Microbes in Human Welfare Class 12 Biology Important Questions
Please refer to Microbes in Human Welfare Class 12 Biology Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare in NCERT Book for Class 12 Biology have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 12 Biology for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare
All Microbes in Human Welfare Class 12 Biology Important Questions provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of Standard 12 Biology. Please learn them and let us know if you have any questions.
Objective Type Question
Question. Large holes in swiss cheese are due to bacterium
(a) Propionibacterium
(b) Streptococcus
(c) Diplococcus
(d) Sacchoromyces cerevisiae
Answer
A
Question. Dough kept overnight in warm weather becomes soft and spongy because of
(a) Cohesion
(b) Osmosis
(c) Absorption of careban dioxide from atmosphere
(d) Fermentation
Answer
D
Question. Cheese is prepared from
(a) Lactobacillus
(b) Streptococcus
(c) Myrothecium
(d) Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, and Leuconostoc
Answer
D
Question. The puffed up appearance of dough in bakery is due to
(a) CO2 production during fermentation by yeast
(b) CO2 production during aerobic respiratiom by yeast
(c) Death of yeast
(d) Spoiling of the dough due to death of yeast and production of many gases
Answer
A
Question. Lactic acid is produced by
(a) Lactobacillus bulgaricus
(b) Streptococcus lactis
(c) Rhizopus oryzae
(d) All the above
Answer
D
Question. The initial step in prepartion of beer is
(a) Malting
(b) Carboxylation
(c) Clarification
(d) Distillation
Answer
A
Question. Match the following list of microbes and their importance
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae | I. Production of immunosuppressive agents |
| B. Monascus purpureus | II. Ripening of swiss cheese |
| C. Trichoderma polysporum | III. Commercial production of ethanol |
| D. Propionibacterium sharmanii | IV. Production of blood cholesterol lowering agents |
Options :
(A) A – III, B – III, C – I, D – IV
(B) A – IV, B – II, C – I, D – III
(C) A – III, B – I, C – IV, D – II
(D) A – III, B – IV, C – I, D – II
Answer
D
Question. Enzymes can be immobilised by
(a) Cross linking enzyme to a solid support
(b) Covalently attaching to a solid support
(c) Entrapping them in gel
(d) All the above
Answer
D
Question. Sir Alexander Flemming extracted penicillin from
(a) Penicillum citrinum
(b) Penicillium notatum
(c) Penicillum chrysogenum
(d) Bacillus brevis
Answer
B
Question. Monascus purpureus is a yeast used commercially in the production
(a) Vitamin B Ethanol
(b) Streptokinase for removing clots from the blood vessels
(c) Citric acid
(d) Blood cholesterol lowering agent
Answer
D
Assertion-Reasoning MCQs
Direction : Each of these questions contains two statements, Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Each ofthese questions also has four alternative choices, any one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A (b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Question. Assertion (A) Primary treatment is also known as physical treatment.
Reason (R) It involves physical removal of small and large, floating and suspended solids from sewage through filtration and sedimentation.
Question. Assertion (A) The type of gas produced by microbes during their growth depends upon the microbes.
Reason (R) These bacteria are methanogens.
Question. Assertion (A) Chemical fertilisers are used in increasing amounts.
Reason (R) This results in an increased agricultural output.
Each of these questions contains two statements, Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, any one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) A is false, but R is true
Question. Assertion (A) Yeasts such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae are used in baking industry.
Reason (R) Carbon dioxide produced during fermentation causes bread dough to rise by thermal expansion.
Answer : (b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question. Assertion (A) Beer and wine are called soft liquours.
Reason (R) These beverages have lower percentage of alcohol.
Answer : (a)
Question. Assertion (A) Biogas is used as fuel for cooking and lighting.
Reason (R) It is considered as an ecofriendly and a pollution free source of energy.
Answer : (b)
Question. Assertion (A) Disadvantages of synthetic pesticides can be overcome by the use of biopesticides.
Reason (R) Biopesticides control weeds and pest without causing any damage to living organisms.
Answer : (a)
Question. Assertion (A) Chemical pesticides are preferred over biopesticides.
Reason (R) These are mostly expensive, hazardous and pollute the atmosphere.
Answer : (d)
Case Based MCQ
1. Direction Read the following passage and ans the questions that follows.
In modern agricultural system, the farmers have increased the use of chemicals such as insecticides, weedicides, etc., to control plant diseases and pests.
These chemicals however, are harmful and toxic for human beings, animals and have been polluting environment (soil, groundwater), fruits, vegetables and crop plants, with their increased use. Thus, it is better to use biological agents to save our crop plants from pests, etc. Biocontrol refers to the use of biological methods for controlling plant diseases and pests.
Question. Which of the following can be used as a biocontrol agent in the treatment of plant disease?
(a) Chlorella
(b) Anabaena
(c) Lactobacillus
(d) Trichoderma
Answer : (d)
Question. Bacillus thuringiensis is used as
(a) biofungicide
(b) biopesticide
(c) biocontrol agent
(d) bioweapon
Answer : (c)
Question. A biocontrol agent to be a part of an integrated pest management should be
(a) species-specific and symbiotic
(b) free-living and broad spectrum
(c) narrow spectrum and symbiotic
(d) species-specific and inactive on non-target organisms
Answer : (d)
Question. Which of the following statements is correct with reference to biocontrol agents?
(a) Ladybird and dragonflies help in getting rid of aphids and mosquitoes, respectively
(b) Nucleopolyhedrovirus are considered the best candidates to be the part of IPM
(c) Trichoderma are free-living fungi
(d) All of the above
Answer : (d)
Question. Assertion (A) Biocontrol refers to the use of biological methods for controlling pests and diseases.
Reason (R) Our dependence on toxins and chemicals will remain same even after introduction of biocontrol agents.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true, but R is false
(d) Both A and R are false
Answer : (c)
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
Villagers in a place near Chambur started planning to make power supply for agricultural purposes from cow dung. They have started a biogas plant for the purpose. Study the flow chart for biogas production given below and answer the following questions.
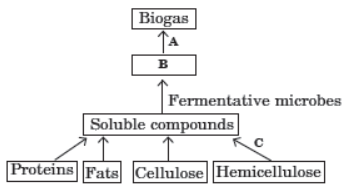
Question. What is represented by ‘B’ in the flow chart?
(a) Carbohydrates
(b) Protein polymers
(c) Organic acids
(d) Fat globules
Answer
C
Question. In the given flow chart, ‘A’ denotes
(a) aerobic bacteria
(b) methanogenic bacteria
(c) cellulose degrading bacteria
(d) yeast and protozoa.
Answer
B
Question. If ‘A’ is not added in the procedure
(a) methane will not be formed
(b) CO2 will not be formed
(c) organic compounds will not be converted to H2S
(d) O2 will not be formed.
Answer
A
Question. ‘C’ in the given flow chart causes
(a) aerobic breakdown of complex organic compounds
(b) anaerobic digestion of complex organic compounds
(c) fermentation of organic compounds
(d) fermentation of monomers.
Answer
B
Question. Biogas is composed of majorly
(a) methane, CO2 and O2
(b) CO2, H2S and H2O
(c) methane, CO2 and H2S
(d) H2S, H and O2.
Answer
C
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question numbers 51-60, two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Curdling is required in the manufacture of cheese.
Reason : Lactic acid bacteria and rennet is used for the purpose.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Acetic acid is prepared by acetic acid bacteria.
Reason : Alcoholic fermentation and the conversion of alcohol to acetic acid are aerobic processes.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Aspergillus niger produces lactic acid.
Reason : Aspergillus niger carry out fermentation.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : The alcoholic content of fortified wines are high.
Reason : The fermentation is stopped before all the sugars are being converted.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Champagne gives off bubbles.
Reason : Alcoholic content is 12 – 16% in champagne.
Answer
B
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is the economic value of Spirulina?
Answer : Spirulina is single cell protein (SCP), which is rich in high quality protein and is used for consumption as human food and animal feed.
Question. Name the enzyme produced by Streptococcus bacterium. Explain its importance in medical sciences.
Answer : Streptokinase is produced by bacterium Streptococcus. Streptokinase is modified by genetic engineering which is further used as a ‘clot bluster’ for removing clots from the blood vessels of the patients who have undergone myocardial infarction leading to heart attack.
Question. BOD of two samples of water A and B were 120 mg/L and 400 mg/L respectively. Which sample is more polluted?
Answer : Water body having high BOD is more polluted as compared to water body having low BOD. Hence water sample having BOD 400 mg/L is more polluted as compared to water sample having BOD 120 mg/L.
Question. List two advantages that a mycorrhizal association provides the plant.
Answer : Mycorrhiza perform following functions for the plant :
(i) Absorption of water and minerals like phosphorus from the soil and passing it to the plants.
(ii) Solubilisation of organic matter of the soil humus and their transfer to roots.
Question. Name the nutrient that gets enhanced while curdling of milk by Lactobacillus.
Answer : The curdling of milk by Lactobacillus changed milk into curd and its nutritional quality is enhanced due to increase in vitamin B12 content.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name a genus of baculovirus. Why are they considered good biocontrol agents?
Or Describe the role of Nucleopolyhedrovirus, in the integrated pest management programmes.
Answer : A genus of baculoviruses is Nucleopolyhedrovirus.
They are considered good biological control agents because of their species-specific and narrow spectrum insecticidal applications. They do not have any negative impact on plants, mammals, birds, fish or even on non-target insects.
Thus, making them useful in overall integrated pest management programme.
Question. Given below is a list of six microorganisms. State their usefulness to humans
(i) Nucleopolyhedrovirus
(ii) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
(iii) Monascus purpureus
(iv) Trichoderma polysporum
(v) Penicillium notatum
(vi) Propionibacterium shermanii
Answer : (i) Nucleopolyhedrovirus is widely used biopesticide in crop fields.
(ii) Saccharomyces cerevisiae commonly called brewer’s yeast, is used for fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices to ethanol.
(iii) Statins are produced by yeast, Monascus purpureus.
These have been commercialised as blood cholesterol lowering agents.
(iv) Cyclosporin-A is produced by the fungus,Trichoderma polysporum and it is used as an immunosuppressive agent in case of organ transplants.
(v) Penicillium notatum is used for the production of penicillin.
(vi) Propionibacterium shermanii is used to produce Swiss cheese.
Question. Following is the list of some commercially important products. Give the name of microorganisms responsible for producing each of these products.
(i) Citric acid
(ii) Acetic acid
(iii) Butyric acid
(iv) Lactic acid
Answer : Microorganisms (microbes) responsible for producing each of these products are (Image 32)
Question. Which enzymes play an important role in detergents that we use for washing clothes?
Answer : Enzymes like lipases are used in detergents formulations which causes breakdown of oils and thus help in removing oily and greasy stains from the clothes. These enzymes are obtained from Candida lipolytica and Geotrichum candidum.
Question. Why do organic farmers do not recommend eradication of insect-pests? Explain giving reason.
Answer : Organic farmers do not recommend eradication of insect-pests as without them, the beneficial predatory and parasitic insects which depend upon pests as food or hosts would not be able to survive.
Question. (i) How do organic farmers control pests? Give two examples.
(ii) State the difference in their approach from that of conventional pest control methods.
Answer : (i) The organic farmers control pests by the use of insect pests resistant varieties. The two examples are
(a) The Pusa Gaurav variety of Brassica is resistant to aphids.
(b) Pusa Sawani variety of okra is resistant to shoot and fruit borer.
(ii) The use of resistant variety is safer to control the pests as it does not involve chemical pesticides which are used in conventional method of controlling pests.
Thus, it is environmental friendly method and reduce soil pollution.
Question. Microbes can be used to decrease the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides. Explain how this can be accomplished.
Answer : Microbes can be used to decrease the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides as
(i) Microbes play an important role in organic farming, which reduce the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides, etc.
(ii) They act as biofertilisers which help in increasing the fertility of the soil. They also help in improving plant growth by supplying plant nutrients. Many species of bacteria and cyanobacteria help in fixing the nitrogen in the soil.
(iii) Many biological agents like ladybird and Bacillus thuringiensis, etc., are useful in eradicating pests.
Question. How do biofertilisers enrich the fertility of the soil?
Answer : The main sources of biofertilisers are bacteria, fungi and cyanobacteria. They help in enriching the fertility of the soil in many ways
(i) Rhizobium that forms nodules on the roots of leguminous plants (a symbiotic association) fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms, which is used by the plant as nutrient.
(ii) Azospirillum and Azotobacter fix atmospheric nitrogen, while living freely and enriching the nitrogen content of the soil.
(iii) Many members of the genus–Glomus (fungi) form symbiotic associations with plant known as mycorrhiza that
(a) absorb phosphorus from soil and pass it to the plant.
(b) help the plants to develop resistance to root-borne pathogens.
(iv) Cyanobacteria autotrophic microbes, e.g. Anabaena, Nostoc, Oscillatoria can fix atmospheric nitrogen in aquatic and terrestrial environment and also add organic matter to the soil and increase its fertility.
Question. Why is Rhizobium categorised as a symbiotic bacterium? How does it act as a biofertiliser?
Answer : Rhizobium lives in the root nodules of leguminous plants and fixes the atmospheric nitrogen in the soil as nitrogenous compounds that can be utilised by the plants as nutrients. Since, both are mutually benefitted, it is called symbiotic bacterium. Hence, Rhizobium acts as a biofertiliser.
Question. Your advice is sought to improve the nitrogen content of the soil to be used for cultivation of a non-leguminous terrestrial crop.
(a) Recommend two microbes that can enrich the soil with nitrogen.
(b) Why do leguminous crops not require such enrichment of the soil?
Answer : (a) Azotobacter and Azospirillum.
(b) Leguminous crops have symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria such as Rhizobium that live in the root nodules of these plants. These bacteria obtain food and shelter from the plant and in return they trap nitrogen directly from the atmosphere which they provide to the plant.
Question. Describe the functions of anaerobic sludge digester in a sewage treatment plant.
Answer : In secondary sewage treatment, the sediment of settling tank is called activated sludge. A part of it is used as inoculum in aeration tank. The remaining is passed into a large tank called anaerobic sludge digester. It is designed for continuous operation. The aerobic microbes present in the sludge get killed. Anaerobic microbes digest the organic mass as well as aerobic microbes of the sludge. They are of two types, nonmethanogenic and methanogenic. Methanogenic bacteria produce a mixture of gases containing methane, H2S and CO2. The mixture called biogas is inflammable and is a source of energy. The spent sludge can be used as manure or part of compost.
Question. (a) Organic farmers prefer biological control of diseases and pests to the use of chemicals for the same purpose. Justify.
(b) Give an example of a bacterium, a fungus and an insect that are used as biocontrol agents.
Answer : (a) Chemical pesticides used in agricultural fields are toxic and they kill even useful organisms along with harmful ones, harm human beings and animals, pollute soil, water and crop plants. It is estimated that despite the use of chemical pesticides 30% of the agricultural produce is lost to pathogens and pests because these continue to develop resistance against various pesticides. Now, organic farmers prefer biological control of diseases and pests to the use of chemicals. Biopesticides are the biological agents that control the growth of weeds, insects and pathogens in an agricultural field. They have targeted actions and are harmless to the crop plants, other beneficial field animals and humans. In organic farming, pests and pathogens are not eradicated but kept at manageable levels by a system of checks and balances as operating in ecosystem. An organic farmer holds the view that eradicating pests is undesirable because without them the beneficial predatory and parasitic organisms which depend upon them for food would also be annihilated.
(b) Bacterium as a biocontrol agent : Bacillus thuringiensis is effective against the cabbage looper. Fungi as a biocontrol agent : Trichoderma found in root ecosystem exerts biocontrol over several plant pathogens. Insect as a biocontrol agent : Lady bird beetle and dragonflies feeds on aphids and prey upon mosquitoes, respectively.
Question. (a) Give the metabolic pathway involved in the puffing up of idli dough.
(b) Name the two different categories of microbes naturally occurring in sewage water.
Explain their role in cleaning sewage water into usable water.
Answer : (a) The metabolic pathway involved in the puffing up of idli dough is fermentation in which incomplete oxidation of glucose is achieved under anaerobic conditions by sets of reactions that produces CO2. Carbon dioxide produced during fermentation causes puffing up of idli dough.
(b) Aerobic heterotrophs like bacteria and fungi occur in sewage water. They are natural decomposers and digest a lot of organic matter present in the polluted water thereby releasing minerals and reducing organic waste. Hence, they play an important role in cleaning water and making it fit for various domestic uses.
Question. Choose any three microbes from the following which are suited for organic farming which is ingreat de mand these days for various reasons.
Mention one application of each one chosen.
Mycorrhiza; Monascus; Anabaena; Rhizobium; Methanobacterium; Trichoderma.
Answer : Among the given microbes, the ones which are in great demand for organic farming are: Mycorrhiza, Anabaena and Rhizobium. Mycorrhiza is a mutually beneficial or symbiotic association of a fungus with the roots of a higher plant. Mycorrhizal roots show a sparse or dense wooly growth of fungal hyphae on their surface. Plants having mycorrhizal associations show resistance to root-borne pathogens. Anabaena is free living and symbiotic nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic and have the property of nitrogen fixation. They add organic matter as well as extra nitrogen to the soil. Cyanobacteria are an extremely low cost biofertilisers. Rhizobium is symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria. They form a mutually beneficial association with the plants. The bacteria obtain food and shelter from plants. In return, they give a part of their fixed nitrogen to the plants, thus enhancing the availability of nutrient to crops. It forms nodules on the roots of legume plants. They develop the ability to fix nitrogen only when they are present inside the root nodules.
Question. Explain the role of baculoviruses as biological control agents. Mention their importance in organic farming.
Answer : Baculoviruses (a group of viruses) are known to infect the larval stages of many harmful insects such as ants, wasps, gnats and beetles. These biological weapons are not only effective as potential biological control of these insects, but are also harmless to non-target organisms (plants, mammals, birds, fish, or even non-target insects). Majority of baculoviruses belong to the genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus and are used as biopesticides during organic farming. Organic farming is a technique of raising crops through the use of manure, fertilizers and pesticides of biological origin.
Question. (a) What are the properties of an antibiotic?
(b) Explain the scientific reason for growing Azolla pinnata in the rice field.
Answer : (a) Antibiotics are chemical substances produced by some microbes which in small concentration can kill or retard the growth of harmful microbes without adversely affecting the host. Broad spectrum antibiotic can kill or destroy a number of pathogens that belong to different groups with different structures and wall compositions. Specific antibiotics are effective only against one type of pathogen. Good antibiotics should be harmless to host with no side effects. They should be harmless to beneficial microorganism of alimentary canal and should be effective against all strains of pathogen. They should also be quick in action.
(b) Azolla pinnata supplies nitrogen, increases physicochemical properties of soils such as soil structure, texture, water holding capacity, cation exchange capacity and pH by providing several nutrients and sufficient organic matter. So, Azolla pinnata grows in rice field to increase productivity.
Question. Name the blank spaces a, b, c and d in the table given below.

Answer : a = Lactobacillus bulgaricus
b = Trichoderma polysporum
c = Yeast (Fungus)
d = Penicillin
Question. Study the given flow chart and answer the following questions.

(a) Identify the labelled parts A, B and C in the given flow chart.
(b) Briefly explain biofertiliser C.
(c) How is biofertiliser A different from B?
Answer : (a) In the given flow chart A represents free living nitrogen fixing bacteria, B represents loose association of nitrogen fixing bacteria and C represents symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria. (b) Symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria form a mutually beneficial association with the plants. The bacteria obtain food and shelter from plants. In return, they give a part of their fixed nitrogen to the plants. The most important symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria is Rhizobium. It forms nodules on the roots of legume plants. There are about a dozen species of Rhizobium which form association with different legume roots, e.g., R. leguminosarum, R. lupini, R. trifolii, R. meliloti, R. phaseoli. These bacteria, live freely in the soil but cannot fix nitrogen except for a strain. They develop the ability to fix nitrogen only when they are present inside the root nodules. In the nodule cells, bacteria (bacteroids) lie in groups surrounded by membrane of the host which is lined by a pink-red pigment called leghaemoglobin.
(c) Differences between free living (A) and loosely associating (B) nitrogen fixing bacteria are: (Table 39)
Question. During the production of curd, a small amount of curd is added as a starter to the fresh milk at a suitable temperature. Explain the changes the milk undergoes when it sets into curd.
Answer : The starter or inoculum used in preparation of milk products actually contains millions of lactic acid bacteria. Curd is prepared by inoculating cream and skimmed milk with Lactobacillus acidophilus at a temperature of about 40° C or less. Lactobacillus converts lactose sugar of milk into lactic acid which causes coagulation and partial digestion of milk protein casein and milk gets changed into curd, which also improves its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin B12 content.
Question. Define the term biofertilizers? How does each of the following serve as a biofertilizer?
(i) Rhizobium (ii) Ectomycorrhiza
Answer : Biofertilizers are microorganisms which bring about nutrient enrichment of soil by enhancing the availability of nutrients like nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) to crops. The microorganisms which act as biofertilizers are bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue green algae) and mycorrhizal fungi.
(i) Rhizobium is one of the most important symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria. It forms nodules on the roots of legume plants. They develop the ability to fix nitrogen only when they are present inside the root nodules. In the nodule cells, bacteria (bacteroids) lie in groups surrounded by membrane of the host which is lined by a pink-red pigment called leghaemoglobin. Leghaemoglobin in root nodules rapidly combines with oxygen and protects the enzyme nitrogenase by any inhibitory effect of oxygen.
(ii) In ectotrophic mycorrhiza, the fungal mycelium completely encloses the feeder rootlets forming sheath or mantle. The mantle of fungal hyphae increases the absorptive surface of roots and hence serve better intake of nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium and potassium from the surrounding soil. The major functions which ectomycorrhiza perform are
(a) absorption of water,
(b) solubilisation of complex organic molecules into simple inorganic nutrients, their absorption and transfer to the roots, and
(c) protection of plants from attack of disease-inciting pathogens by secreting antimicrobial substances. Ectomycorrhizae are known to occur in Pinus, Quercus, Betula, Eucalyptus, peach, etc.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What are biofertilisers? Describe their role in agriculture. Why are they preferred over chemical fertilisers?
Answer : Biofertilisers are microorganisms which bring about nutrient enrichment of soil by enhancing the availability of nutrients like nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) to crops. Biofertilisers includes–nitrogen fixing bacteria, nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria and mycorrhiza. Azotobacter occurring in fields of cotton, maize, jowar and rice, not only increases yield but also saves nitrogen fertiliser upto 10–25 kg/ha. A number of free living cyanobacteria or blue-green algae have the property of nitrogen fixation, e.g., Anabaena, Nostoc, Oscillatoria, Tolypothrix. Cyanobacteria are extremely low cost biofertilizers.
The most important of the symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria is Rhizobium. It forms nodules on the roots of legume plants. There are about a dozen species of Rhizobium which form association with different legume roots, e.g., R. leguminosarum, R. lupini, R. trifolii, R. meliloti, R. phaseoli. Nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria (blue–green algae) form symbiotic association with several plants, e.g., cycad roots, lichens, liverworts, Azolla (fern). Azolla–Anabaena association is of great importance to agriculture. Azolla pinnata is a free floating fresh water fern which multiplies rapidly, doubling every 5–7 days. The fern can coexist with rice plants because it does not interfere with their growth. In some South-East Asian countries, especially China, the rice fields are regularly provided with Azolla.
Chemical fertilisers cause pollution of water bodies as well as ground water, besides getting stored in crop plants. Therefore, farmers are pressing for switch over to organic farming which includes the use of manures biofertilisers, biopesticides. Biofertilisers are microorganisms which bring about nutrient enrichment of soil by enhancing the availability of nutrients to crops. The microorganisms which act as biofertilisers are bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue green algae) and mycorrhizal fungi. Bacteria and cyanobacteria have the property of nitrogen fixation while mycorrhizal fungi preferentially withdraw minerals from organic matter for the plant with which they are associated. Phosphate is also solubilised by some bacteria and by some fungi that form association with plant roots.
Question. (a) Explain the process of sewage water treatment before it can be discharged into natural water bodies.
(b) Why is this treatment essential?
Answer : (a) Sewage water can be purified by passing it through sewage treatment plants with the action of microorganisms. A sewage treatment plant separates solids from liquids by physical processes and purifies the liquid by biological processes. There are three stages of this treatment; primary, secondary and tertiary. Primary treatment is physical, secondary biological and tertiary chemical.
Primary treatment phase of sewage treatment removes floating and suspended solids from sewage through two processes of filtration and sedimentation. First floating matter is removed through sequential filtration. The filtrate is kept in large open settling tanks where grit settles down. Aluminium or iron sulphate is added in certain places to flocculation and settling down of solids. The sediment is called primary sludge while the supernatant is called effluent. The primary sludge traps a lot of microbes and debris. It is subjected to composting or land fill where anaerobic digestion removes the organic matter.
During secondary treatment, the primary effluent is taken to aeration tanks. A large number of aerobic heterotrophic microbes grow in the aeration tank. They form flocs which are masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh like structures. The microbes digest a lot of organic matter, converting it into microbial biomass and releasing a lot of minerals. As a result the BOD of the waste matter is reduced to 10-15% of raw sewage, which is then passed into settling tank. In settling tank, the bacterial flocs are allowed to undergo sedimentation. The effluent or supernatant is generally passed into natural water bodies and sediment of settling tank is called activated sludge.
(b) This treatment prevents water pollution and water borne diseases. So, it is essential in order to protect the natural water bodies from sewage pollution.
Question. Explain the process of sewage water treatment before it can be discharged into natural water bodies. Why is this treatment essential?
Answer : The sewage treatment is essential before being released into water bodies as it leads to water pollution and as a consequence increased incidence of waterborne diseases.
This treatment is carried out in two stages Primary Treatment It is also known as physical treatment because it basically involves physical removal of small and large,floating and suspended solids from sewage through filtration and sedimentation. Initially, floating debris is removed by sequential filtration.
Then, the grit (soil and small pebbles) are removed by sedimentation in settling tanks. Aluminium or iron sulphate is added in certain places for flocculation.
All solids that settle form the primary sludge. It traps lots of microbes and debris. The supernatant forms the effluent. This effluent is then taken from the primary settling tank for secondary treatment.
Secondary Treatment This treatment is also known as biological treatment because it involves the use of microbes or microbiota for the treatment of sewage.
n The effluent from primary treatment is passed into large aeration tanks, where it is constantly, mechanically agitated and air is pumped into it which helps in the growth of useful aerobic microbes into flocs. While growing, these microbes consume major part of the organic matter converting it into microbial biomass and releasing lot of minerals. This significantly
reduces the Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD).
The sewage water is treated till the BOD is reduced.
n When the BOD of effluent is reduced significantly, it is then passed into a settling tank, where the bacterial ‘flocs’ are allowed to sediment. This sediment is called activated sludge. A small part of the activated sludge is then pumped back into the aeration tank to serve as the inoculum. n The remaining part of the sludge is pumped back into
large tanks called anaerobic sludge digesters, in which other anaerobic bacteria (methanogens) are also present.
They digest the organic mass as well as aerobic microbes (bacteria and fungi of the sludge). During the digestion, mixture of gases like methane (CH4 ), hydrogen sulphide (H2S), carbon dioxide (CO2), etc., are produced.
n These gases form biogas that is used as a source ofen ergy because it is inflammable. The effluent from secondary treatment plant is released into natural water
bodies like rivers and streams.
Question. (i) Name the category of microbes naturally occurring in sewage and making it less polluted during the treatment.
(ii) Explain the different steps involved in the secondary treatment of sewage.
Answer : (i) Hetrotrophic microbes are naturally occurring in sewage which make it less polluted during sewage treatment.
(ii) Refer to Long Q. No. 1.
Question. Describe the main idea behind the biological control of pests and diseases.
Answer : The main idea behind the biological control of pests and diseases is to use is a method of controlling pests in agriculture that relies on natural predation and not on chemicals.
Organic farmers believe that ‘biodiversity furthers health’. The more diversity a landscape has, the more sustainable it is.
Therefore, they work to create a system where the insects (pests) are not eradicated, but kept at manageable levels by a complex system of checks and balance within a living and vibrant ecosystem.
It is different from ‘conventional’ farming practices that use chemical methods to kill both useful and harmful life forms. This is a holistic approach, as it seeks to develop an understanding of the webs of interaction between the myriad of organisms, including both flora and fauna in the field.
Biological farming approach requires familiarity with various life forms, their habitat, predators as well as pest,their life cycle, patterns of feeding, etc., to use them in biocontrol measures and reduce the dependence on chemicals and pesticides.
Examples of biological control agents are
(i) Ladybird and dragonflies are useful to get rid of aphids and mosquitoes, respectively.
(ii) To control butterfly caterpillars, bacteria such as Bacillus thuringiensis are used in the form of sprays or sachets as dry spores.
Question. What are biofertilisers? Name the categories of organisms used as biofertilisers with an example for each. How do they function in organic farming?
Answer : Biofertilisers are organisms that enrich the nutrient quality of soil by enhancing the availability of nutrients to the crops.
The categories of organisms used as biofertilisers are as given below
(i) Bacteria Nitrogen-fixing bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen into organic form, which is used by the plant as nutrient, e.g. Rhizobium is a symbiotic bacterium that lives in the root nodules of legumes and fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic compounds.
(ii) Fungi They also form symbiotic association with plants, i.e. mycorrhiza, which absorb phosphorus from soil and passes it to the plants. Many members of genus–Glomus form mycorrhiza. Plants with mycorrhizal association show other benefits also such as
(i) Resistance to root-borne pathogens.
(ii) Tolerance to salinity and drought.
(iii) Increase in plant growth and development.
(iii) Cyanobacteria These are autotrophic microbes
found in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Most of them fix atmospheric nitrogen, e.g. Anabaena, Nostoc, Oscillatoria, etc. In paddy fields, cyanobacteria serve as important biofertiliser.
Blue-Green Algae (BGA) also add organic matter to the soil. Thus, increasing its fertility.
All of these play a vital role in organic farming as there is no indulgence of chemicals fertilisers and hence, no polluting water bodies.
l Case Based Questions
Question. Direction Read the following passage and ans the questions that follows.
Microbes or microorganisms form a big part of the biological systems of the world. They are present everywhere–within the soil, around us, in water, both in and around our body. They are microscopic in nature and have variable shapes and sizes.
People are of the belief that all microorganisms are harmful for us. However, it is to be made sure that not all microbes are harmful, some useful microbes benefit humans in a variety of ways.
Microbes and their products are used in everyday life in different fields of work. Surprisingly, microbes like fungi and bacteria can be cultured in laboratory on nutritive media to form colonies.
Question. Microorganisms are termed as ‘ubiquitous’.Explain.
Answer : Ubiquitous means present or found everywhere. Since, microbes can be found anywhere around us from air, water to the soil, they are called ‘ubiquitous’.
Question. Name the different types of microorganisms.
Answer : The different types of microorganisms include algae, bacteria, fungi, virus and Protozoa.
Question. There is no life without microorganisms? Discuss.
Answer : Microorganisms, especially bacteria, help in decomposing the dead and decaying matter and are also responsible for oxygen in the air which is essential for our survival.
Question. Explain the role of microorganisms in various fields (Any two).
Answer : Microbes and their products are used in everyday life in different fields such as
(a) Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used for fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices to produce ethanol.
(b) Some microorganisms also work as biocontrol agents, e.g. Bacillus thuringiensis, to control butterfly, catterpillars.
Question. Name the toxic released by Bacillus thuringiensis.
Answer : Thurioside is released by Bacillus thuringiensis.
2. Direction Read the following passage and ans the questions that follows.
Antibiotics are the chemical substances, produced by some microbes that can kill or retard the growth of other disease causing microbes. The first antibiotic discovered was penicillin. Alexander Fleming, while working on Staphylococci bacteria, found a mould growing in one of his culture plates.
This mould produced a chemical, which inhibits the bacterial growth.
However, the production of antibiotics has become widespread by the pioneering efforts of Ernst Chain and Howard Florey on chemotherapeutic effectiveness of penicillin during 1939-41.
Penicillin was extensively used in treating American soldiers wounded in World War-II.
Question. Who coined the term ‘antibiotics’?
Answer : The term antibiotics was coined by Waksman in the year 1942.
Question. From which microorganism, penicillin was obtained?
Answer : Penicillin was extracted from Penicillium notatum. It was extracted by Alexander Fleming in the year 1929.
Question. Name the microorganism that inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus bacteria in culture plate.
Answer : Penicillium notatum
Question. Why antibiotics cannot be used to cure viral disease?
Answer : Antibiotics cannot cure viral disease because virus do not possess cell wall like bacteria that can be attacked by antibodies, instead they are protected by a protein coat.
Therefore antibiotics are helpful in treating bacterial diseases like plague, diphtheria and whooping cough.
Question. What would happen if antibiotics were not discovered?
Answer : The mortality rate would have increased due to no antibiotic availability for curing disease caused by microorganisms.
3. Observe the diagram given below and ans the questions that follows. (Image 38)
Question. What is the label B represent in the figure?
Answer : B represents digester. It is used to anaerobically decompose biodegradable materials to produce biogas.
Question. What is biogas?
Answer : Biogas is methane rich fuel gas produced by anaerobic breakdown of waste biomass by methanogenic bacteria.
Question. Which is the main raw material used in biogas production?
Answer : Cattle (cow) dung has been recognised as the main raw material for biogas plants.
Other materials like night soil, poultry litter and agricultural wastes are also used.
Question. Which source of energy is biogas?
Answer : Biogas is a renewable and non-conventional resource as its production and usage cycle is continuous and generates no CO2.
Question. Which group of microbes observed in a biogas plant?
Answer : The group of microbes observed in a biogas plants are called methanogens. These bacteria grow anaerobically on cellulosic material and produce large amounts of methane along with carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas.

