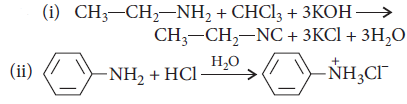Amines Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions
Please refer to Amines Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 13 Amines in NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Amines
All Amines Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of Standard 12 Chemistry. Please learn them and let us know if you have any questions.
Short Answer Questions :
Question. Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions :
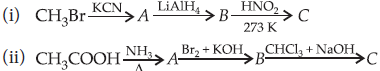
Answer : (i)
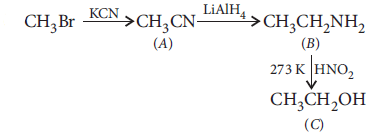
(ii)

Question. Complete the following reactions :
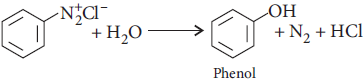
C6H5N2 +Cl– → H2O(Room temp.)
Answer :
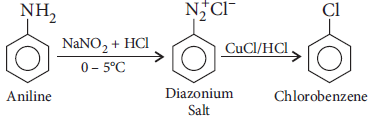
Question. How will you bring about the following conversion :
Aniline to chlorobenzene Write the chemical equation involved.
Answer :
Question. Describe the following giving the relevant chemical equation :
Carbylamine reaction
Answer : Carbylamine reaction is the reaction in which 1° amines produce a bad smelling compound when treated with chloroform in the presence of alkali.
RNH2 + CHCl3 + 3KOH → R—N ≡C + 3KCl + 3H2O
It is the test for primary amines.
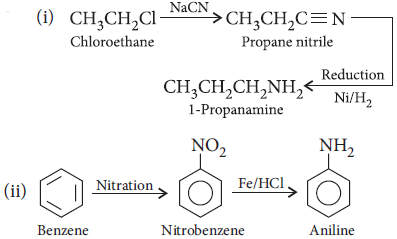
Question. How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) CH3CH2Cl to CH3CH2CH2NH2
(ii) Benzene to aniline.
Answer :
Question. Give IUPAC names of the following compounds :

Answer : (a) But-3-en-2-amine
(b) N-phenylethanamide
Question. Why is an alkylamine more basic than ammonia?
Answer : Electron density of N-atom increases due to the +I effect of the alkyl group. Hence, alkylamines are stronger bases than ammonia.
¨NH3, R → ¨NH2
Question. Arrange the following in the decreasing order of their basic strength in aqueous solutions :
CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3N and NH3
Answer : (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > NH3
Question. Account for the following :
Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not.
Answer : Ethylamine is soluble in water due to formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, in aniline due to large hydrophobic aryl group the extent of hydrogen bonding decreases considerably and hence aniline is insoluble in water.
Question. An aromatic compound ‘A’ of molecular formula C7H7ON undergoes a series of reactions as shown below. Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions :

Answer :

Question. An aromatic compound ‘A’ on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound ‘B’ which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound ‘C’ of molecular formula C6H7N. Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B and C.
Answer : Formula of the compound ‘C’ indicates it to be an amine. Since it is obtained by the reaction of Br2 and KOH with the compound ‘B’ so compound ‘B’ can be an amide. As ‘B’ is obtained from compound ‘A’ by reaction with ammonia followed by heating so, compound ‘A’ could be an aromatic acid. Formula of compound ‘C’ shows it to be aniline, then ‘B’ is benzamide and compound ‘A’ is benzoic acid. The sequence of reactions can be written as follows :

Question. (i) Arrange the following in an increasing order of basic strength in water :
C6H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N and NH3.
(ii) Arrange the following in increasing order or basic strength in gas phase :
C6H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N and CH3NH2.
Answer : (i) The increasing order of basic strength in water of the given amines and ammonia follows the following order :
C6H5NH2 < NH3 < (C2H5)3N < (C2H5)2NH
(ii) The increasing order of basic strength in gas phase of the given amines follows the order :
CH3NH2 < C2H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH < (C2H5)3N
Question. Account for the following observations :
(i) pKb for aniline is more than that for methylamine.
(ii) Methylamine solution in water reacts with ferric chloride solution to give a precipitate of ferric hydroxide.
(iii) Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Answer : (i) In aniline, the lone pair of electrons of N-atom are delocalised over the benzene ring. As a result, electron density on the nitrogen decreases. In contrast, in CH3—NH2, +I effect of —CH3 group increases the electron density on the N-atom.
Therefore, aniline is a weaker base than methylamine and hence, its pKb value is higher than that of methylamine.
(ii) Methylamine forms hydroxide ions when dissolved in water due to the following acid – base equilibrium.
CH3—NH2 + H2O ⇔ CH3—NH3++ OH–
These OH– ions react with Fe3+ ions to form ferric hydroxide.
2Fe + 6OH– → 2Fe(OH)3
(iii)

Question. How will you convert the following :
(i) Nitrobenzene into aniline
(ii) Ethanoic acid into methanamine
Answer :

Question. Which of the two is more basic and why?

Answer : CH3(C6H4)NH2 is more basic than C6H5NH2 due to electron releasing nature of methyl group which pushes electrons towards nitrogen.
Question. How would you achieve the following conversions :
(i) Nitrobenzene to aniline.
(ii) An alkyl halide to a quaternary ammonium salt.
Write the chemical equation with reaction conditions in each case.
Answer :

(ii) Alkyl halides when treated with ethanolic solution of ammonia give a mixture of primary, secondary, tertiary amines and quaternary ammonium salt.

Question. How do you convert the following :
Ethanenitrile to ethanamine
Answer : CH3CN + 4[H] →Na + C2H5OH CH3CH2NH2
Ethanenitrile Ethanamine
Question. Give reasons for the following :
(i) Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
(ii) (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution.
Answer : (i) In Friedel – Crafts reaction, AlCl3 is added as a catalyst which is a Lewis acid. It forms a salt with aniline due to which the nitrogen of aniline acquires positive charge. this positively charged nitrogen acts as a strong deactivating group, hence aniline does not undergo Friedel – Crafts reaction.

(ii) In aqueous solution 2° amine is more basic than 3° amine due to the combination of inductive effect, solvation effect and steric reasons.
Question. Why cannot primary aromatic amines be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
Answer : Aromatic amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide.
Question. Assign reason for the following :
The pKb of aniline is higher than that of methylamine.
Answer : In aniline, the lone pair of electrons of N-atom are delocalised over the benzene ring. As a result, electron density on the nitrogen decreases. In contrast, in CH3—NH2, +I effect of —CH3 group increases the electron density on the N-atom.
Therefore, aniline is a weaker base than methylamine and hence, its pKb value is higher than that of methylamine.
Question. Write chemical equations for the following conversion :
Benzyl chloride to 2-phenylethanamine.
Answer :

Question. Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength :

Answer : (i) C6H5CH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < C6H5CH2NH2
C6H5NH2 and C6H5NHCH3 are less basic than aliphatic amine C6H5CH2NH2 due to lone pair of nitrogen is in conjugation with benzene ring. But due to +I effect of —CH3 group in C6H5NHCH3, it is more basic than C6H5NH2.
(ii)

Electron withdrawing group (–NO2) on benzene ring decreases the basicity and electron donating group (–CH3) on benzene ring increases the basicity of compound.
Question. Arrange the following in increasing order of basic strength :
C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, C6H5N(CH3)2
Answer : Increasing order of basic strength in gaseous state is as follows :
C6H5NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < C6H5N(CH3)2
As the number of —CH3 groups (+I effect) attached to nitrogen increases, its basicity its basicity will increases.
Question. Rearrange the following in an increasing order of their basic strengths :
C6H5NH2, C6H5N(CH3)2, (C6H5)2NH and CH3NH2
Answer : (C6H5)2NH < C6H5NH2 < C6H5N(CH3)2 < CH3NH2
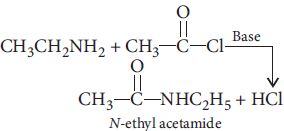
Question. Illustrate the following reactions giving suitable example in each case :
(i) Ammonolysis
(ii) Acetylation of amines
Answer : (i) Alkyl halides when treated with ethanolic solution of ammonia give a mixture of primary, secondary, tertiary amines and quaternary ammonium salt.

(ii) Acetylation of amines : The process of introducing an acetyl group
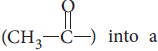
into a molecule is called acetylation.
Question. How would you account for the following :
(i) Aniline is a weaker base than cyclohexylamine.
(ii) Methylamine in aqueous medium gives reddish-brown precipitate with FeCl3.
Answer : (i) Aniline is weaker base than cyclohexylamine because of resonance. Due to electromeric effect, the lone pair on nitrogen is attracted by benzene ring.
Hence, donor tendency of —NH2 group decreases. There is no resonance in cyclohexylamine. Electron repelling nature of cyclohexyl group further increases the donor property of NH2 group. So, cyclohexylamine is a stronger base.

(ii) Methylamine forms hydroxide ions when dissolved in water due to the following acid – base equilibrium.
CH3—NH2 + H2O ⇔ CH3—NH3++ OH–
These OH– ions react with Fe3+ ions to form ferric hydroxide.
2Fe + 6OH– → 2Fe(OH)3
Question. Give one chemical test each to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Ethylamine and aniline
(ii) Aniline and N-methylaniline
Answer : (i) Aniline gives white or brown precipitate with bromine water.

Ethylamine does not react with bromine water.
(ii) Aniline gives carbylamine test, i.e., on treatment with alc. KOH and chloroform followed by heating it gives offensive odour of phenylisocyanide but N-methylaniline being secondary amine, does not show this test.
Question. (i) Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of basic strength :
C6H5NH2, C6H5N(CH3)2, (C2H5)2NH and CH3NH2
(ii) Arrange the following compounds in a decreasing order of pKb values :
C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, (C2H5)2NH and C6H5NH2
Answer : (i) Increasing order of basic strength is
C6H5NH2 < C6H5N(CH3)2 < CH3NH2 < (C2H5)2NH
(ii) Stronger the base lower will be its pKb value hence, the decreasing order of pKb values :
C6H5NH2 > C6H5NHCH3 > C2H5NH2 > (C2H5)2NH
Question. Give the chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Ethylamine and aniline
(ii) Aniline and benzylamine
Answer : (i) Aniline gives white or brown precipitate with bromine water.

Ethylamine does not react with bromine water.
(ii) Aniline and benzylamine : Benzylamine reacts with nitrous acid to form a diazonium salt which is unstable at low temperature and decomposes with evolution of N2 gas.
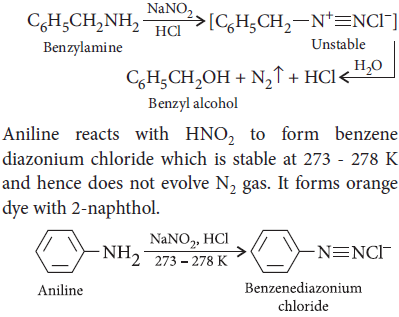
Question. Complete the following reactions :

Answer :