Biotechnology Principles and Processes MCQs Class 12 Biology
Please refer to Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and Processes MCQ Class 12 Biology with answers below. These multiple-choice questions have been prepared based on the latest NCERT book for Class 12 Biology. Students should refer to MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology with Answers to score more marks in Grade 12 Biology exams. Students should read the chapter Biotechnology Principles and Processes and then attempt the following objective questions.
MCQ Questions Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and Processes
The Biotechnology Principles and Processes MCQ Class 12 Biology provided below covers all important topics given in this chapter. These MCQs will help you to properly prepare for exams.
Question. Which of the following is a plasmid?
(a) pBR 322
(b) Bam H I
(c) Sal I
(d) Eco RI
Answer
A
Question. The first restriction endonuclease reported was
(a) Hind II
(b) EcoRI
(c) Hind III
(d) BamHI
Answer
A
Question. There is a restriction endonuclease called EcoRI. What does .co part in it stand for ?
(a) Colon
(b) Coelom
(c) Coenzyme
(d) coli
Answer
D
Question. The enzyme used for joining two DNA fragments is called
(a) ligase
(b) restriction endonuclease
(c) DNA polymerase
(d) gyrase
Answer
A
Question. DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by
(a) polymerase chain reaction
(b) electrophoresis
(c) restriction mapping
(d) centrifugation
Answer
B
Question. In genetic engineering, the antibiotics are used
(a) as selectable markers.
(b) to select healthy vectors.
(c) to keep the cultures free of infection.
(d) as sequences from where replication starts.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following enzyme is used in case of fungus to cause release of DNA along with other macromolecules ?
(a) Lysozyme
(b) Cellulase
(c) Chitinase
(d) Amylase
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is a natural genetic engineer of plants ?
(a) Yeast
(b) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(c) E. coli
(d) Mycoplasma
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is used as vector for cloning genes into higher organisms?
(a) Baculovirus
(b) Salmonella typhimurium
(c) Rhizopus nigricans
(d) Retrovirus
Answer
D
Question. In agarose gel electrophoresis
(a) DNA migrates towards the negative electrode.
(b) supercoiled plamids migrate slower than their nicked counterparts.
(c) larger molecules migrate faster than smaller molecules.
(d) ethidium bromide can be used to visualize the DNA.
Answer
D
Question. For transformation, micro-particles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of
(a) silver or platinum
(b) platinum or zinc
(c) silicon or platinum
(d) gold or tungsten
Answer
D
Question. The first step in the PCR is
(a) denaturation
(b) primer extension
(c) annealing
(d) cooling
Answer
A
Question. Stirred-tank bioreactors have been designed for
(a) addition of preservatives to the product.
(b) purification of the product.
(c) ensuring anaerobic conditions in the culture vessel.
(d) availability of oxygen throughout the process.
Answer
D
Question. After completion of biosynthetic stage, the product has to be subjected through a series of processes before it is ready to marketing as a finished product. This series of processes is called
(a) upstream processing
(b) downstream processing
(c) elution
(d) insertional inactivation
Answer
B
Question. The construction of the first recombinant DNA was done by using the native plasmid of-
(a) E. Coli
(b) Salmonella typhimurium
(c) B.Thuringiensis
(d) Yeast
Answer
B
Question. Restriction endonucleases:
(a) Cleave DMA at highly specific recognition sequences
(b) Are inserted into bacteria by bacteriophages
(c) Are made only by eukaryotic ceHs
(d) Add methyl groups to specific DNA sequences.
Question. The tumour-inducing capacity of Agrobacterium tumifaciens is located in large extrachromosomal plasmids called
(a) Ri plasmids
(b) plasmid pBR 322
(c) lamb: phage
(d) Tiplasmid
Answer
D
Question. The experimental manipulation of DMA of different species, producing recombinant DMA is known as
(a) electroporesis
(b) recombinant DMA technology
(c) transformation
(d) somatic hybridization
Answer
B
Question. Plasmids :
(a) Are circular protein molecules
(b) Are required by bacteria
(c) Are tiny bacteria
(d) Confer resistance to antibiotics
Answer
D
Question.The controlled use of biological agents, such as microorganisms or cellular components, for beneficial use is called
(a) plant biology
(b) biochemistry
(c) biotechnology
(d) molecular biology
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following restriction endonuclease is obtained from Escherichia coli?
(a) BamH1
(b) Sua3A1
(c) Hind III
(d) EcoR1
Answer
D
Question. Cay endo borins obtained from Bacillum thuriagemiss are effective against
(a) Nenatodes
(b) Boll worms
(c) Mosquitoes
(d) Flies
Answer
B
Question. Plasmids are-
(a) DNA
(b) Mitochondrial DNA
(c) Circular extra chromosomal DNA bacteria
(d) viral RNA
Answer
C
Question. Identify the plasmid-
(a) Eco RI
(b) pBR322
(c) AlUl
(d) Hind II
Answer
B
Question. For transformation with recombinant DNA, the bacterial cells must first be made ‘competent’ which means
(a) Should increase their metabolic reactions
(b) Should decrease their metabolic reactions
(c) Increase efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium
(d) Ability to divide fast
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not applicable to Agrobacterium tumifaciens?
(a) Pathogen of several dicot plants
(b) Has ability to transform normal plant cells
(c) Delivers gene of our interest
(d) Ti plasmid of it is always pathogenic to plants without any exception
Answer
D
Question. The structure involved in genetic engineering is:
(a) Plasmid
(b) Plastid
(c) Codon
(d)Anticodon.
Answer
A
Question. Since DMA has a _______ charge, it moves towards the ______ electrode of the electrophoretic chamber
(a) positive
(b) positive, negative
(c) negative, positive
(d) natural, neutral
Answer
C
Question. Which is being synthesized by genetic engineering :
(a) Insulin
(b) Renin
(c) Thyroxine
(d) Progesterone.
Answer
A
Question. The most commonly used bioreactor is of stirring type. The stirrer facilitates
(a) Temperature control
(b) pH control
(c) Oxygen availability
(d) Product removal
Answer
C
Question. During isolation of DMA, addition of which of the following causes precipitation of purified DMA?
(a) Chilled ethanol
(b) Ribonuclease enzyme
(c) DMA polymerase
(d) Proteases
Answer
C
Question. DMA finger printing is based on :
(a) Clones of DMA
(b) DMA segments formed by RE enzymes
(c) Human efforts
(d) Gene library.
Answer
A
Question. One of the key factors, which makes the plasmid the vector in geretic engineering in that-
(a) It is resistant to antibiotics
(b) It is resistant to restriction enzymes
(c) Its ability to carry a foreign gene
(d) Its ability to cause infection in the host
Answer
C
Question. Transgenic plants are developed by-
(a) Clone and genetically modified genes
(b) Introduction of foreign geres
(c) Genetic engineering
(d) Purified genes
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following method can be used for making the bacterial cell ‘competent’?
(a) Treating with specific cone, of divalent cation (Ca2+)
(b) Treating with specific cone, of monovalent cation (K+)
(c) Heat shock
(d) Both (a) & (c)
Answer
D
Question. Insertional inactivation is related to
(a) Microinjection
(b) Gene gun
(c) Gel electrophoresis
(d) Selection of recombinants
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is the correct sequence of PCR or polymerase chain reaction?
(a) Denaturation -> Anne ng -> Extension
(b) Extension -> Denaturation -» Anne ng
(c) Anne ng -> Extension -> Denaturation
(d) Denaturation -> Extension -> Anne ng
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following enzyme is used in case of fungus to cause release of DMA along with other macromolecules?
(a) Lysozyme
(b) Cellulase
(c) Chitinase
(d) Amylase
Answer
D
Question. During gel electrophoresis for separation of DMA fragment
(a) Smallest fragment will move to the farthest point towards cathode
(b) Smallest fragment will move to the farthest point towards anode
(c) Largest fragment will move to the farthest point towards cathode
(d) Largest fragment will move to the farthest point towards anode
Answer
B
Question. After completing the transformation experiment involving the coding sequence of enzyme a-galactosidase, the recombinant colonies should
(a) Give blue colour
(b) Not give blue colour
(c) Have active a -galactosidase
(d) Both (b) & (c)
Answer
B
Question. DNA fingerprinting is done by a technique called: …. .
(a) ELISA
(b) Northern blotting
(c) Southern blotting
(d) RIA.
Answer
C
Question. X technique is now routinely used to detect HIV in suspected AIDS patients. It is being used to detect mutations in genes in suspected cancer patients too. It is a powerful technique to identify many other genetic disorders. Identify X-
(a) X = PCR
(b) X = DMA fingerprinting
(c) X = Bioinformatic
(d) X = X-ray defraction
Answer
A
Question. One of the following in tramgereic of organisms-
(a) Holly sheep and cotton Bt
(b) Dolly sheep and cotton Bt
(c) Flaa save tomato and cotton Bt
(d) Holly sheep and flove save tomato
Answer
C
Question. What must be done before placing DNA into the electrophoretic chamber?
(a) It must be ground up with mortar and pestle
(b) It must be cut by restriction endonucleases
(c) It must be treated with RNAase
(d) None
Answer
B
Question. In DNA fingerprinting:
(a) The variability of repeated sequences between two restriction sites is evaluated.
(b) Exonuclease enzyme digests/generate unique fragments
(c) Amplifies fewer DNA
(d) Protein is identified.
Answer
A
Question. When gerotype of an organism is improved by the addition of foreign genes the process sin called-
(a) Biotechnology
(b) Tissue culture
(c) Genetic engineering
(d) Genetic diversity
Answer
C
Question. Ligase in used for-
(a) Separating DNA
(b) Joining two DNA fragments
(c) DNA polymerase reaction
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. During heat shock to the bacterium, the temperature used for giving thermal shock is
(a) 82°C
(b) 100°C
(c) Liquid nitrogen
(d) 42°C
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following techniques can be used to introduce foreign DNA into cell?
(a) Using disarmed pathogen
(b) Microinjection
(c) Gene gun
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following has the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells in animals?
(a) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(b) Retroviruses
(c) DNA-viruses
(d) Plasmids
Answer
B
Question. Process by which we can add or delete certain gene is :
(a) Gene therapy
(b) Biotechnology
(c) Genetic engineering
(d) Cytogenetics.
Answer
C
Question. Plasmid present in bacterial cells are :
(a) Circular double helical DMA molecules
(b) Linear double helical DMA molecules
(c) Circular double helical RNA molecules
(d) Linear double helical RNA molecules.
Answer
A
Question. The procedure through which a piece of DNA is introduced in a host bacterium is called
(a) Cloning
(b) Transformation
(c) PCR
(d) Clonal selection
Answer
B
Question. The term humulin is associated with :
(a) Insulin hormone produced by transgenic E.co//
(b) Lysosomal enzyme
(c) Isoenzymes of LDH
(d) Antibiotic produced by transgenic Penicillium.
Answer
A
Question. Which are among the following in fist a closing plasmid and not an expression plasmid ?
(a) pBAD-18Cam
(b) pBCSK
(c) pUC18
(d) PET
Answer
C
Question. Molecular scissors which cut DNA at specific site in-
(a) Pectinase
(b) Polymerase
(c) Restriction Endonudease
(d) Ligand
Answer
C
Question. ECORI cleaves DNA at-
(a) G A A T T C
(b) T A T A G C
(c) A A g g T T
(d) g A T A T C
Answer
A
Question. Which enzymes are used to break the cell to release DMA?
(a) Lysozyme
(b) Cellulase
(c) Chitinase
(d) AII of these
Answer
D
Question. T-DNA is found in
(a) Saccharomyces
(b) Agrobacterium
(c) Penicillium
(d) Puccini a
Answer
B
Question. The first restriction endonuclease reported was
(a) Hind II
(b) Eco RI
(c) Hind III
(d) Bam HI
Answer
A
Question Pairing of fragments derived from DNA is a process called
(a) Staggering
(b) Anne ng
(c) Augmenting
(d) Fragmenting
Answer
A
Question. Autonomously replicating circular extrachromosomal DMA is called
(a) B-chromosome
(b) jumping gene
(c) plasmid
(d) recombinant DMA
Answer
C
Question. Restriction enzymes are used in genetic engineering because:
(a) They can cut DMA at specific base sequence
(b) They are nuclease that can cut DMA at variable sites
(c) They can join different DMA fragments
(d) They are proteolytic enzymes which can degrade harmful proteins.
Answer
A
Question. Polyethylene glycol method in used for-
(a) Biodiesal production
(b) Scedless furit production
(c) Energy production from sewage
(d) Gene transfer without a vector.
Answer
D
Directions : In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as :
(A) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(B) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs
Question. Assertion (A) : DNA is positively charged molecule.
Reason (R) : DNA moves towards the positive electrode (anode).
Answer : (D)
Question. Assertion (A) : Restriction enzymes belongs to class nucleases.
Reason (R) : Nucleases are of two kinds : exo and endonucleases. Exonucleases remove nucleotides within the DNA.
Answer : (C)
Question. Assertion (A) : β-galactosidase coding sequence act as a selectable marker.
Reason (R) : Enzyme galactosidase converts the galactose into lactose.
Answer : (A)
Question. Assertion (A) : It is essential to have few cloning sites in cloning vector.
Reason(R) : It helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants.
Answer : (B)
Question. Assertion (A) : EcoRI is restriction endonuclease enzyme.
Reason (R) : Exonuclease removes nucleotides from the ends of DNA.
Answer : (B)
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same :
The term “Biotechnology” refers to the use of living organisms or their products to modify human health and their human environment. For example, ‘testtube’ programme, synthesis of a gene or correcting a defective gene are all part of the biotechnology.
The basis of the modern biotechnology are genetic engineering and maintenance of sterile conditions.
Genetic engineering is the technique that alter the chemistry of genetic material i.e., DNA and RNA,then this genetic material is introduced into host organisms, which alter the phenotype of the host organism.
Question. The cutting of DNA at specific locations became possible with the discovery of :
(a) Ligases
(b) Restriction enzymes
(c) Probes
(d) Selectable markers.
Answer : (b)
Question. The specific DNA sequence where EcoRI cuts is :
(a) GATTCG
(b) GAATTC
(c) GTTCAA
(d) TTCCAA.
Answer : (b)
Question. Discovery of _________ molecule made genetic engineering possible.
(a) Restriction exonuclease
(b) Restriction endonuclease
(c) Ribozyme
(d) DNA polymerase
Answer : (b)
Question. DNA fragments are :
(a) Positively charged
(b) Negatively charged
(c) Neutral
(d) Either positively or negatively charged depending on their size.
Answer : (b)
Question. The recognition sequence of the first restriction enzyme isolated was ________base pair long.
(a) four
(b) six
(c) five
(d) two.
Answer : (b)
III. A schematic representation of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) up to the extension stage is given below.
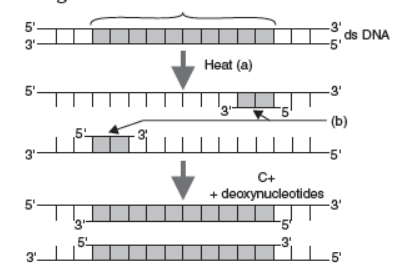
Question. Identify ‘b’
(a) Termination
(b) Annealing primer
(c) Denaturation
(d) Extension
Answer : (b)
Question. Which among the following is not an application of PCR ?
(a) ELISA
(b) Diagnosis of pathogens
(c) DNA fingerprinting
(d) In palaeontology.
Answer : (b)
Question. How many DNA duplex is obtained from one DNA duplex after 3 cycles of PCR?
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) 16
Answer : (c)
Question. Name the process ‘a’
(a) Termination
(b) Annealing
(c) Denaturation
(d) Extension
Answer : (c)
Question. PCR technique is best for :
(a) DNA synthesis
(b) Protein amplification
(c) DNA amplification
(d) DNA ligation.
Answer : (c)

We hope you liked the above Reproduction in Organisms MCQ Class 12 Biology. In case you have any questions please put them in the comments box below and our teachers will provide you a response.
