His support to the Ahmedabad mill workers’ strike in 1918 and his Satyagraha against the Rowlatt Act kept him in close touch with the masses. He became Father of the Nation.
10. He was the first Indian nationalist leader who identified his life and his manner of living with that of the common people and earned the title of ‘Mahatma’. He was only political thinker whose Gandhism got exclamation all over the world.
OR
Assess the role of Mahatma Gandhi in the National Movement with special reference to the methods adopted by him.
Answer : When India was ruled by the Britishers, the Indians were torched by them directly or indirectly. In such conditions Mahatma Gandhi to arrived here from South Africa. He studies the conditions thoroughly. He took the help of non-violence to improve the condition of Indians. He put his views before Indians. He put agitation before Britishers to reform the condition. Among all the movements led by Gandhiji following were important :
1. Salt March On 12 March 1930 Gandhiji started salt march from Sabarmati Ashram (Ahmedabad) to Dandi 240 kms the Costal belt of Gujarat. Thousands of people come to meet Gandhiji. This was the mark of Civil Disobedience Movement against British Government.
2. Champaran : Gandhiji launched the Satyagrah to inspire the peasants to struggle against the oppressive plantation system.
3. Kheda He launched the Kheda Satyagrah to support the peasants who were not in a position to pay the revenue due to the crop failure.
4. Role of women in the Civil Disobedience Movement : Gandhi had made a special appeal to women to present people from going to the shops selling foreign clothes and liquor. Women participated m protest marches. Rural women from rich families reach there and joined the movement. Again in 1918 A.D. Gandhiji intervened in the mill worker’s strike at Ahemedabad and helped them to get their pay raised for which he had started a fast unto death.
10. Describe five human factors responsible for the location of industries.
Answer : 1. Availability of raw material : The factory needs to be close to the location of raw materials if they are heavy and bulky to transport. For example, iron and steel and cement industries are located near the source of raw materials. It cuts down the cost of transportation.
2. Labour A large and cheap labour force IS required for labour-intensive manufacturing industries. High-tech industries have to locate where suitable skilled workers are available.
3. Power Power supply is needed for working of the machines in a factory. Earlier industries were near to coalfields. Today, electricity allows more freedom.
4. Capital This is the money that is invested to start the business. The amount of capital will determine the size and location of the factory.
5. Transport : A good transport network helps to reduce costs and made the movement of raw materials and finished goods easier.
6. Market : An accessible place to sell the products is essential.
7. Government policies Industrial development is encouraged in some areas and restricted in others. Industries that are located in deprived areas may receive financial incentives and assistance from the government in the form of low rent and tax rebates.
OR
Why is textile industry second largest after agriculture in India ? Explain the reasons.
Answer : Textile industry IS the second largest after agriculture due to the following reasons
1. Textile industry contributes significantly to industrial production (about 14 per cent).
2. It generates more employment (35 million persons directly).
3. Its foreign exchange earnings are about 24.6 per cent.
4. It contributes 4 per cent to our Gross Domestic Products (GDP).
5. It is the only industry in the country which is self-reliant.
Section D
11. Read the passage below :
Nannu is a daily wage earner. He lives in Welcome Mazdoor Colony, a slum habitation in East Delhi. He lost his ration card and applied for a duplicate one in January, 2004. He made several rounds of the local Food and Civil Supplies Office for the next three months. But the clerks and officials would not even look at him, leave alone do his job or bother to tell him the status of his application. Ultimately, when he filed an application under the Right to Information Act asking for the daily progress made on his application, names of the officials who were supposed to act on his application and what action would be taken against these officials for their inaction. Within a week of filing application under Right to Information Act, he was visited by an inspector from the Food Department, who informed him that the card had been made and he could collect it from the office. When Nannu went to collect his card next day, he was given a very warm treatment by the Food and Supply Officer (FSO), who is the head of a circle. The FSO offered him tea and requested him to withdraw his application under Right to Information, since his work had already been done. [Impact of Right]
Question:
11.1. What does Nannu ‘s example show ?
Answer : Nannu’s example show that Right to Information Act is very important, useful and it forces the government official and head of the department to initiate action on time promptly asa a part of duty.
11.2. What impact did Nannu’s action have on officials ?
Answer : The such offences in Food and Civil Supplies Department would strength the duty implementation applications of people like Nannu in future.
11.3. Ask your parents their experiences when they approach government officials to attend to their problems ?
Answer : I have asked my parents about their experiences when they approach government official to attend their problems. They told me that likewise carelessness is adopted by officials in each government department or offices. They make people wandering to and fro even for the matters that fall in their routine. But overall of somehow protect the right’s of civilian.
12. Read the sources given below and answer the questions that follow:
Source A : Production across countries
Until the middle of the twentieth century, production was largely organised within countries. What crossed the boundaries of these countries were raw material, food stuff and finished products. Colonies such as India exported raw materials and food stuff and imported finished goods. Trade was the main channel connecting distant countries. This was before large companies called Multinational Corporations (MNCs) emerged on the scene.
Source B : Foreign trade and integration of markets
Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets, i.e., markets of their own countries, Producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country but can also compete in markets located in other countries of the world. Similarly, for the buyers, import of goods produced in another country is one way of expanding the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced.
Source C : Impact of globalisation in India
Globalisation and greater competition among producers–both local and foreign producers–has been of advantage to consumers, particularly the well-off sections in the urban areas. There is greater choice before these consumers who now enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products. As a result, these people today, enjoy much higher standards of living than was possible earlier.
Question :
12.1. How are MNCs a major force in connecting the countries of the world ?
Answer : MNCs play an important role in the process of globalisation. They bring not only their products to a country but also the new business policies and cultures. They also help in increasing competitiveness among the Indian companies. At present, most of us are able to use the latest models of cars and this could be possible because of globalisation. Because of hordes of MNCs in our country, most of the urban Indians have become broad-minded in their outlook.
12.2. How does foreign trade become a main channel in connecting countries ?
Answer : The foreign trade becomes a main channel in connecting countries because trade in the past was restricted to finished goods being produced in one market, and sold in other markets. In today’s time, besides trade; capital, technology, people, and service flow is also taking place all over the world. Today, the world is connected in a way that even production takes place across different countries.
12.3. How is globalisation beneficial for consumers ?
Answer : The benefits of the globalisation for the consumers are given below :
(i) It created opportunities in terms of investment, employment for many developing and underdeveloped countries and brought about greater integration of economies.
(ii) It enhances choices to the consumers, brought about increased movement of goods, people, and ideas.
(iii) It has led to the establishment of many foreign brands in the country, widening our choices and created preferences.
(iv) It has expanded the scope of the market.
Section E
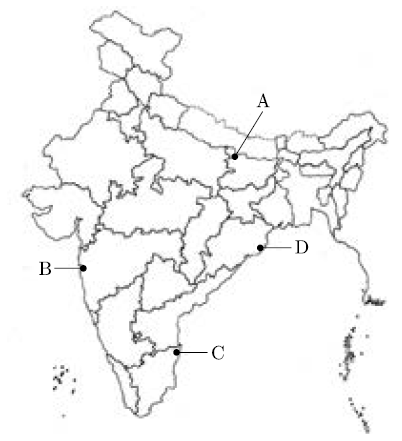
13. On the given outline Political Map of India, locate the following:
A. The place where the indigo planters movement took place
B. Mumbai Cotton Textile Industry
OR
C. Chennai Software Technology Park
D. Paradip Port
Answer : A. Champaran (Bihar)
B. Mumbai Cotton Textile Industry
OR
C. Chennai Software Technology Park
D. Paradip Port