The Solid State MCQ Class 12 Chemistry
Please refer to Chapter 1 The Solid State MCQ Class 12 Chemistry with answers below. These multiple-choice questions have been prepared based on the latest NCERT book for Class 12 Chemistry. Students should refer to MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry with Answers to score more marks in Grade 12 Chemistry exams. Students should read the chapter The Solid State and then attempt the following objective questions.
MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State
The Solid State MCQ Class 12 Chemistry provided below covers all important topics given in this chapter. These MCQs will help you to properly prepare for exams.
Question. Which of the following represents monoclinic crystal system?
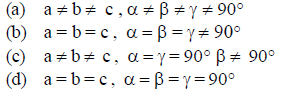
Answer
B
Question. CsBr crystallises in a body centered cubic lattice. The unit cell length is 436.6 pm. Given that the atomic mass of Cs = 133 and that of Br = 80 amu and Avogadro number being 6.02 × 1023 mol–1, the density of CsBr is
(a) 0.425 g/cm3
(b) 8.5 g/cm3
(c) 4.25 g/cm3
(d) 82.5 g/cm3
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following oxides shows electrical properties like metals ?
(a) SiO2
(b) MgO
(c) SO2 (s)
(d) CrO2
Answer
D
Question. The total number of tetrahedral voids in the face centred unit cell is ______.
(a) 6
(b) 8
(c) 10
(d) 12
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is not true ?
(a) Paramagnetic substances are weakly attracted by magnetic field.
(b) Ferromagnetic substances cannot be magnetised permanently
(c) The domains in antiferromagnetic substances are oppositely oriented with respect to each other.
(d) Pairing of electrons cancels their magnetic moment in the diamagnetic substances.
Answer
B
Question. Pottasium has a bcc structure with nearest neighbour distance 4.52 Å. Its atomic weight is 39. Its density (in kg m–3) will be
(a) 454
(b) 804
(c) 852
(d) 910
Answer
D
Question. Magnetic moment of electron is due to which of the following reason?
(a) Due to its orbital motion around the nucleus.
(b) Due to its spin around its own axis.
(c) Due to negative charge on electron.
(d) Both (a) and (b).
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not a characteristic property of solids?
(a) Intermolecular distances are short.
(b) Intermolecular forces are weak.
(c) Constituent particles have fixed positions.
(d) Solids oscillate about their mean positions.
Answer
B
Question. Most crystals show good cleavage because their atoms, ions or molecules are
(a) weakly bonded together
(b) strongly bonded together
(c) spherically symmetrical
(d) arranged in planes
Answer
D
Question. AB; crystallizes in a body centred cubic lattice with edge length ‘a’ equal to 387 pm. The distance between two oppositely charged ions in the lattice is :
(a) 335 pm
(b) 250 pm
(c) 200 pm
(d) 300 pm
Answer
A
Question. A perfect crystal of silicon interchange is doped with some elements as given in the options. Which of these options show n-type semiconductors ?
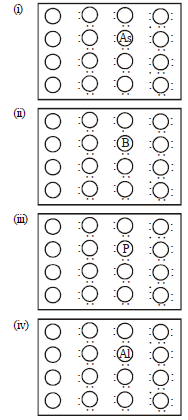
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii)
Answer
A
Question. A metal crystallizes in 2 cubic phases fcc and bcc whose unit cell lengths are 3.5 Å and 3.0Å respectively. The ratio of their densities is
(a) 0.72
(b) 2.04
(c) 1.46
(d) 3.12
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following has Frenkel defects?
(a) Sodium chloride
(b) Graphite
(c) Silver bromide
(d) Diamond
Answer
C
Question. If we mix a pentavalent impurity in a crystal lattice of germanium, what type of semiconductor formation will occur?
(a) p-type
(b) n-type
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the two.
Answer
B
Question. Which defect is shown in the given figure?
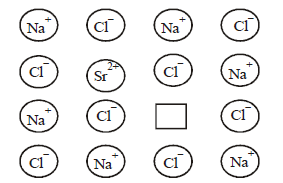
(a) Frenkel defect
(b) Impurity defect
(c) Schottky defect
(d) Vacancy defect
Answer
B
Question. The number of octahedral voids present in a lattice is A .The number of closed packed particles, the number of tetrahedral voids generated is B the number of closed packed particles
(a) A- equal, B- half
(b) A- twice, B- equal
(c) A- twice , B- half
(d) A- equal, B- twice
Answer
D
Question. When electrons are trapped into the crystal in anion vacancy, the defect is known as :
(a) Schottky defect
(b) Frenkel defect
(c) Stoichiometric defect
(d) F-centre
Answer
D
Question. Crystal defect indicated in the diagram below is
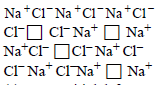
(a) Interstitial defect
(b) Schottky defect
(c) Frenkel defect
(d) Frenkel and Schottky defects
Answer
B
Question. Which statement does not make sense?
(a) Frenkel defect is not found in alkali metal halides
(b) Schottky defect is very common in alkali metal halides
(c) Schottky defect lowers the density of the crystal
(d) Frenkel defect lowers the density of the crystal.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following defects is also known as dislocation defect ?
(a) Frenkel defect
(b) Schottky defect
(c) Non – stoichiometric defect
(d) Simple interstitial defect
Answer
A
Question. In stoichiometric defects, the types of compound exhibit Frenkel defects have/has
(a) Low co-ordination nos.
(b) High co-ordination
(c) Small difference in the size of cations and anions
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Iron crystallizes in a b.c.c. system with a lattice parameter of 2.861 Å. Calculate the density of iron in the b.c.c. system
(Atomic weight of Fe = 56, NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol–1)
(a) 7.92 g ml–1
(b) 8.96 g ml–1
(c) 2.78 g ml–1
(d) 6.72 g ml–1
Answer
A
Question. The crystal with metal deficiency defect is
(a) NaCl
(b) FeO
(c) KCl
(d) ZnO
Answer
B
QuestioN. The fraction of total volume occupied by the atoms present in a simple cube is

Answer
D
Question. Which of the following crystals does not exhibit Frenkel defect?
(a) AgBr
(b) AgCl
(c) KBr
(d) ZnS
Answer
C
Question. How many chloride ions are surrounding sodium ion in sodium chloride crystal ?
(a) 4
(b) 8
(c) 6
(d) 12
Answer
C
Question. When a single substance can crystallize in two or more forms under different conditions provided, it is called as _________
(a) Polymorphous
(b) Isomorphous
(c) Semimorphous
(d) Multimorphous
Answer
A
Question. Cations are present in interstitial sites in
(a) Frenkel defect
(b) Schottky defect
(c) Vacancy defect
(d) Metal deficiency defect
Answer
A
Question. Close packing is maximum in the crystal which is
(a) bcc
(b) fee
(c) simple cubic
(d) end centred cubic
Answer
B
Question. In diamond, carbon atom occupies FCC lattice points as well as alternate tetrahedral voids. If the edge length of the unit cell is 356 pm, then the radius of the carbon atom is
(a) 77.07 pm
(b) 154.14 pm
(c) 251.7 pm
(d) 89 pm
Answer
A
Question. Amorphous solids are actually super cooled liquids.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is a covalent crystal?
(a) Rock salt
(b) Ice
(c) Quartz
(d) Dry Ice
Answer
C
Question. Lithium metal crystallizes in a body-centered cubic crystal. If the length of the side of the unit cell of lithium is 351 pm, the atomic radius of lithium will be
(a) 151.8 pm
(b) 75.5 pm
(c) 300.5 pm
(d) 240.8 pm
Answer
A
Question. The lattice site in a pure crystal cannot be occupied by _________.
(a) molecule
(b) ion
(c) electron
(d) atom
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is true for an amorphous solid?
(a) Long range order is present
(b) Short range order is present
(c) There is no orderly arrangement
(d) Complete order is present at lower temperatures
Answer
B
Question. Graphite is a good conductor of electricity due to presence of –
(a) lone pair of electrons
(b) free valence electrons
(c) cations
(d) anions
Answer
B
Question. An AB2 type structure is found in
(a) NaCl
(b) CaF2
(c) Al2O3
(d) N2O
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is true about the value of refractive index of quartz glass ?
(a) Same in all direction
(b) Different in different directions
(c) Cannot be measured
(d) Always zero
Answer
A
Question. A metal crystallises with a face-centered cubic lattice. The edge of the unit cell is 408 pm. The diameter of the metal atom is
(a) 288 pm
(b) 408 pm
(c) 144 pm
(d) 204 pm
Answer
A
Question. In the crystals of which of the following ionic compounds , the distance between centres of the cations and anions is the maximum ?
(a) LiF
(b) CsF
(c) CsI
(d) LiI
Answer
C
Question. The molal elevation constant depends upon
(a) nature of solute.
(b) nature of the solvent
(c) vapour pressure of the solution.
(d) enthalpy change.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following transition metal oxides is paramagnetic?
(a) TiO
(b) VO
(c) Cu2O
(d) Mn2O3
Answer
B
Question. Alkali halids do not show Frenkel defect because
(a) cations and anions have almost equal size
(b) there is a large difference in size of cations and anions
(c) cations and anions have low coordination number
(d) anions cannot be accommodated in voids
Answer
A
Question. The appearance of colour in solid alkali metal halides is generally due to
(a) Schottky defect
(b) Frenkel defect
(c) F-centre
(d) Interstitial position
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following conditions favours the existence of a substance in the solid state?
(a) High temperature
(b) Low temperature
(c) High termal energy
(d) Weak cohesive forces
Answer
B
Question. Percentage of free space in body centred cubic unit cell is :
(a) 34 %
(b) 28 %
(c) 30 %
(d) 32 %
Answer
D
Question. The van’t Hoff factor (i) accounts for
(a) degree of solubilisation of solute.
(b) the extent of dissociation of solute.
(c) the extent of dissolution of solute.
(d) the degree of decomposition of solution.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is an amorphous solid ?
(a) Graphite
(b) Quartz Glass ( SO2 )
(c) Chrome Alum
(d) Silicon Carbide ( SiC )
Answer
B
Question. Iodine molecules are held in the crystals lattice by ……………..
(a) London forces
(b) Dipole – dipole interactions
(c) Covalent bonds
(d) Coulombic forces
Answer
A
Question. Volume occupied by atoms in fee is
(a) 74%
(b) 68%
(c) 52.4%
(d) 75%
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is true about the charge acquired by p-type semiconductors?
(a) positive
(b) neutral
(c) negative
(d) depends on concentration of p impurity
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following crystals does not exhibit Frenkel defect?
(a) AgBr
(b) AgCl
(c) KBr
(d) ZnS
Answer
C
Question. Which kind of defects are introduced by doping?
(a) Dislocation defect
(b) Schottky defect
(c) Frenkel defects
(d) Electronic defects
Answer
D
Question. Co – ordination number of sodium ion Na+ in NaCl is
(a) four
(b) three
(c) six
(d) five
Answer
C
Question. The edge length of fee cell is 508 pm. If radius of cation is 110 pm, the radius of anion is
(a) 110 pm
(b) 220 pm
(c) 285 pm
(d) 144 pm
Answer
D
Question.The type defect observed in ionic crystals which large difference in the size of ions is:
(a) Interstitial defect
(b) Frenkel defect
(c) Schottky Defect
(d) Stoichiometric Defect
Answer
B
Question. The empty space within hep arrangement is
(a) 34%
(b) 47.6%
(c) 32%
(d) 26%
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following exists as covalent crystals in the solid state ?
(a) Sulphur
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Iodine
(d) Silicon
Answer
D
Question.The defect produced when NaCl is doped with SrCl 2 is:
(a) Thermodynamic Defect
(b) Interstitial Defect
(c) Frenkel Defect
(d) Vacancy Defect (Metal deficiency type)
Answer
D
Question. Close packing is maximum in the crystal which is
(a) bcc
(b) fee
(c) simple cubic
(d) end centred cubic
Answer
B
Question. The presence of F-centres in a crystal make it
(a) conducting
(b) non-conducting
(c) coloured
(d) colourless
Answer
C
Question. In F.C.C the unit cell is shared equally by how many unit cells?
(a) 10
(b) 8
(c) 6
(d) 2
Answer
C
Question. In a body centred cubic structure, the space occupied is about
(a) 74%
(b) 20%
(c) 68%
(d) 52.4%
Answer
C
Question. Amorphous solid is
(a) rubber
(b) plastic
(c) glass
(d) all
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following oxides shows ferro-magnetism ?
(a) CrO2
(b) MnO2
(c) Fe3O4
(d) V2O5
Answer
A
ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contain two statements,Assertion and Reason. Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : The packing efficiency is maximum for the fcc structure.
Reason : The cordination number is 12 in fcc structures.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : In crystal lattice, the size of the tetrahedral hole is larger than an octahedral hole.
Reason : The cations occupy less space than anions in crystal packing.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : In close packing of spheres, a tetrahedral void is surrounded by four spheres whereas an octahedral void is surrounded by six spheres.
Reason : A tetrahedral void has a tetrahedral shape whereas an octahedral void has an octahedral shape.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : On heating ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic substances, they become paramagnetic.
Reason : The electrons change their spin on heating.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Crystalline solids have long range order.
Reason : Amorphous solids have short range order.
Answer
B
Question.Assertion : Electrical conductivity of semiconductors increases with increasing temperature.
Reason : With increase in temperature, large number of electrons from the valence band can jump to the conduction band.
Answer
A
Question.Assertion: Glass panes fixed to windows or panes of old buildings are found to be slightly thicker at the bottom.
Reason: Amorphous solids have a tendency to flow.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : In any ionic solid (MX) with Schottky defects,the number of positive and negative ions are same.
Reason : Equal number of cation and anion vacancies are present.
Answer
A

We hope you liked the above The Solid State MCQ Class 12 Chemistry. In case you have any questions please put them in the comments box below and our teachers will provide you a response.
