Sources of Energy Notes for Class 10 Science
IMPORTANT TERM & CONCEPTS
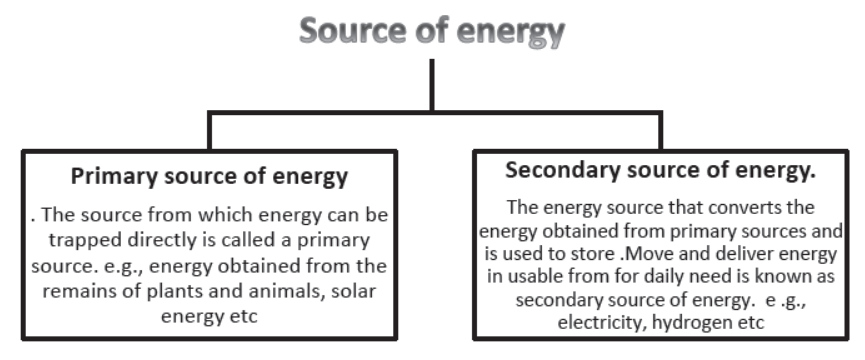
Source of energy: the actual from which energy can be harnessed directly or indirectly is called source energy.
Properties of good source of energy :
1.Perform large amount of work per unit volume or mass .
2.Easily available .
3.Economical
4.Easy to store and transport.
• Source of energy based on origin:
Source of energy based on the basis of exhaustibility :
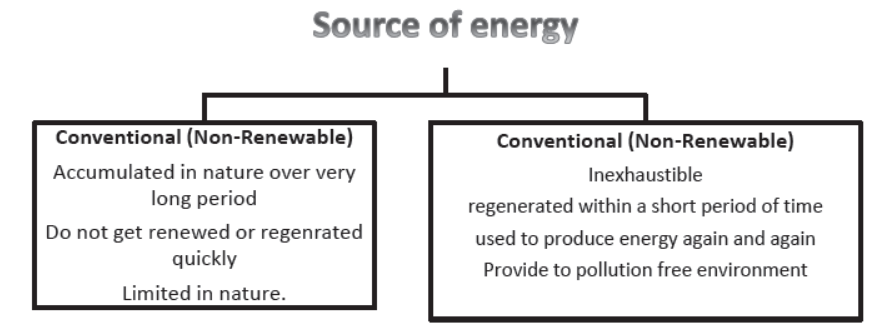
Renewable source of energy /Non-conventional source of energy. A renewable source of energy is constantly being created in nature and is inexhaustible i.e., it always available
for use. e.g., Polar energy, wind energy, ocean energy, geothermal energy, hydro energy, bio energy.
Non-renewable/conventional energy sources: The sources of energy that do not get renewed or regenerated quickly, as they have been formed in the earth over millions of years ago are known as non-renewable energy source. They are called non-renewable because they are being used much faster then they can be formed. e.g., fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, natural gas) and nuclear power. Fossil fuels are a non-renewable resource, so it important to conserve them as they are limited resources.
There are new technologies under development that could make burning of fossil fuels much more efficient, much cleaner and less expensive. Some of these technologies are new commercially available. But the implementation for getting the clean fuel technology is still relatively small and may take more time to develop.
Forms of energy: Energy comes in different forms and one form of energy can be converted into another. Some different forms of energy are:
I. Potential energy VI. Kinetic energy
II. Chemical energy VII. Heat energy
III. Light energy VIII. Electrical energy
IV. Sound energy IX. Solar energy
V. Nuclear energy X. Geothermal energy
Relationship between Different Forms Energy: All the form of energy stated above follow the law of conservation of energy. According to the law, ‘’the total energy in the universe always remain constant. i.e., energy can neither be created nor destroyed. But can only be transformed from one form into another e.g., friction turns kinetic energy into thermal energy.
Qualities of an ideal source of energy.
I. Free from any kind of pollution.
II. Easy to store and transport.
III. Easily accessible.
IV. Economical.
V. Having a high calorific value.
VI. Having a low content of non-combustible substances i.e., It should leave less residue on burning.
VII. Easily converted to energy forms used in day to day operations.
These can be considered as qualities of an ideal fuel.

Fossil fuels are those fuels which are formed form the organic remains of prehistoric plants and animals. e.g., coal, oil and natural gas (petroleum). Millions of years ago, large plants, ancient creatures died, they decomposed and were buried layer upon layer under the ground. Their decomposed remains gradually changed over the years. Due to excess of heat and high pressure generated over the millions ofyears, these layers converted into a hard, black rock (coal), a thick liquid (petroleum) and natural gas- The three major forms of fossil fuel.
Limitations of fossil fuels
• Fossil fuel burning causes Pollution
• Fossil fuel burning causes Acid rain
• Fossil fuel residue like ash have disposal problem
• Also cause global warming and greenhouse effect
Thermal power plant: A power-generating plant which uses heat energy to generate electricity
I. Such plants use coal, petroleum and natural gas to produce electricity.
II. The steam produced by burning of fossil fuels runs the turbine to generate electricity.
III. The transmission of electricity is more efficient.
IV. These plants are setup near coal or oil fields to minimise the cost of transportationand production.
Hydroelectric (hydel) power plants: A power generating plant that uses the energy of flowing water to produce electricity is called hydroelectric power plant. The electricity
generated is called hydroelectricity.
Principal of generation of hydroelectricity Stored water behind the dam is allowed to fall freely from a suitable height on the blades of a turbine. This rotates the armature coil of generator rapidly and electricity is generated.

Energy transformation:
Inspite of benefits, some of the disadvantages in harnessing the hydro energy lead the people to oppose the construction of Tehri Dam on the river Ganga and Sardar sarover project on the river Narmada.
A schematic view of hydroelectric power generation is shown in the given figure.

Biomass: The residue of living organisms such of plants, animals and their products from which fuel can be obtained is called biomass
• Biomass is a renewable source of energy.
• It includes
a) Biodegradable materials from industries
b) Organic waste materials.
c) Agriculture and forest residue.
• Biomass can be used
a) As a bio fuel
b) For the production of fibre, paper. Chemicals or heat
c) As a source of energy in industries
d) To generate electricity
e) Produce biogas by its anaerobic digestion.
Charcoal: Charcoal is formed when any other carbon-containing compound is heated in a limited supply of oxygen.
Wood charcoal: Wood charcoal is obtained by burning of dry wood in a limited supply of oxygen. Volatile materials present in it get removed and cooled to get wood tar and wood gas. The residue then left is known as wood charcoal.
Important uses of wood charcoal:
a. It is porous and can absorb liquids and gases on its porous surface. Therefor, it is used in water filters, gas masks.
b. It is used as a decolourising agent.
c. It is an important component of gun powder.

Biogas. The mixture of gases produced during decomposition of bio mass such as cowdung.
Various plant materials like residue of harvested corps. Vegetable waste and sewage in the absence of oxygen is called bio gas.
It is also known as ‘gobar gas’ since cow dung is the starting materials for its production.
Biogas is mixture of methane (75%), carbon dioxide (25%) with the traces of hydrogen, nitrogen and hydrogen Sulphide.
Uses of biogas: Biogas can be used for:
• Cooking and heating
• Running tubewells and water pump engines
• As an illuminant in gas lanterns
• In bio-diesel production
• As a vehicle fuel
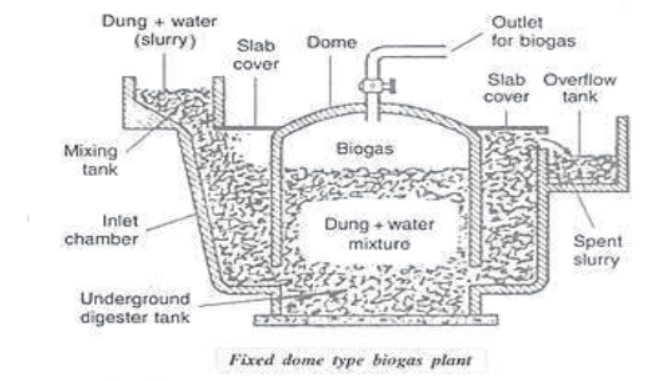
Biogas plant: The schematic view of fixed type bio gas plant for the production of biogas is shown in figure. It consists of:
a. Mixing tank. A tank where slurry of cow-dung and water is made and it is present above the ground level.
b. Inlet chamber. It connects the mixing tank and the digester tank. It is having a slope to ensure smooth flows slurry into the digester.
c. Digester. It is a sealed underground chamber covered with a dome like ceiling. Atthe top of dome, there is an outlet valve for the extraction of biogas. It opens into an outlet chamber from the bottom.
d. Outlet chamber. It is the chamber where spent slurry gets collected from thedigester. It is connected with the overflow tank.
e. Overflow tank. Spent slurry is removed from here.
Working of a fixed domed type biogas plant
I. Slurry is made by mixing animal dung with an equal amount of water in a mixing tank.
II. Slurry is fed into the underground digester tank through a sloping inlet chamber.
III. The anaerobic microorganisms that do not require oxygen decompose or break down complex compounds of cow dung slurry in about 50-60 days to produce bio gas.
IV. The produced biogas is collected inside the dome built over the digested tank.
V. As more and bio gas starts collecting, the pressure exerted by the biogas increases, there forces the spent slurry into over flow tank via outlet chamber.
VI. The collected biogas is taken out through the outlet valve and is supplied wherever it is required.
VII. The spent slurry is periodically removed and is used as manure for plants.
VIII. To get the continuous supply of gas, prepared slurry is fed into the plant regularly.
Wind energy: The kinetic energy possessed by the blowing wind is called wind energy.
The factors responsible for the blowing wind are:
I. Uneven heating of equatorial region and polar region of earth by sun rays.
II. Rotation of earth about its own axis.
III. Prevailing local condition in the region.
Note : Minimum 15 km/h speed of wind is required to produce electricity.
What causes the wind to blow? Equatorial regions of earth receive more solar heat radiations fro the sun as compared to other parts of the earth. Therefore, the air in these regions warms and rises up. As a result movement of air takes place which forms the wind.
Uses of wind energy. The uses of wind energy are well known to mankind for centuries.
The harnessing of wind energy can be done in the following ways:
I. It is used to generate electricity.
II. It helps to propel gliders, sail boats in the desired direction.
III. It rotates the blades of wind mill for pumping water or to run the flour mills.
Wind mill: It is a turbine which rotates due to the force exerted by wind on its adjustable vanes or sails. It converts kinetic energy of wind into rotational mechanical energy.
Its structure is similar to large electric fan erected at some height on a rigid support. The blades are connected to a drive shaft that is connected to other devices like water pump,
grinder or electric generator.
Principle: When wind passes through the blades of a windmill, the blades experience an upward force, due to its peculiar shape known as aerodynamic air foil shape. This produces
a lift and generates the torque which rotates the blades.
Use of wind mill: The rotatory motion of windmill can be utilized to Lift water from a well (water lifting pump) Turn the turbine of electric generator that generates electricity Grind the grain into flour
Wind Energy Farm: the place where a large number of windmills are erected over a large area is called wind energy farm. The energy output of each wind-mill is coupled together to get the electric power on a large scale.
In India, largest wind energy farm is established near Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu. It generates 380 MW of electricity. Now scientist are trying to establish the wind energy farms that floats on the surface of sea water to capture the high speed wind on the open sea.
Solar Energy: The enormous amount of energy radiated by the sun in all direction in the form of heat and light is called solar energy.
• It is the ultimate source of energy.
• Nuclear fusion of deuterium is the main cause which generates energy on the sun.
• Under clear sky conditions, India receives solar energy from 4 to 7 kWh/m2 daily.
Harnessing of solar energy: Solar energy can be harnessed directly or indirectly.
Direct harnessing: Solar energy can be converted into electricity directly by the use of solar cells or its heat energy can be used by solar cookers or solar water heaters.
Indirect harnessing: Solar energy is responsible for photosynthesis reaction in plants, movement of wind; ocean thermal energy, hydroelectricity and other forms due to difference
in temperature at different levels are the various ways through which solar energy can be indirectly harnessed.
Uses of solar energy: Solar energy can be used:
I. To generate electricity by using solar power plants.
II. To obtain salt from the sea water by evaporation.
III. To preserve sea food, vegetables and fruits for long time by using sun-drying method.
IV. To heat water food and remove moisture content from the grains.
V. Solar energy is used in watches and calculators.
Solar Constant: The amount of energy received at the outer edge of the earth’s atmosphere per unit area per second exposed perpendicularly to the rays of sun at an average distance between the sun and earth is known as solar constant. Solar constant at a place in the outer atmosphere is 1.4 kJ/s/m2 or 1.4 kW/m2. It means that energy received per second by 1 m2 area is 1.4 kJ/s.
Solar Cooker: The device which cooks the food without using any conventional cooking fuel and converts solar energy directly into heat energy is known as solar cooker.
• It works on the principle that black surface absorbs more heat as compared to white or a reflecting surface under identical conditions.
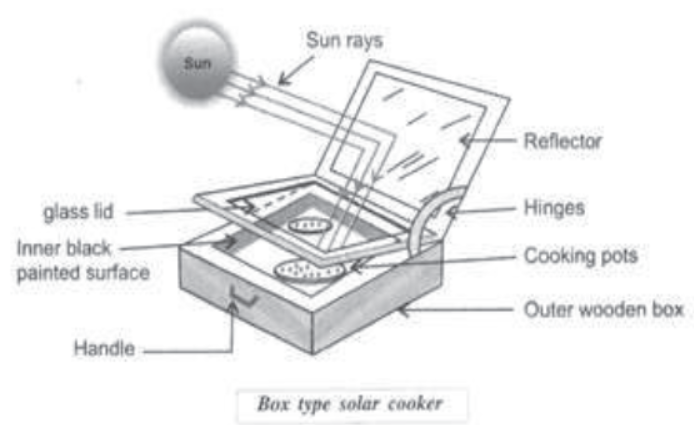
• It consists of a well metallic or wooden box which is painted dull black.
• The collection of solar energy is done either by using a plane mirror or a large concave mirror which acts as a reflector attached to one of the top edges of the box.
• The top of the box exposed to the sun and covered by one or more transparent cover such as glass plate to trap the heat inside the box.
• Similar to greenhouse effect, the glass lid allows the heat radiation (infrared rays) from sun to enter inside but does not allow the reflected heat radiation to escape or go outside the box. This heat is absorbed by the blackened surface. Thus the heat loss is reduced due to reflection.
• Temperature inside the box increases slowly and rises from 100 to 140℃ in two-three hours on a clear sunny day.
• This heat is utilised to cook the food. Thus solar cooker saves substantial amount of cooking fuel and contributes towards the economy of a family.
Spherical reflector type solar cooker:
• Concave or parabolic reflector is used to concentrate the solar energy at its focus.
• These solar cookers can achieve temperature of over 200℃ which is hot enough for frying or baking the food.
Solar Cell: The device that converts solar energy directly into electrical energy is called solar cell. They are made from special grade semiconducting materials like silicon, germanium, gallium etc.
A single solar cell produces a potential difference of 0.5−1 V and generates about 0.7 W of electricity, when solar radiations are incident on it.
Advantage associated with solar cell
• It has no moving parts and eco-friendly too .
• It requires little maintenance ,compare to cost of other renewable sources
• It can be setup in remote area
• Easy to install
Disadvantage of solar cell
• Limited availability of silicon for making solar cell
• Silver is used for interconnection of cells in the solar panels increase it cost
• Need of storage batteries for continuous supply of electric power during night further increase the investment cost considerably ,
Solar Panel: It consists of a large number of solar cells joined together in a particular pattern to obtain large electrical power for practical uses.
Uses of solar panel/solar cells.
They are used-
I. as a source of electric power in satellites and space probes.
II. to provide electric power to off-shore drilling rig platforms and light house.
III. for recharging the batteries during day.
IV. for operating traffic lights, water pumps, and other household electrical appliances in remote areas.
V. in calculators and electronic watches.
VI. by TV relay stations or wireless transmission systems located in remote areas use solar panels.
Energy from Sea:
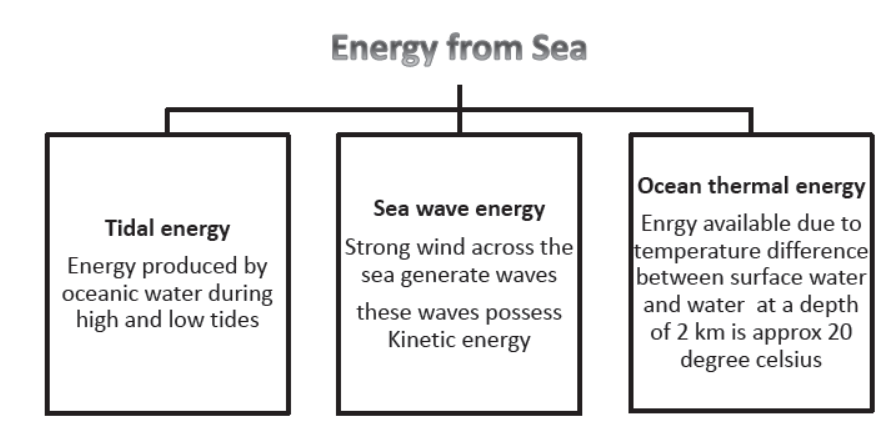
The oceans cover about 70% of the earth’s surface area. They contain a lot of energy because water has a high specific heat capacity. Ocean acts as a renewable source of energy. The energy from oceans is available in different forms.
I. Tidal energy: The energy produced by the surge of ocean water during high and low tides due to difference in sea levels is called tidal energy. The high and low tides occur due to the gravitational pull of the moon. This causes enormous movement of water.
Tidal energy is harnessed by construction a dam near the shores. During high tides water flows into the dam and during low tides, water flows out. This flowing water rotates the turbine, present at the opening of dam and produces electricity.
II. Sea-wave Energy:
• The strong wind blowing across the sea generates waves in the sea.
• Kinetic energy possessed by these sea waves can be used to generate electricity.
• The harnessing of sea wave energy would be a viable proposition only where waves are very strong.
• Technology is still in developing stage to get more efficient devices to trap sea wave energy.
• These devices convert the wave energy into rotational motion of the shaft which is used to produce electricity with the help of an electric generator.
III. Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion(OTEC):
• Water at the surface of an ocean or sea warms up by the solar energy while the deeper remains cold.
• The temperature difference between the surface water and water at a depth of 2 km is approximately 20℃ (293 K) or more.
• The energy available due to this temperature difference is called ocean thermal energy.
• This ocean thermal energy (OTE) can be utilised to run OTEC plant.
• In OTEC plan, the energy of warm surface water is used to convert liquid ammonia into gaseous state. The vapours of ammonia at high pressure are used to run the turbines of generators to produce electricity.
• The used vapours pass through the condenser where cold water pumped from the deeper parts of ocean condenses if to liquid again.
• This process is repeated again and again to get continuous production of electricity.
Geothermal Energy: The heat energy of the interior of the earth is called geothermal energy.
• It is not related directly or indirectly to the sun’s energy.
• At some depth below the surface of earth, the rocks get heated due to fission of radioactive materials present in it which liberates large amount of energy.
• Due to geological changes these molten rocks in the interior of earth are pushed upwards and trapped in certain regions. These regions are called ‘hot spots’.
• The underground water which comes in contact with these hot spots gets heated and is converted into steam.
• The steam trapped inside the rocks at high pressure is taken out through a pipe to a turbine to generate electricity.
• In some places hot water comes to the surface through some outlets. These outlets are called ‘hot-springs or geysers’.
• Geothermal energy based power plants operate at geysers steam field in California (largest in the world), USA, and New Zealand etc.
• In India, geysers are found in Madhya Pradesh, Sohna (Gurgaon district of Haryana) and at Manikaran. Kullu district of Himachal Pradesh.
• Limitations of geothermal energy : cost required for construction of geothermal power plant and its drilling wells which requires advance tech
• Enhanced geothermal system can trigger earthquakes thereforeit nology .
• Cannot be easily transported unlike other source of energy ,.
Nuclear Energy: The energy produced during nuclear reaction such as nuclear fission or fusion is called nuclear energy. Einstein, by his theory of relativity, provides mass energy relation. According to his theory, every substance has energy due to its mass also. If a substance loses and amount ‘Δm, of its mass, an equivalent amount ΔE of energy is produced, where ΔE=(Δm)c2
Where c is the speed of light which is equal to 3×108 m/s. this relation i
• There are very limited number of places where geothermal power plant are likely to operate. affect land stability severely
• High up front installation
s known as ‘Einstein’s mass energy relation.
Nuclear Fission: the process in which a heavy nucleus is broken into two nearly equal fragments due to bombardment of suitable projectile a tremendous amount of energy is released. This process is called nuclear fission.
Uranium ,Plutonium or thorium is used as fuel Large amount of energy is produced Controlled fission reaction is used in nuclear reactor to produce electricityThe lost mass between the sum of masses of disintegrated nucleus and original nucleus reappears in the form of energy according to Einstein’s mass energy relation.
• This phenomenon is the basis of nuclear reactors to produce electricity, useful products and nuclear bomb also.
• Example:
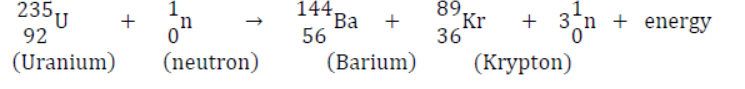
Nuclear Fusion: The process in which lighter nuclei moving at very high speed fuse together to form a singly heavier nucleus, releases a tremendous amount of energy called nuclear fusion Hydrogen or its isotopes is used as fuel Large amount of uncontrolled energy produced . e.g.,
Two nuclei of heavy hydrogen or deuterium (12H ) fuse together to form a helium atom as shown below.
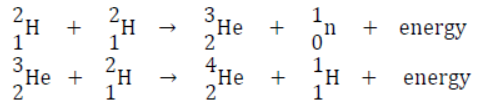
• In practice, nuclear fusion is very difficult process.
• It needs millions of degrees of temperature and millions of Pascals of pressure to carry it.
• Hydrogen bomb is based on this phenomenon.
Merits of Fusion: Fusion process has some merits over the fission process which are:
I. Fusion products are non-radioactive and thus harmless.
II. Causes less pollution problems.
III. Gives more energy as compared to fission.
IV. Fuel in the form of hydrogen is available in plenty.
Major disadvantage is that the energy obtained from fusion process could not be controlled so far.
Nuclear Reactor: The device where a self-sustaining chain reaction produced in a fissionable material such as uranium or plutonium that releases energy in a controlled manner is called nuclear reactor.
• The energy obtained is utilised for many useful purposes such as
I. Electric power generation.
II. Propulsion of ships, submarines and air crafts.
III. Neutron beam for treatment of cancer, nuclear research etc.
• Artificial radioactive isotopes of many elements produced in the nuclear reactor can be utilised in medicine, industry and agriculture.
• The energy produced during nuclear reactions is often expressed in units of electron volts (eV); 1eV = 1.602 ×10-19).
• Energy released by 1 atomic mass unit (amu) = 931 MeV where 1 MeV = 1.602 ×10-13) .
Nuclear Power: The power generated with the help of nuclear reactor is called nuclear power. In India, nuclear power plants are located at
I. Tarapore (Maharashtra)
II. Rana Pratap Sagar, Kota (Rajasthan)
III. Kalpakkam (Tamil Nadu)
IV. Narora (Uttar Pradesh)
V. Kakrapara (Gujarat) and
VI. Kaiga (Karnataka)
Major Hazards and Limitations of Nuclear Power Generation:
I. Environmental contamination due to improper nuclear waste storage and its disposal.
II. High cost of installation.
III. Limited availability of nuclear fuel.
IV. Risk of accidental leakage of harmful radiation during processing of nuclear fuel or damage. If any in nuclear reactor.
V. Land becomes barren.
Environmental Consequences of Increasing Demand for Energy:
I. Burning of fossil fuels pollutes the air and water.
II. Production of greenhouse gasses, like CO2 methane, increases the global warming.
III. Depletion of ozone layer increases the ultraviolet radiation in the environment causing harmful effects on the living things.
Steps to reduce the energy consumption:
I. Avoid misuse of conventional sources of energy which are limited in nature.
II. Alternate sources of energy such as solar energy, wind energy, hydro energy, etc., should be used instead of non-renewable source of energy.
III. Efficiency of energy sources should be repeatedly maintained for getting the maximum efficiency.
IV. Research should be continued to produce long lasting alternate sources of energy devices so that the environmental damage caused by assembly of devices gets minimized.



