The p – Block Elements Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions
Please refer to The p – Block Elements Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 1 The p – Block Elements in NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The p – Block Elements
All The p – Block Elements Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of Standard 12 Chemistry. Please learn them and let us know if you have any questions.
Case Based Questions
1. All the elements of group 16 have ns2 np4 configuration in their outermost shell. Therefore, the atoms of these elements try to gain or share two electrons to achieve noble gas configuration. Sulphur and other elements of group 16 are less electronegative than oxygen, so they cannot accept electrons easily. By sharing of two electrons with other elements, these element acquire ns2np6 configuration and exhibit +2 oxidation state. Except oxygen, group 16 elements have vacant d-orbitals in their valence shell to which electrons can be promoted from p- and s-orbitals of the same shell. As a result, they can show +4 and +6 oxidation states also.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. Like sulphur, oxygen is not able to show +4 and +6 oxidation states because
(a) oxygen is a gas while sulphur is a solid.
(b) sulphur has high ionisation enthalpy as compared to oxygen.
(c) oxygen has no d-orbitals in its valence shell.
(d) oxygen has high electron affinity as compared to sulphur. Ans. (c) Oxy
Question. Compounds of sulphur with +4 oxidation state acts as a/an
(a) oxidising agent.
(b) reducing agent.
(c) both oxidising as well as reducing agent.
(d) Cannot be predicted.
Answer
C
Question. Oxidation State of sulphur in Na2S4O6 is
(a) 7/2
(b) 5/2
(c) 1/2
(d) 3/2
Answer
B
Question.The Oxidation State of sulphur in S8, SO3 and H2S are respectively
(a) O, +6 and –2
(b) +6, 0 and –2
(c) –2, 0 and +6
(d) +2, +6 and –2
Answer
A
Question. Oxygen shows +2 oxidation state in
(a) OF2
(b) H2O
(c) Cl2O
(d) H2O2
Answer
A
2. Ozone is an unstable, dark blue diamagnetic gas. It absorbs the UV radiation strongly, thus protecting the people on earth from the harmful UV-radiation from the sun. The use of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) in aerosol and refrigerators and their subsequent escape into the atmosphere, is blamed for making holes in the ozone layer over the Antarctica. Ozone acts as a strong oxidising agent in acidic and alkaline medium. For this property, ozone is used as a germicide and disinfectant for sterilizing water. It is also used in laboratory for the ozonolysis of organic compounds and in industry for the manufacture of potassium permanganate, artificial silk, etc.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. Ozone gives carbonyl compounds with
(a) alkyl chloride.
(b) alkanes.
(c) alkenes followed by decomposition with Zn/ H2O.
(d) alcohols followed by decomposition with Zn/ H2O.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is not correct for ozone?
(a) It oxidises lead sulphide.
(b) It oxidises potassium iodide.
(c) It oxidises mercury.
(d) It cannot act at bleaching agent in dry state.
Answer
D
Question. The colour of ozone molecule is
(a) white
(b) blue
(c) pale green
(d) pale yellow
Answer
B
Question. Ozone acts as an oxidising agent due to
(a) liberation of nascent oxygen.
(b) liberation of oxygen gas.
(c) both (a) and (b).
(d) none of these
Answer
A
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Which is a stronger reducing agent, SbH3 or BiH3, and why?
Answer. BiH3 : Because it is stronger reducing agent as its tendency to liberate H is maximum.
Question. Write a reaction to show the reducing behaviour of H3PO2.
Answer. H3PO2 reduces AgNO3 to metallic Ag :
4AgNO3 + 2H2O + H3PO2 → 4Ag + 4HNO3 + H3PO4
Question. Which is a stronger oxidizing agent Bi(v) or Sb(v)?
Answer. Bi(v) is stronger oxidizing agent due to inert pair effect.
Question. Why does PCl3 fume in moisture?
Answer. PCl3 hydrolyses in moisture giving fumes of HCl.
PCl3 + 3H2O → H3PO3 + 3HCl
Question. Why does NO2 dimerise ?
Answer. NO2 contains odd number of valence electrons. It behaves as a typical odd molecule. On dimerisation, it is converted to stable N2O4 molecule with even number of electrons.
Question. Why is ICl more reactive than I2?
Answer. ICl is more reactive than I2 because I-Cl bond is weaker than I-I bond of I2.
Question. Of PH3 and H2S which is more acidic and why?
Answer. H2S, because of higher electronegativity of sulphur.
Question. Fluorine does not exhibit any positive oxidation state. Why?
Answer. Since fluorine is the most electronegative element and does not have d-orbitals in its valence shell, therefore, it cannot expand its octet and hence does not show positive oxidation state (O.S.) while other halogens have d-orbitals and therefore exhibit many oxidation states.
Question. Give the IUPAC name of the following compound :
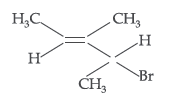
Answer. IUPAC name : 2-Bromo-3-methylpent-3-ene
Question. Why is BiH3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of group 15 elements?
Answer. Reducing nature depends upon the stability of MH bond. As the stability of the bond decreases from N to Bi hydrides, BiH3 is the strongest reducing agent.
Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question. Draw the structural formulae of the following compounds :
(i) H4P2O5 (ii) XeF4
Answer. (i) H4P2O5 (Pyrophosphorous acid) : (ii) XeF4 :

Question. Complete the following chemical reaction equations :

Answer.
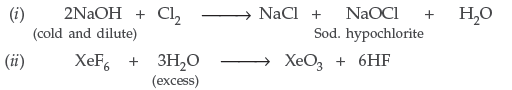
Question. Complete the following equations :
(i) Ag + PCl5 →
(ii) CaF2 + H2SO4 →
Answer. (i) Ag + PCl5 → 2AgCl + PCl3
(ii) CaF2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2HF
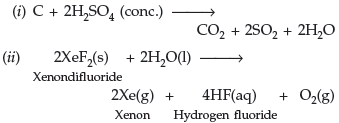
Question. Complete the following equations :
(i) C + conc. H2SO4 →
(ii) XeF2 + H2O →
Answer.
Question. Draw the structures of the following compounds :
(i) H2SO3 (ii) N2O5
Answer. (i) H2SO3 (ii) N2O5

Question. Account for the following :
(i) The two oxygen-oxygen bond lengths in ozone molecule are identical.
(ii) Most of the reactions of fluorine are exothermic.
Answer.
(ii) Due to much higher electrode potential, high electro-negativity and low bond dissociation enthalpy of F2.
Question. Complete the following chemical reaction equations :
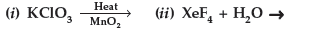
Answer.

Question. Complete the following chemical equations :
(i) P4 + SOCl2 →
(ii) F2 (Excess) + Cl2 300°C ⎯⎯⎯⎯→
Answer. (i) P4 + 8SOCl2 → 4PCl3 + 4SO2 + 2S2Cl2
(ii) 3F2 + Cl2 300°C → 2ClF3
(excess)
Question. Complete the following chemical reaction equations :
(i) P4 (s) + NaOH (aq) + H2O (l) ⎯⎯→
(ii) I– (aq) + H2O (l) + O3 (g) ⎯⎯→
Answer.

Question. What happens when
(i) PCl5 is heated? (ii) H3PO3 is heated?
Write the reactions involved. (Delhi)
Answer. (i) On heating PCl5 decomposes into PCl3 + Cl2
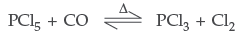
(ii) Orthophosphorous acid on heating disproportionates to give orthophosphoric acid and phosphine.

Question. Explain the following :
(i) Nitrogen is much less reactive than phosphorus.
(ii) NF3 is an exothermic compound but NCl3 is an endothermic compound.
Answer. (i) Due to presence of weak single bond in P – P than N ≡ N, phosphorous is more reactive than nitrogen and also because of high bond dissociation enthalpy of N ≡ N.
(ii) Due to smaller size of F as compared to Cl, the N– F bond is much stronger than N – Cl bond while bond dissociation energy of F2 is much lower than that of Cl2. Therefore, energy released during the formation of NF3 molecule is more than the energy needed to break N2 and F2 molecules into individual atoms. In other words, formation of NF3 is an exothermic reaction.
The energy released during the formation of NCl3 molecule is less than the energy needed to break N2 and Cl2 molecules into individual atoms. Thus formation of NCl3 is an endothermic reaction.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Draw the structures of the following molecules :
(i) H3PO2 (ii) ClF3
(b) Explain the following observations :
(i) Nitrogen is much less reactive than phosphorus.
(ii) Despite having greater polarity,hydrogen fluoride boils at a lower temperature than water.
(iii) Sulphur has greater tendency for catenation than oxygen in the same group.
Answer.
(ii) ClF3 :

(b) (i) Because P–P bond is weaker than N ≡ N bond, N2 is inert due to the presence of triple bond.
(ii) In water O is larger than F therefore Vander-Waals forces of attraction increase with increase in size and hence the boiling point increases.
(iii) It is because S – S bond is stronger than O – O bond as there is more interelectronic repulsion in O – O than in S – S.
Question. (a) Draw the structures of the following :
(i) N2O5 (ii) XeOF4
(b) Explain the following observations :
(i) The electron gain enthalpy of sulphur atom has a greater negative value than that of oxygen atom.
(ii) Nitrogen does not form pentahalides.
(iii) In aqueous solutions HI is a stronger acid than HCl.
Answer.
(b) (i) Because enthalpy of dissociation of S – S bond is higher than O – O bond and the hydration energy of S2– is less than that of O2– ion.
(ii) Due to absence of empty d-orbitals, N2 does not form pentahalides.
(iii) Due to lower bond dissociation energy and higher degree of ionization, HI acts as stronger acid than HCl in aqueous solution.
Question. (a) Draw the structures of the following molecules :
(i) N2O5 (ii) HClO4
(b) Explain the following observations :
(i) H2S is more acidic than H2O.
(ii) Fluorine does not exhibit any positive oxidation state.
(iii) Helium forms no real chemical compound.
Answer.
(b) (i) H2S is more acidic than H2O because bond dissociation enthalpy of H – S bond in H2S is less than that of H – O bond in H2O.
(ii) F is the most electronegative element. It has no d-orbitals and therefore, there is no scope for any electron promotion. So it can only show oxidation state of – 1 in its compounds.
(iii) Helium has very high ionisation enthalpy and no vacant d-orbitals,therefore no chemical compound of helium is known.
Question. (a) Complete the following chemical equations
(i) XeF4 + SbF5 →
(ii) Cl2+ F2 (excess) →
(b) Explain each of the following :
(i) Nitrogen is much less reactive thanphosphorus.
(ii) The stability of +5 oxidation state decreases down group 15.
(iii) The bond angles (O – N – O) are not of the same value in NO2– and NO2+ .
Answer. (a) (i) XeF4 + SbF5 → [XeF3]+ [SbF6]–
(ii) Cl2+ 3F2 (excess) → 2ClF3
(b) (i) Due to presence of triple bond between two nitrogen atoms/high bond dissociation enthalpy of nitrogen, whereas in phosphorus molecule there is single bond between four atoms of phosphorus so have low bond dissociation enthalpy.
(ii) Because the participation of outer selectron pair goes on decreasing down the group due to inert pair effect.
(iii) Because NO2– has sp2 hybridisation whereas NO2+ has sp hybridisation.
Question. (a) Describe the conditions and the steps involved in the manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process. Write the necessary reactions. (No diagram is required)
(b) Give reasons :
(i) Bond dissociation energy of F2 is less than that of Cl2.
(ii) Nitric oxide becomes brown when released in air.
Answer. (a) Contact Process : Burning sulphur in an excess of air S + O2 → SO2 (g)
or, By heating sulphide ores like pyrites in an excess of air :
4FeS2 + 11O2 → 2Fe2O3 + 8SO2
In either case, an excess of air is used so that the SO2 produced is already mixed with oxygen for the next stage. This is reversible reaction and the formation of SO3 is
exothermic in the presence of catalyst V2O5 at 720K.
2SO2 + O2 2SO3 ΔH = –196 KJ/mol
This cannot be done by simply adding water to the SO3. The reaction is so uncontrollable that it creates a fog of H2SO4. Instead, the SO3 is first dissolved in conc. H2SO4.
H2SO4 + SO3 → H2S2O7
The product is known as fuming sulphuric acid or oleum to which water is added to get H2SO4 H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4
(b) (i) Bond dissociation energy of F2 is less than that of Cl2 because of large electronelectron repulsion among the lone pair in F2 molecule.
(ii) Nitric oxide becomes brown when released in air because of the formation of NO2 gas.
Question. (a) Draw the molecular structure of following compounds :
(i) XeF6 (ii) H2S2O8
(b) Explain the following observations :
(i) The molecules NH3 and NF3 have dipole moments which are of opposite direction.
(ii) All the bonds in PCl5 molecule are not equivalent.
(iii) Sulphur in vapour state exhibits paramagnetism.
Answer.
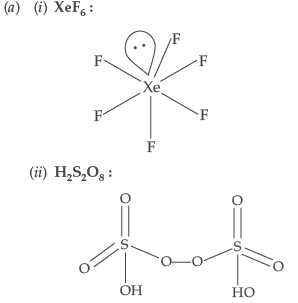
(b) (i) Because F is more electronegative than N in NF3 whereas N is more electronegative than H in NH3.
(ii) Because PCl5 has a trigonal bipyramidal structure in which the three equatorial P-Cl bonds are equivalent while the two axial bonds are longer than equatorial bonds.
(iii) Because sulphur in vapour state has two unpaired electrons in the antibonding π* orbitals like O2.
Question. (a) Elements of Gr. 16 generally show lower value of first ionization enthalpy compared to the corresponding periods of Gr. 15. Why?
(b) What happens when
(i) Concentrated H2SO4 is added to CaF2?
(ii) Sulphur dioxide reacts with chlorine in the presence of charcoal?
(iii) Ammonium chloride is treated with Ca(OH)2?
Answer.(a) Elements of group 16, i.e., oxygen family have general electronic configuration of ns2np4 while elements of group 15, i.e., nitrogen family have general electronic configuration of ns2np3 which is a relatively stable half-filled configuration with high exchange energy and therefore require more ionization energy to release electrons from this stable configuration.

Question. Give reasons for the following :
(i) Oxygen is a gas but sulphur is a solid.
(ii) O3 acts as a powerful oxidising agent.
(iii) BiH3 is the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of Group 15 elements.
Answer.(i) Due to small size and high electronegativity, oxygen forms pπ-pπ multiple bonds and thus forms diatomic. O2 molecule are held together by weak van der Waals forces of attraction which can be easily overcome by collisions at room temperature. Therefore O2 is gas at room temperature. On the other hand due to higher tendency for catenation and lower tendency for pπ-pπ multiple bonds, intra-atomic S8 has strong forces of attraction which cannot be overcome by collisions. Therefore S is solid at room temperature.
(ii) O3 is a powerful oxidising agent due to its high energy content than oxygen and hence decomposes to give diatomic oxygen and atomic oxygen
O3 (g) → O2 (g) + O(g)
Ozone Dioxygen Atomic oxygen
(iii) As we move down the group, the E—H bond length increases and their strength decreases. Bi—H bond is the weakest. It can break easily and evolves Ha2 gas which acts as the reducing agent.
Question. Account for the following :
(i) Chlorine water loses its yellow colour on standing.
(ii) BrCl3 is more stable than BrCl5.
(iii) Fluorine does not form oxoacids.
(iv) PCl5 acts as an oxidising agent.
(v) SO2 is an air pollutant.
Answer. (i) Cl2
water on standing loses its yellow colour due to the formation of HCl and HOCl. HOCl is unstable and decomposes to HCl. As a result, yellow colour disappears.
Cl2 + H2O → HCl + HOCl
2HOCl → 2HCl + O2
(colourless)
(ii) In BrCl3 , Br can accommodate three chlorine atoms around it and hence it is stable but in BrCl5 , five Cl atoms cannot be accommodated around Br and hence it is unstable.
(iii) Due to high electonegativity and small size F does not form oxoacids.
(iv) In PCl5, the oxidation state of phosphorus is +5. Thus, it cannot increase its oxidation state beyond +5. So PCl5 cannot act as a reducing agent. However, it can decrease its oxidation state from +5 to +3 or to some lower value.
Thus, it acts as an oxidising agent.
(v) SO2 is a pungent and irritating gas. It acts as an air pollutant due to the following reasons:
• It causes throat and eye irritation as it is absorbed readily by respiratory tract.
• It combines with moisture forming sulphurous acid. It is then converted into H2SO4. Both these acids cause acid rain and destroy the marble, corrode metals, deteriorate fabrics, paper, leather etc.
Question. (a) Give reasons for the following:
(i) Bond enthalpy of F2 is lower than that of Cl2.
(ii) PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3.
(b) Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(i) ClF3 (ii) (HPO3)3 (iii) XeF4
Answer. (a) (i) Due to smaller size of F than Cl as a result of which electron-electron repulsions between the lone pairs of electrons are very large than that of Cl, hence bond dissociation enthalpy of F2 is less than that of Cl2.
(ii) PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3 because PH3 cannot form hydrogen bonds like NH3.
(b) (ii) (HPO3)3 : Cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid

Question. (a) Account for the following:
(i) Helium is used in diving apparatus.
(ii) Fluorine does not exhibit positive oxidation state.
(iii) Oxygen shows catenation behaviour less than sulphur.
(b) Draw the structures of the following molecules:
(i) XeF2 (ii) H2S2O8
Answer. (a) (i) Helium is used in diving apparatus because of its very low solubility in blood and therefore an oxygen-helium mixture is used for artificial respiration.
(ii) Because it is most electronegative element and does not have d-orbitals for octet expansion, therefore it shows only a negative oxidation state of – 1.
