Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques MCQ Class 11 Chemistry
Please refer to Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques MCQ Class 11 Chemistry with answers below. These multiple-choice questions have been prepared based on the latest NCERT book for Class 11 Chemistry. Students should refer to MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry with Answers to score more marks in Grade 11 Chemistry exams. Students should read the chapter Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques and then attempt the following objective questions.
MCQ Questions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques
The Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques MCQ Class 11 Chemistry provided below covers all important topics given in this chapter. These MCQs will help you to properly prepare for exams.
Question. 1.2 g of an organic compound on Kjeldahl station liberates ammonia which consumes 30cm3 of 1 N HCI. The percentage of nitrogen in the organic compound is
(a) 30
(b) 35
(c) 46.67
(d) 20.8
Answer
B
Question. Identify the binary mixture(s) that can be separated into individual compounds, by differential extraction as shown in the given scheme.

(a) C6H5OH and C6H5 ,COOH
(b) C6H5COOH and C6H5CH2OH
(c) C6H5CH2OHand C6H5OH
(d) C6H5CH2OHand C6H5CH2COOH
Answer
B.D
Question. An organic compound on heating with CuO produces CO2 but no water. The organic compound may be
(a) carbon tetrachloride
(b) chloroform
(c) methane
(d) ethyl iodide
Answer
A
Question. Match the following columns.

Codes
A B C D E
(a) 5 4 1 2 3
(b) 4 5 1 6 2
(c) 6 4 1 3 2
(d) 5 4 6 2 3
(e) 4 6 2 3 5
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following complex formation indicates presence of sulphur in the organic compound when sodiwn nitroprusside is added to sodium extract of the compound?
(a) Fe4 [Fe(CN)6]3
(c) Fe4 (CNS)3
(b) Na2 [Fe(NO)(CN)5 ]
(d) Na4 [Fe(CN)5 NO5]
Answer
D
Question. Naphthalene can be easily purified by
(a) sublimation
(b) crystallisation
(c) distillation
(d) vaporisation
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following compounds precipitate with AgNO3 ?

Answer
B
Question. A mixture of camphor and benzoic acid can be separated by
(a) sublimation
(b) extraction with a solvent
(c) chemical method
(d) fractional crystallisation
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following reagents will be fruitful for separating a mixture of nitrobenzene and aniline?
(a) Aq. NaHCO3
(b) H2O
(c) Aq. HCl
(d) Aq. NaOH
Answer
C
Question. KI in acetone undergoes SN 2 reaction with each P,Q, R The rates of reaction vary as
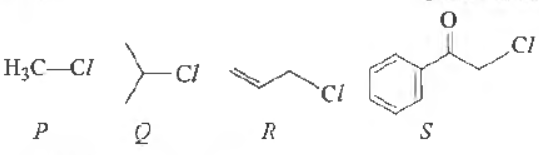
(a) P > Q > R >S
(b) S >P >R >Q
(c) P >R > Q> S
(d) R >P > S> Q
Answer
B
Question. Fractional distillation is a process by which the separation of different fractions from mixture of solution is carried by making use which of the following property of the fractions ?
(a) Freezing point
(b) Boiling point
(c) Melting point
(d) Solubility
Answer
B
Question. On complete combustion, 0.246 g of an organic compound gives 0.198 g of CO2 and 0.1014 g of H2O. The ratio of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the compound is
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 2: 5
(d) 2: 7
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following will most readily dehydrated in acidic solution?

Answer
B
Question. For the reaction represented by the equation. CX4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2X 2O.9.0 g of CX4 completely reacts with 1.74 g of oxygen. The approximate molar mass of X will be
(a) 20
(b) 40
(c) 60
(d) 80
Answer
D
Question. In estimation of nitrogen, by Kjeldahl’s method, CuSO4 acts as an
(a) oxidising agent
(b) reducing agent
(c) catalysing agent
(d) hydrolysing agent
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following is an intermediate in the reaction of benzene with CH3 Cl in the presence of anhydrous AlCI3 ?

Answer
C
Question. Which of the substances is purified by sublimation ?
(a) Benzoic acid
(b) Camphor
(c) Naphthalene
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. On combustion, a gaseous hydrocarbon gives 0.72 g of water and 3.08 g of CO2 . The empirical formula of the hydrocarbon is
(a) C2H4
(b) C3H4
(c) C6H5
(d) C7H8
Answer
D
Question. An oxygen contauung organic compound was found to contain 52% carbon and 13% hydrogen. Its vapour density is 23. The compound reacts with sodiwn metal to liberate hydrogen. A functional isomer of this compound is
(a) ethanal
(b) methoxy methane
(c) methoxy ethane
(d) ethanol
Answer
B
Question. The ease of nitration of the following three hydrocarbons follows the order

(a) II = III ,,, I
(b) II > I > III
(c) III > II > I
(d) I =Ul>II
Answer
B
Question. The sodium extract of an organic compound on acidification with acetic acid and addition of lead acetate solution gives a black precipitate. The organic compound contains
(a) nitrogen
(b) halogen
(c) sulphur
(d) phosphorous
Answer
C
Question. Which method is used to separate sugars ?
(a) Fractional crystallisation
(b) Sublimation
(c) chromatography
(d) Benedict’s reagent
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following has the most nucleophilic nitrogen?
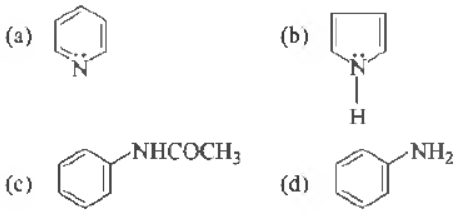
Answer
A
Question. During the fusion of an organic compound with sodium metal, nitrogen of the compound is converted into
(a) NaNO2
(b) NaNH2
(c) NaCN
(d) NaNC
Answer
C
Question. Lassaigne’s test for the detection of nitrogen fails in
(a) H2N—CO—NHNH2 · HCl
(b) NH2—NH2 · HCl
(c) NH2—CO—NH2
(d) C6H5—NH—NH2 · HCl
(e) C6H5CONH2
Answer
B
Question. Consider the following compounds,

Arrange the above compounds in the con-ect order according to their reactivity towards electrophile.
(a) II > III > I
(b) III < I < II
(c) I > II > III
(d) l=dl > III
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following process is suitable for the purification of aniline?
(a) Simple distillation
(b) Fractional distillation
(c) Fractional crystallisation
(d) Steam distillation
(e) Azeotropic distillation
Answer
D
Question. Acidified sodium fusion extract on addition with ferric chloride solution gives confirm the presence of blood red colouration which
(a) Sand Cl
(b) N and S
(c) N
(d) S
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following would react most readily with nucleophiles?

Answer
C
Question. Presence ofhalogen in organic compounds can be detected by using
(a) Leibig’s test
(b) Duma’s test
(c) Kjeldahl’s test
(d) Beilstein’s test
Answer
D
Question. For the purification, isolation and separation of organic compounds, the latest technique followed is
(a) chromatography
(b) steam distillation
(c) fractional crystallisation
(d) sublimation
Answer
A
Question. In the compound

Ring I Ring II
electrophilic substitution occurs at
(a) ortho/para-position at ring I
(b) meta-position at ring I
(c) ortholpara-position at ring II
(d) meta-position at ring II
Answer
C
Question. When SCN– is added to an aqueous solution containing Fe(NO3)3, the complex ion produced is
(a) [Fe(OH2)2 (SCN)]2+
(b) [Fe(OH2)5 (SCN)]2+
(c) [Fe(OH2)8 (SCN)]2+
(d) [Fe(OH2)(SCN)]6+
Answer
B
Question. The best method to separate the mixture of ortho and para nitrophenol (1:1) is
(a) vaporisation
(b) colour spectrum
(c) distillation
(d) crystallisation
Answer
C
Question. The least active electrophile is

Answer
C
Question. 0.25 g of an organic compound on Kjeldahl’s analysis gave enough ammonia to just neutralise 10 cm3 of 0.5 M H2SO4 . The percentage of nitrogen in the compound is
(a) 28
(b) 56
(c) 14
(d) 112
(e) 42
Answer
B
Question. 29.5 mg of an organic compound containing nitrogen was digested according to Kjeldahl’s method and the evolved ammonia was absorbed in 20 mL of 0.1 M HCI solution. The excess of the acid required 15 mL of 0.1 M NaOH solution for complete neutralisation. The percentage of nitrogen in the compound is
(a) 59.0
(b) 47.4
(c) 23.7
(d) 29.5
Answer
C
Question. In Kjeldahl’s method, ammonia from 5g of food neutralises 30cm3 of 0.1 N acid. The percentage of nitrogen in the food is
(a) 0.84
(b) 8.4
(c) 16.8
(d) 1.68
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following will be easily nitrated?

Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements is not true for SNI reaction ?
(a) 3° alkyl halides generally react through SNI reaction
(b) The rate of the reaction does not depend upon the molar concentration of the nucleophile
(c) 1 ° alkyl halides generally react through SNI reaction
(d) It is favoured by polar solvents
Answer
C
Question. The ease of dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides with alcoholic KOH is
(a) 3° < 2° < 1°
(b) 3° > 2° > 1°
(c) 3° < 2° > 1°
(d) 3° > 2° < 1°
Answer
B
Question. Dehydration of alcohol usually goes by
(a) E1 mechanism
(b) E2 mechanism
(c) E1 cb mechanism
(d) SN2 mechanism
Answer
A
Question.
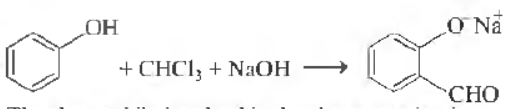
The electrophile involved in the above reaction is
⊕
(a) dichloromethyl cation (CHCl2)
(b) dichlorocarbene (:CCl2)
(c) trichloromethyl anion (CCI3)
⊕
(d) fonnyl cation (CHO)
Answer
B
Question. Under identical conditions, the SNI reaction will occur most efficiently with
(a) tert-butyl chloride
(b) 1-chlorobutane
(c) 2-methyl-1-chloropropane
(d) 2- chlorobutane
Answer
A
Question. The total number of possible alkenes by dehydrobromination of 3-bromo-3-cyclopentylhexane using alcoholic KOH is
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 7
Answer
B
Question. The compound formed in the positive test for nitrogen with the Lassaigne’ s solution of an organic compound is
(a) Fe4 [Fe(CN)6]3
(b) Na3 [Fe(CN)6 ]
(c) Fe(CN)3
(d) Na4 [Fe(CN)5 NOS]
Answer
A
Question. The decreasing order of nucleophilicity following nucleophiles is
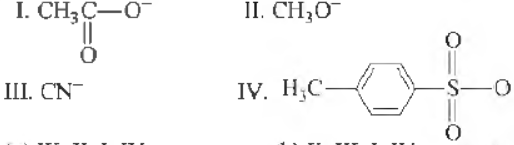
(a) Ill, II, I, IV
(b) II, III, I, IV
(c) IV, III, II, I,
(d) I, n, III, IV
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following compounds does not follow Markownikoffs rule?
(a) CH3—CH=CH2
(b) CH3CH=CHCH3
(c) CH3—CH—CH=CH2
l
CH3
(d) CH3—CH2—CH=CH2
Answer
B
Question. In SNI reaction, the racemisation takes place. It is due to
(a) inversion configuration
(b) retention of configuration
(c) conversion of configuration
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
D
Question. An organic compound which produces a bluish green coloured flame on heating in presence of copper is
(a) chlorobenzene
(b) benzaldehyde
(c) aniline
(d) benzoic acid
Answer
A
Question. An organic compound having molecular mass 60 is found to contain 20% C, 6.67% H and 46.67% N while rest is oxygen. On heating, it gives NH3 along with a solid residue. The solid residue gives violet colour with alkaline copper sulphate solution. The compound is
(a) CH3CH2CONH2
(b) (NH2)2 CO
(c) CH3CONH2
(d) CH3NCO
Answer
B
Question. Na2S+ Na2 [Fe(CN)5 NO]→ purple colour. It is due to
(a) Na4 [Fe(CN)3 NOS]
(b) Na3 [Fe(CN)5 NOS]
(c) Na4 [Fe(CN)5 NO]
(d) Na4 [Fe(CN)5 NOS]
Answer
D
Question. 5.6 g of an organic compound on burning with excess of oxygen gave 17.6 g of CO2 and 7.2 g of H2O. The organic compound is
(a) C6H6
(b) C4H8
(c) C3H8
(d) CH3COOH
(e) CH3CHO
Answer
B
Question. I. CH3CH2Br →LAH C2H6 and
II. (CH3)3 CBr →LAH alkene,
The reason for this is
(a) (I) SN2, (II) E1 mechanism
(b) (I) SN1, (II) E2 mechanism
(c) (I) SN1, (II) E1 mechanism
(d) (I) SN2 , (JI) E2 mechanism
Answer
D
Question. Vinyl chloride undergoes
(a) Only addition reactions
(b) Only elimination reactions
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) substitution reactions
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following cannot undergo nucleophilic substitution under ordinary conditions ?
(a) Chlorobenzene
(b) Tert-butylchloride
(c) Isopropyl chloride
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. Protic solvent is
(a) diethyl ether
(c) acetone
(b) n-hexane
(d) ethanol
Answer
D
Question. Arrange the following compounds in order of their decreasing reactivity towards an electrophile, E⊕ .
I. Chlorobenzene
II. 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene
III. p-nitrochlorobenzene
(a) III > II > I
(c) I > III > II
(b) II > III > I
(d) I > II > III
Answer
C
Question. C2H5Cl + aq. NaOH → C2H5OH + NaCl this reaction is
(a) electrophilic substitution ofl order
(b) electrophilic substitution of II order
(c) nucleophilic substitution ofl order
(d) nucleophilic substitution of II order
Answer
D
Question. 0.765 g of an acid gives 0.535 g of CO2 and 0.138 g of H2O. Then, the ratio of the percentage of carbon and hydrogen is
(a) 19 : 2
(b) 18 : 11
(c) 20 : 17
(d) 1 : 7
Answer
A
Question. Liebig’s test is used to estimate
(a) H
(b) C
(c) Both C and H
(d) N
Answer
C
Question. How much of sulphur is present in an organic compound, if 0.53 g of the compound gave 1.158 g of BaSO4 on analysis?
(a) 10%
(b) 15%
(c)20%
(d) 25%
(e) 30%
Answer
E
Question. Conversion of chlorobenzene to phenol involves
(a) electrophilic substitution
(b) nucleophilic substitution
(c) free radical substitution
(d) electrophilic addition
Answer
B
Question. During nitration of benzene, the attacking electrophile is
(a) NO–3
(b) NO–2
(c) NO+2
(d) HNO3
Answer
C
Question. The function of AlCl3 in Friedel-Craft’s reaction is
(a) to absorb HCI
(b) to absorb water
(c) to produce nucleophile
(d) to produce electro phi le
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following solvents are aprotic?
I. NH3
II. SO2
III. CH3CN
IV. CH3CO2H
(a) I, II, III
(b) I, III, IV
(c) II, III
(d) I, III
Answer
A
Question. The Kolbe’s electrolysis proceeds via
(a) nucleophilic substitution mechanism
(b) electrophilic addition mechanism
(c) free radical mechanism
(d) electrophilic substitution reaction
Answer
C
Question. Grignard reagent adds to
(a) C = 0
{b) —C= N
(c) C = S
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Dehydration of alcohol is an example of which type of reaction ?
(a) Substitution
(b) Elimination
(c) Addition
(d) Rearrangement
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is arranged according to the nature indicated ?
(a) Electrophile – NO2+ , Br+,
Nucleophile -CH3 OH, N–3
(b) Electrophile – NO+2 , CH3OH,
Nucleophile – Br+, N–3
(c) Electrophile – CH3OH,N–3 .
Nucleophile – N+2 , Br+
(d) Electrophile – Br+ , N–3 ,
Nucleophile -CH3OH, NO2
Answer
A
Question. Reaction of methyl bromide with aqueous sodium hydroxide involves
(a) racemisation
(b) SNI mechanism
(c) retention of configuration
(d) SN2 mechanism
Answer
D
Question. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the nitro group is meta-directing because it
(a) decreases electron density at ortho and para-positions
(b) decreases electron density at meta-position
(c) increases electron density at meta-position
(d) increases electron density at ortho and para-positions
Answer
C
Question. The electrophile involved in the sulphonation of benzene is
(a) SO+3
(b) SO2-3
(c) H3O+
(d) SO3
Answer
D
Question. In which of the following ways, does the hydride ion tend to function ?
(a) An electrophile
(b) A nucleophile
(c) A free radical
(d) An acid
Answer
B
Question. Following reaction,
(CH3)3 CBr + H2O → (CH3)3 COH + HBr
is an example of
(a) elimination reaction
(b) free radical substitution
(c) nucleophilic substitution
(d) electrophilic substitution
Answer
C
Question. Formation of cyanohydrin from a ketone is an example of
(a) electrophilic addition
(b) nucleophilic addition
(c) electro phi lie substitution
(d) nucleophilic substitution
Answer
B
Question. RX + I– →R – I+x– is an example of ……. reaction.
(a) nucleophilic addition
(b) nucleophilic substitution
(c) electrophilic addition
(d) elimination
Answer
B
Question. The reaction,
O O
ll ll
R—C—X—Nu– → R—C—Nu+X–
fastest when Xis
(a) OCOR
(b) OC2H5
(c) NH2
(d) Cl
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is least reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction?
(a) (CH3)3 C—Cl
(b) CH2=CHCl
(c) CH3CH2Cl
(d) CH2=CHCH2CI
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is an electrophile?
(a) H2O
(b) SO3
(c) NH3
(d) ROR
Answer
B
Question. The following compound will undergo substitution more readily than benzene electrophilic
(a) nitrobenzene
(b) benzoic acid
(c) benzaldehyde
(d) phenol
Answer
D
Question. Nitration of benzene is
(a) electrophilic substitution
(b) electrophilic addition
(c) nucleophilic substitution
(d) nucleophilic addition
Answer
A
Question. The ammonia evolved from the treatment of 0.30 g of an organic compound for the estimation of nitrogen was passed in 100 mL of 0.1 M sulphuric acid. The excess of acid required 20 mL of 0.5 M sodium hydroxide solution for complete neutralisation. The organic compound is
(a) acetamide
(b) benzamide
(c) urea
(d) thiourea
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is most reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction ?
(a) CH2 = CH—Cl
(b) C6H5Cl
(c) C6H5CH2Cl
(d) ClCH2—CH = CH2
Answer
C
Question. Alkyl halide can be converted into alkene by
(a) nucleophilic substitution reaction
(b) elimination reaction
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) rearrangement
Answer
B
Question. In the nucleophilic substitution reactions (SN2 or SNI), the reactivity of alkyl halides follows the sequence
(a) R – I > R – Br > R – Cl > R – F
(b) R – CI > R – F > R – Br> R – I
(c) R – F > R – Cl > R – Br > R – I
(d) R – I > R – F > R – Cl > R – Br
Answer
A
Question. Quantitative measurement of nitrogen in an organic compound is done by the method
(a) Berthelot method
(b) Beilstein’s method
(c) Lassaigne’s test
(d) Kjeldahl’s method
Answer
D
Question. The reaction of sodium ethoxide with iodoethane to form diethyl ether is termed as
(a) electrophilic substitution
(b) nucleophilic substitution
(c) electrophilic addition
(d) radical substitution
Answer
B

We hope you liked the above Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques MCQ Class 11 Chemistry. In case you have any questions please put them in the comments box below and our teachers will provide you a response.
