The p-Block Elements MCQ Class 11 Chemistry
Please refer to Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements MCQ Class 11 Chemistry with answers below. These multiple-choice questions have been prepared based on the latest NCERT book for Class 11 Chemistry. Students should refer to MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry with Answers to score more marks in Grade 11 Chemistry exams. Students should read the chapter The p-Block Elements and then attempt the following objective questions.
MCQ Questions Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
The The p-Block Elements MCQ Class 11 Chemistry provided below covers all important topics given in this chapter. These MCQs will help you to properly prepare for exams.
Question. Boron halides behave as Lewis acids because of their ………. nature.
(a) proton donor
(b) covalent
(c) electron deficient
(d) ionising
Answer
C
Question. Name of the alloy of aluminium which is used in aeroplane is
(a) duralumin
(b) bell metal
(c) y-alloy (gamma alloy)
(d) aluminium bronze
Answer
A
Question. Aluminium metal is refined by
(a) Serpeck’s process
(b) Baeyer’s process
(c) Hall’s process
(d) Hoope’s process
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is the correct statement ?
(a) Boric acid is a protonic acid
(b) Beryllium exhibits coordination number of six
(c) Chlorides of both beryllium and aluminium have b1idged chloride structures in solid phase
(d) B2H6 · 2NH3 is known as inorganic benzene
Answer
C
Question. Aluminium is obtained by
(a) reducing AI2O3 with coke
(b) electrolysing AI2O3 dissolved in Na3AlF6
(c) reducing AI2O3 with chromium
(d) heating alumina with cryolite
Answer
B
Question. The correct statements for orthoboric acid is/are
(a) it behaves as a weak acid in water due to self ionisation
(b) acidity of its aqueous solution increases upon addition of ethylene glycol
(c) it has a three-dimensional structure due to hydrogen bonding
(d) it is a weak electrolyte in water
Answer
A,D
Question. Aluminium oxide is not reduced by chemical reactions since
(a) reducing agent contaminate
(b) the process pollute the environment
(c) aluminium oxide is highly stable
(d) aluminium oxide is reactive
Answer
C
Question. Bauxite ore is made up of Al2O3 + SiO2 + TiO2 + Fe2O3 . This ore is treated with cone. NaOH solution at 500 Kand 35 bar pressure for few hours and filtered hot. In the filtrate the species present, are
(a) NaAl (OH)4
(b) Na2 Ti(OH)6
(c) NaAl(OH)4 and Na2SiO3
(d) Na2SiO3
Answer
A
Question. Correct formula of aluminium nitride is
(a) Al2N2
(b) AlN3
(c) AlN2
(d) AlN
Answer
D
Question. Aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3 is insoluble in water, but dissolves readily in both acidic and basic solutions. Such behaviour is characteristic of
(a) polyprotic behaviour
(b) hydrophilic behaviour
(c) a buffer
(d) amphoteric behaviour
Answer
D
Question. For the properties mentioned the correct trend for the different species is in
(a) strength as Lewis acid – BCi3 > AlCl3 > GaCl3
(b) inert pair effect – Al > Ga > In
(c) oxidising property – Al3+ > In3+ > Tl3+
(d) first ionisation enthalpy – B > Al > Tl
Answer
A,B
Question. In alumino thermic process, Al is used as
(a) reducing agent
(b) oxidising agent
(c) catalyst
(d) electrolyte
Answer
A
Question. BCI3 + H2O → X, the products formed in the reaction are
(a) B2O3 + HOCI
(b) H3BO3 + HCI
(c) B2H6 + HCl
(d) No reaction
Answer
B
Question. The ratio of Fe2O3 and Al by weight in therrnite is
(a) 1: 3
(b) 1: 2
(c) 3: 1
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Potash alum dissolves in water to give a/an
(a) acidic solution of H2SO4
(b) alkaline solution
(c) acidic solution of HCI
(d) neutral solution
Answer
A
Question. Aluminium chloride exists as dinmr, Al2Cl6 in solid state as well as in solution of non-polar solvents such as benzene. When dissolved in water, it gives
(a) Al3+ + 3Cl–
(b) [Al(H2O)6]3+ + 3Cl–
(c) [AI(OH)6]3- + 3HCI
(d) AI2O3 + 6HCI
Answer
B
Question. B(OH)3 + NaOH ⇌ NaBO2 + Na [B(OH)4 ] + H2O How can this reaction is made to proceed in forward direction ?
(a) Addition of cis-1, 2-diol
(b) Addition of borax
(c) Addition of trans-1, 2-diol
(d) Addition of Na2HPO4
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following compounds, is not a protonic acid ?
(a) SO(OH)2
(b) SO2 (OH)2
(c) B(OH)3
(d) PO(OH)3
Answer
C
Question. The mass of carbon anode consumed (giving only carbon dioxide) in production of270 kg of aluminium metal from bauxite by the Hall process is (Atomic mass of Al = 27)
(a) 180 kg
(b) 270 kg
(c) 540 kg
(d) 90 kg
Answer
D
Question. Alum is added to muddy water because
(a) it acts as disinfectant
(b) it results in coagulation of clay and sand
(c) clay is soluble in alum, hence removes it
(d) it makes water alkaline which is good for health
Answer
B
Question. An element ‘X’ which occurs in the first short period has an outer electronic structure s2p1 • What is the formula and acid-base character of its oxides?
(a) XO3 , basic
(b) X2O3 , basic
(c) X2O3 , acidic
(d) XO2 , acidic
Answer
C
Question. Which is a co1Tect statement about diborane structure?
(a) All HBH bond angles are equal
(b) All H—B bond lengths are equal
(c) It has two 3-centre-2 electron bonds
(d) All hydrogen and boron atoms are in one plane
Answer
C
Question. Boron cannot form which one of the following anions?
(a) BF3-6
(b) BH–4
(c) B(OH)–4
(d) BO–2
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following correctly represents the variation of electronegativity (EN) with atomic number (Z) of group 13 elements?
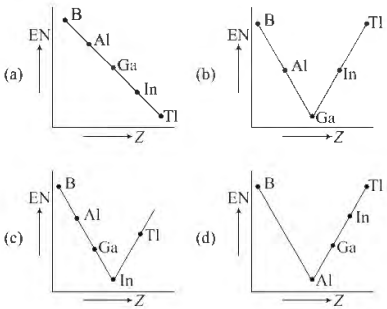
Answer
D
Question. The chief impurity present in red bauxite is
(a) SiO2
(b) Fe2O3
(c) K2SO4
(d) NaF
Answer
B
Question. In the electrolytic method of obtaining aluminium from purified bauxite, cryolite is added to the charge in order to
(a) minimise the heat loss due to radiation
(b) protect aluminium produced from oxygen
(c) dissolve bauxite and render it conductor of electricity
(d) lower the melting point of bauxite
Answer
D
Question. Magnalium contains
(a) Al + Mg
(b) Mg + Cu
(c) Mg + Fe
(d) Mg + Ag
Answer
A
Question. In diborane the two H—B—H angles are nearly
(a) 60°, 120°
(b) 97°, 120°
(c) 95°, 150°
(d) 120°, 180°
Answer
B
Question. Inorganic benzene is
(a) B3H3N3
(b) BH3NH3
(c) B3H6N3
(d) H3B3N6
Answer
C
Question. Alums are used for
(a) tanning of leather
(b) coagulation of blood
(c) purification of water
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is a use of alum ?
(a) Making explosives
(b) Bleaching clothes
(c) Water softening
(d) All of the above
Answer
C
Question. Purification of Al by electrolysis method is called
(a) Hall’s process
(b) Baeyer process
(c) Ostwald process
(d) Hoope’s process
Answer
D
Question. Aluminium reacts with caustic soda to form
(a) aluminium hydroxide
(b) aluminium oxide
(c) sodium metaaluminate
(d) sodium tetraaluminate
Answer
C
Question. Heating an aqueous solution of aluminium chlotide to dryness will give
(a) AI(OH)CI2
(b) AI2O3
(c) AI2Cl6
(d) AICl3
Answer
B
Question. The order of acidic strength of boron trihalides
(a) BF3 < BCI3 < BBr3 < BI3
(b) BI3 < BBr3 < BCI3 < BF3
(c) BCI3 < BBr3 < BI3 < BF3
(d) BBr3 < BCI3 < BF3 < BI3
(e) BF3 < BI3 < BCI3 < BBr3
Answer
A
Question. Observe the following statements regarding purification of bauxite.
I. During Hall’s process, silica is removed as Si (vapour).
II. Bauxite ore contaminated with Fe2O3 is purified in Baeyer’s process.
III. During Serpeck’s process, AIN is formed. The correct answer is
(a) I, II and III
(b) I and II
(c) I and III
(d) II and III
Answer
D
Question. The structure of diborane (B2H6) contains
(a) four 2c -2e– bonds and four 3c- 2e– bonds
(b) two 2c-2e– bonds and two 3c-2e– bonds
(c) two 2c -2e– bonds and four 3c – 2e– bonds
(d) four 2 c -2e– bonds and two 3c – 2e–
Answer
D
Question. In Goldschmidt aluminothermic process, thermite contains
(a) 3 parts of AI2O3 and 4 parts of Al
(b) 3 parts of AI2O3 and 2 parts of Al
(c) 3 parts of AI2O3 and 1 part of Al
(d) 1 part of AI2O3 and 1 part of Al
Answer
C
Question. Carbon cannot be used in the reduction of Al2O3 because
(a) it is an expensive proposition
(b) the enthalpy of formation of CO2 is more than that of Al2O3
(c) pure carbon is not easily available
(d) the enthalpy of formation of Al2O3 is too high
Answer
D
Question. Tincal is
(a) Na2CO3 · 10H2O
(b) NaNO3
(c) Na2B4O7 · 10H2O
(d) NaCl
Answer
C
Question. Aluminium is extracted by the electrolysis of
(a) alumina
(b) bauxite
(c) molten cryolite
(d) alumina mixed with molten cryolite
Answer
D
Question. Purification of alumina takes place by
(a) Bosch process
(b) Hall’s process
(c) Hoope’s process
(d) quartation process
Answer
B
Question. Boric acid is used in carrom boards for smooth gliding of pawns because
(a) H3BO3 molecules are loosely chemically bonded and hence soft
(b) its low density makes it fluffy
(c) it can be powdered to a very small grain size
(d) H-bonding in H3BO3 gives it a layered structure
Answer
D
Question. Muddy water can be purified through coagulation by using
(a) common salt
(b) alums
(c) sand
(d) lime
Answer
B
We hope you liked the above The p-Block Elements MCQ Class 11 Chemistry. In case you have any questions please put them in the comments box below and our teachers will provide you a response.
