Surface Chemistry Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions
Please refer to Surface Chemistry Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions with answers below. These solved questions for Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry in NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. Students should learn these solved problems properly as these will help them to get better marks in your class tests and examinations. You will also be able to understand how to write answers properly. Revise these questions and answers regularly. We have provided Notes for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters in your textbooks.
Important Questions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry
All Surface Chemistry Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of Standard 12 Chemistry. Please learn them and let us know if you have any questions.
Very Short Answer Questions :
Question. What type of colloid is formed when a gas is dispersed in a liquid? Give an example.
Answer : When a gas is dispersed in a liquid, foam is formed, e.g., froth.
Question. What are lyophobic colloids? Give an example for them.
Answer : Lyophilic sols : The colloidal solution in which particles of the dispersed phase have a strong affinity for the dispersion medium.
These colloidal sols, even if precipitated, change back to the colloid form simply by adding dispersion medium. So, lyophilic sols are reversible in nature. e.g., glue, starch, rubber, etc.
Lyophobic sols : the colloidal solution in which particles of the dispersed phase have no or very little affinity for dispersion medium.
These are irreversible in nature i.e., once precipitated, they have little tendency to get back into the colloidal form on simply adding dispersion medium e.g., As2S3 solution. Lyophobic sols need stabilising agents for their preservation.
Question. What is the basic difference between adsorption and absorption?
Answer : Adsorption is a surface phenomenon. In this process the adsorbate is concentrated on the surface of the adsorbent and does not penetrate into the bulk whereas, absorption of a substance takes place throughout the bulk of the material. In adsorption, concentration of adsorbate is high on the surface of adsorbent, while during absorption concentration is uniform throughout. e.g., water vapour is adsorbed by silica gel whereas absorbed by anhydrous calcium carbide.
Question. Which complex ion is formed when undecomposed AgBr is washed with hypo solution in photography ?
Answer : The developed film is immersed in sodium thiosulphate (hypo) solution which removes unchanged silver bromide as a complex ion.
This is known as fixing.
AgBr + 2Na2S2O3 → Na3[Ag(S2O3 )2] + NaBr
After fixing, the film is not sensitive to light.
Question. Define peptization.
Answer : Peptization is the process of conversion of a precipitate into colloidal state in the presence of some electrolyte.
Question. What is an emulsion?
Answer : An emulsion : It is a colloidal system when both the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium are in the liquid state. e.g., milk.
Question. Write one difference between each of the following :
O/W emulsion and W/O emulsion
Answer : O/W emulsion W/O emulsion
Oil is dispersed Water is dispersed
phase and water is phase and oil is
the dispersion the dispersion
medium. medium.
Question. Write the main reason for the stability of colloidal sols.
Answer : The main reason for the stability of colloids is the electrostatic stabilisation i.e., equal and same type of charge on the colloidal particles which causes repulsion between them and prevents the coagulation of the sol.
Question. What type of colloid is formed when a solid is dispersed in a liquid? Give an example.
Answer : When a solid is dispersed in a liquid, a colloid is formed which is known as ‘sol’ e.g; paints.
Question. How can a colloidal solution and true solution of the same colour be distinguished from each other
Answer : When a powerful beam of light is passed through true and colloidal solutions each kept in a glass vessel then, colloidal solution exhibits tyndall effect whereas true solution does not.
Question. Write the dispersed phase and dispersion medium of butter.
Answer : Dispersed phase : Liquid
Dispersion medium : Solid
Question. Define the following term :
Adsorption
Answer : Adsorption is the phenomenon of attracting and retaining the molecules of a substance on the surface of a liquid or a solid resulting in higher concentration of the molecules on the surface.
Question. Which aerosol depletes ozone layer?
Answer : CFC (Chlorofluorocarbon)
Question. Out of BaCl2 and KCl, which one is more effective in causing coagulation of a negatively charged colloidal sol? Give reason.
Answer : BaCl2 is more effective in causing coagulation of negatively charged colloidal sol.
Because greater the valency of the coagulating ion, greater is its power to bring about coagulation.
Question. Write one difference in each of the following :
Lyophobic sol and lyophilic sol
Answer : Difference between lyophilic and lyophobic colloids.

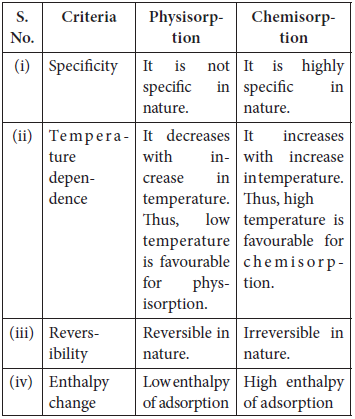
Question. What are physisorption and chemisorption?
Answer : Physisorption : The phenomenon in which adsorbate and adsorbent are held by van der Waals’ forces.
It is reversible in nature. e.g., setting a layer of dust particles on the furniture.
Chemisorption : The phenomenon in which adsorbate and adsorbent are held by chemical bonds.
It is irreversible in nature. e.g., painting on a furniture.
Question. What are the dispersed phase and dispersion medium in milk?
Answer : Liquid fat is the dispersed phase and water is the dispersion medium.
Question. What causes brownian movement in a colloidal solution?
Answer : The continuous rapid zig-zag motion of the colloidal particles in the dispersion medium is called Brownian movement.
Unbalanced bombardment of the particles of dispersed phase by molecules of dispersion medium causes Brownian motion.
This stabilises the sol.
Question. What is the difference between lyophobic sol and lyophilic sol ?
Answer : Lyophilic sols : The colloidal solution in which particles of the dispersed phase have a strong affinity for the dispersion medium.
These colloidal sols, even if precipitated, change back to the colloid form simply by adding dispersion medium. So, lyophilic sols are reversible in nature. e.g., glue, starch, rubber, etc.
Question. Write one difference of the following :
Solution and colloid
Answer : Solution : In true solution, the size of the particles is about 10–10 m.
Colloid : In a colloid, the size of the particles is between 10–7 to 10–9 m.
Short Answer Questions :
Question. Distinguish between micelles and colloidal particles. Give one example of each.
Answer : Micelles : When small particles (ions) of an electrolyte molecule form the aggregate particles which behave like colloidal particles, these aggregated particles are known as micelles.
Examples : Soap and detergents.
Colloidal particles : Colloidal particles have an enormous surface area per unit mass as a result of their small size. Its size ranges between 1 nm to 100 nm. e.g., sulphur sol.
Question. Distinguish between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. What role does adsorption play in heterogeneous catalysis?
Answer : Catalysis is divided into following two groups.
Homogeneous catalysis : When reactants and the catalysts are in the same phase i.e., liquid or gas, the catalysis is known as homogeneous catalysis.

Heterogeneous catalysis: When reactants and the catalysts are in different phases, the catalysis is known as heterogeneous catalysis. In most cases, the catalyst is solid, while reactants are either liquid or gases. Here, the catalyst is usually a metal or an oxide in finely divided form e.g.,
Vegetable oils (l) + H2(g) →Ni(s) Vegetable ghee(s)
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) →pt(s) 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
Role of adsorption in heterogeneous catalysis : The reactant molecules in gaseous state or in solutions are adsorbed on the surface of the solid catalyst by physisorption or chemisorption. As result, the concentration of the reactant molecules on the surface increases and hence, the rate of reaction increases.
Question. What is meant by coagulation of a colloidal solution? Describe briefly any three methods by which coagulation of lyophobic sols can be carried out.
Answer : The process of setting of colloidal particles is called coagulation of the sol. It is also known as precipitation. Following are the three methods by which coagulation of lyophobic sols can be carried out :
(i) Electrophoresis: In this process, the colloidal particles move towards oppositely charged electrodes and get discharged resulting in coagulation.
(ii) Mixing of two oppositely charged sols: When equal proportions of oppositely charged sols are mixed, they neutralise each other resulting in coagulation.
(iii) Dialysis: By this method, electrolytes present in sol are removed completely and colloid becomes unstable resulting in coagulation.
Question. Write one difference in each of the following:
(a) Multimolecular colloid and associated colloid
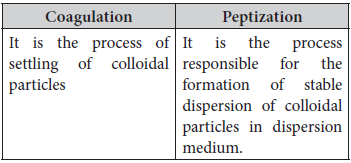
(b) Coagulation and peptization
Answer : (a) Difference between multimolecular colloid and associated colloid :

(b) Difference between coagulation and peptization :
Question. Define the following terms :
(i) Lyophilic colloid
(ii) Zeta potential
(iii) Associated colloids
Answer : (i) Lyophilic sols : The colloidal solution in which particles of the dispersed phase have a strong affinity for the dispersion medium.
These colloidal sols, even if precipitated, change back to the colloid form simply by adding dispersion medium. So, lyophilic sols are reversible in nature. e.g., glue, starch, rubber, etc.
(ii) The difference of potential between fixed layer and diffused layer of a colloidal sol is known as electrokinetic or zeta potential. It is given by
Z = 4πnu/K
Z – Zeta potential
h – Co-efficient of viscosity of sol
u – Velocity of sol particles; K – Dielectric constant.
(iii) Associated colloids : The substances which at low concentration, behave as normal strong electrolytes but at higher concentration exhibit colloidal behaviour due to the formation of aggregated particles, are known as associated colloids.
These are also known as micelles. The formation of micelles takes place only above a particular temperature, called the Kraft temperature and above a particular concentration, called the Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC), e.g., surface active agents such as soaps and synthetic detergents.
Question. Explain the following terms :
(i) Electrophoresis
(ii) Coagulation
(iii) Tyndall effect
Answer : (i) The movement of colloidal particles under an applied electric potential is called electrophoresis. Positively charged colloidal particles move towards the cathode, while negatively charged particles move towards the anode.
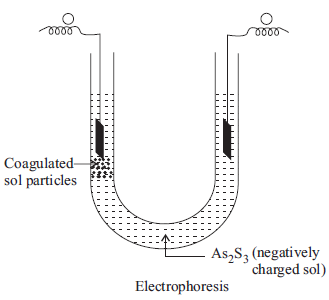
(ii) Coagulation The process of aggregating together the colloidal particles into large sized particle which ultimately settle down under the force of gravity as a precipitate is called coagulation.
(iii) When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution and viewed perpendicular to the path of incident light, the path of beam is illuminated by a bluish light. This phenomenon is called Tyndall effect. This is due to the fact that colloidal particles scatter light in all the directions in space.

Question. How are the following colloidal solutions prepared?
(a) Sulphur in water
(b) Gold in water
Answer : (i) Sulphur sol is prepared by the oxidation of H2S with SO2.
SO2 + 2H2S →(Sol)Oxidation 3S + 2H2O
(ii) Gold sol is prepared by Bredig’s arc process or by the reduction of AuCl3 with HCHO.
2AuCl3 + 3HCHO + 3H2O →(Sol)Oxidation 2Au + 3HCOOH + 6HCl
Question. Explain the following term giving a suitable example.
Homogeneous catalysis
Answer : Catalysis is divided into following two groups.
Homogeneous catalysis : When reactants and the catalysts are in the same phase i.e., liquid or gas, the catalysis is known as homogeneous catalysis.

Heterogeneous catalysis: When reactants and the catalysts are in different phases, the catalysis is known as heterogeneous catalysis. In most cases, the catalyst is solid, while reactants are either liquid or gases. Here, the catalyst is usually a metal or an oxide in finely divided form e.g.,
Vegetable oils (l) + H2(g) →Ni(s) Vegetable ghee(s)
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) →pt(s) 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
Question. Define the following terms :
(i) Aerosol
(ii) Coagulation of colloids.
Answer : (i) Colloid of a liquid in a gas is called aerosol e.g., fog, sprays etc.
(ii) Coagulation The process of aggregating together the colloidal particles into large sized particle which ultimately settle down under the force of gravity as a precipitate is called coagulation.
Question. What is the difference between multimolecular and macromolecular colloids? Give one example of each type. How are associated colloids different from these two types of colloids ?
Answer :

Lyophilic sols : The colloidal solution in which particles of the dispersed phase have a strong affinity for the dispersion medium.
These colloidal sols, even if precipitated, change back to the colloid form simply by adding dispersion medium. So, lyophilic sols are reversible in nature. e.g., glue, starch, rubber, etc.
Question. Define adsorption. Write any two features which distinguish physisorption from chemisorption.
Answer : Adsorption is the phenomenon of attracting and retaining the molecules of a substance on the surface of a liquid or a solid resulting in higher concentration of the molecules on the surface.
Question. Name the two groups into which phenomenon of catalysis can be divided. Give an example of each group with the chemical equation involved.
Answer : Catalysis is divided into following two groups.
Homogeneous catalysis : When reactants and the catalysts are in the same phase i.e., liquid or gas, the catalysis is known as homogeneous catalysis.
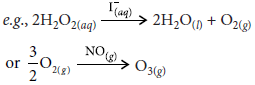
Heterogeneous catalysis: When reactants and the catalysts are in different phases, the catalysis is known as heterogeneous catalysis. In most cases, the catalyst is solid, while reactants are either liquid or gases. Here, the catalyst is usually a metal or an oxide in finely divided form e.g.,
Vegetable oils (l) + H2(g) →Ni(s) Vegetable ghee(s)
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) →pt(s) 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
Question. How are the following colloids different from each other in respect of dispersion medium and dispersed phase? Give one example of each type.
(i) An aerosol
(ii) A hydrosol
(iii) An emulsion
Answer : (i) An aerosol : Colloid of a liquid in a gas is called aerosol e.g., fog, sprays etc.
(ii) A hydrosol : It is a colloidal solution of a solid in water as the dispersion medium. e.g., starch solution.
(iii) An emulsion : It is a colloidal system when both the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium are in the liquid state. e.g., milk.
Question. How do the size of particles of adsorbent, pressure of gas and temperature influence the extent of adsorption.
Answer : Size of adsorbent particles : Smaller the size of adsorbent particles, larger is the surface area and hence, higher is the adsorption.
Pressure : Increase in pressure forces gas molecules to come closer to the surface of adsorbent leading to increase in the amount of adsorption.
Temperature : Adsorption is an exothermic reaction hence is favoured at lower temperature, at higher temperature the K.E. of adsorbate is high and hence extent of adsorption is low.
Question. Explain how the phenomenon of adsorption find application in the following processes :
(i) Production of vaccum
(ii) Heterogeneous catalysis
Answer : (i) Production of Vacuum : Adsorption can be applied to create condition of high vacuum. Vessel which has already been exhausted by vacuum pump is connected to a bulb containing charcoal. The remaining traces of air inspite of low pressure are adsorbed by the charcoal almost completely.
(ii) Role of adsorption in heterogeneous catalysis : The reactant molecules in gaseous state or in solutions are adsorbed on the surface of the solid catalyst by physisorption or chemisorption. As result, the concentration of the reactant molecules on the surface increases and hence, the rate of reaction increases.
Question. (a) Write the dispersed phase and dispersion medium of milk.
(b) Write the chemical method by which Fe(OH)3 sol is prepared from FeCl3.
Answer : (a) Dispersed phase and dispersion medium of milk are liquid and liquid respectively.
(b) Hydrolysis is the chemical method by which Fe(OH)3 sol is prepared from FeCl3.
FeCl3 + 3H2O → Fe(OH)3(sol) + 3HCl
